- Electric and Telecom Plans Free
- Fire and Emergency Plans Free
- Floor Plans Free
- Plant Layout Plans Free
- School and Training Plans Free
- Seating Plans Free
- Security and Access Plans Free
- Site Plans Free
- Sport Field Plans Free
- Business Process Diagrams Free
- Business Process Mapping Free
- Classic Business Process Modeling Free
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts Free
- Event-driven Process Chain Diagrams Free
- IDEF Business Process Diagrams Free
- Logistics Flow Charts Free
- Workflow Diagrams Free
- ConceptDraw Dashboard for Facebook Free
- Mind Map Exchange Free
- MindTweet Free
- Note Exchange Free
- Project Exchange Free
- Social Media Response Free
- Active Directory Diagrams Free
- AWS Architecture Diagrams Free
- Azure Architecture Free
- Cisco Network Diagrams Free
- Cisco Networking Free
- Cloud Computing Diagrams Free
- Computer Network Diagrams Free
- Google Cloud Platform Free
- Interactive Voice Response Diagrams Free
- Network Layout Floor Plans Free
- Network Security Diagrams Free
- Rack Diagrams Free
- Telecommunication Network Diagrams Free
- Vehicular Networking Free
- Wireless Networks Free
- Comparison Dashboard Free
- Composition Dashboard Free
- Correlation Dashboard Free
- Frequency Distribution Dashboard Free
- Meter Dashboard Free
- Spatial Dashboard Free
- Status Dashboard Free
- Time Series Dashboard Free
- Basic Circle-Spoke Diagrams Free
- Basic Circular Arrows Diagrams Free
- Basic Venn Diagrams Free
- Block Diagrams Free
- Concept Maps Free
- Family Tree Free
- Flowcharts Free
- Basic Area Charts Free
- Basic Bar Graphs Free
- Basic Divided Bar Diagrams Free
- Basic Histograms Free
- Basic Line Graphs Free
- Basic Picture Graphs Free
- Basic Pie Charts Free
- Basic Scatter Diagrams Free
- Aerospace and Transport Free
- Artwork Free
- Audio, Video, Media Free
- Business and Finance Free
- Computers and Communications Free
- Holiday Free
- Manufacturing and Maintenance Free
- Nature Free
- People Free
- Presentation Clipart Free
- Safety and Security Free
- Analog Electronics Free
- Audio and Video Connectors Free
- Basic Circuit Diagrams Free
- Chemical and Process Engineering Free
- Digital Electronics Free
- Electrical Engineering Free
- Electron Tube Circuits Free
- Electronic Block Diagrams Free
- Fault Tree Analysis Diagrams Free
- GHS Hazard Pictograms Free
- Home Automation and Wiring Free
- Mechanical Engineering Free
- One-line Diagrams Free
- Power Сircuits Free
- Specification and Description Language (SDL) Free
- Telecom and AV Circuits Free
- Transport Hazard Pictograms Free
- Data-driven Infographics Free
- Pictorial Infographics Free
- Spatial Infographics Free
- Typography Infographics Free
- Calendars Free
- Decision Making Free
- Enterprise Architecture Diagrams Free
- Fishbone Diagrams Free
- Organizational Charts Free
- Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Free
- Seven Management and Planning Tools Free
- SWOT and TOWS Matrix Diagrams Free
- Timeline Diagrams Free
- Public Utilities $25
- Australia Map Free
- Continent Maps Free
- Directional Maps Free
- Germany Map Free
- Metro Map Free
- UK Map Free
- USA Maps Free
- Customer Journey Mapping Free
- Marketing Diagrams Free
- Matrices Free
- Pyramid Diagrams Free
- Sales Dashboard Free
- Sales Flowcharts Free
- Target and Circular Diagrams Free
- Cash Flow Reports Free
- Current Activities Reports Free
- Custom Excel Report Free
- Knowledge Reports Free
- MINDMAP Reports Free
- Overview Reports Free
- PM Agile Free
- PM Dashboards Free
- PM Docs Free
- PM Easy Free
- PM Meetings Free
- PM Planning Free
- PM Presentations Free
- PM Response Free
- Resource Usage Reports Free
- Visual Reports Free
- House of Quality Free
- Quality Mind Map Free
- Total Quality Management TQM Diagrams Free
- Value Stream Mapping Free
- Astronomy Free
- Biology Free
- Chemistry Free
- Language Learning Free
- Mathematics Free
- Physics Free
- Piano Sheet Music Free
- Android User Interface Free
- Class Hierarchy Tree Free
- Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) Free
- DOM Tree Free
- Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) Free
- EXPRESS-G data Modeling Diagram Free
- IDEF0 Diagrams Free
- iPhone User Interface Free
- Jackson Structured Programming (JSP) Diagrams Free
- macOS User Interface Free
- Object-Role Modeling (ORM) Diagrams Free
- Rapid UML Free
- SYSML Free
- Website Wireframe Free
- Windows 10 User Interface Free
Public Utilities
Public utilities are essential services and goods provided by the government or state to society, to both residential and commercial consumers. These include the supply of electricity, water, natural gas, heating, telecommunications, transportation, social services, postal services, waste management, healthcare, education, safety, and many more all around the world. The public utility field plays a vital role in economic and social development, functioning of modern society by providing basic amenities and allowing the population to live their lives comfortably and securely. Many utilities are essential for human life, national defense, and commerce. The ability to satisfy human needs and increase the quality of life is the main characteristic of public utilities.
Public utility companies are public-service corporations, they provide essential services to the public. These are providers of electrical utilities, gas utilities, water utilities, telephone, Internet, transportation, etc. Public utility companies may be private sector or state-owned businesses and offer one or several services. Large companies often offer multiple products, while others specialize in one specific product. Some companies have a monopoly in their particular area. A monopoly is formed when the company finds the best way to minimize its costs by means of scale of production and other companies on the market cannot compete with it in this field. However, the development and breakthroughs in technologies form competition and in some fields may appear the competitive organizations to monopolies. At the same time, a natural monopoly supposes the most cost-effective way in the market to provide consumers with the best quality and price.
Having the alternative in companies, consumers can make informed decisions about their preferences and take the most reliable choice. Sometimes, network operators and service providers are involved in the public utility sector and deliver services to the end consumer. In this case, final consumers often can choose their retail service provider. Modern companies upgrade regularly their infrastructure that is incredibly important to ensure safety, efficiency, and the best quality of their services. Currently, many of them actively invest in sustainable renewable sources that is advantageous for the environment and human health and life.
Most public utilities belong to critical infrastructure and are capital-intensive because of the use of expensive equipment, which needs regular maintenance and replacement. These are also high-risk activities, therefore the companies must adhere to strict regulations set by public authorities to guarantee high-quality, reliable, and safe services, ensure universal access, and avoid breakdowns in the provision of utilities. Because of the critical role of utility companies in society and great responsibility, their operation is strongly supervised and regulated by national, state, and local government agencies. The companies are responsible for keeping smooth provision of services, service quality, and safety. The state government agencies implement public control for the safety of siting process and exploitation, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and regulation of rates. It supports their regular reviewing and ensures fair tariffs to make the services economically accessible to all or most of the population. The active and efficient work of the government in this sector enhances its image and attracts investments. The best solution is in balancing the economic needs of the companies and the social equity needed to guarantee everyone access to primary services. The regulators can directly set a limit on the maximum price, bring safety standards to hold, ensure that consumers’ rights are protected and reliable services are provided at the lowest possible cost. This also stimulates companies to develop cost-reducing technologies and involve sustainable sources.
Public Utilities solution is a thematic toolset for designing infographics and diagrams about public utilities. It provides vector icons libraries and examples for ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software. Use this solution and premade public utility icons to develop innovative strategies for the improvement of public utility services, enhance their efficiency of delivery, and extend reliable access to services to all communities. The solution helps to public utility companies plan their activities efficiently, develop new technologies and make visual presentation, create plumbing plan, heating plan, electrical diagram, or any other technical drawing, make the overview of modern public utilities, increase utility profits, and remain the best in the market.
-
Buy this solution $25 -
Solution Requirements - This solution requires the following products to be installed:
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM v18 - This solution requires the following products to be installed:
-
Helpdesk
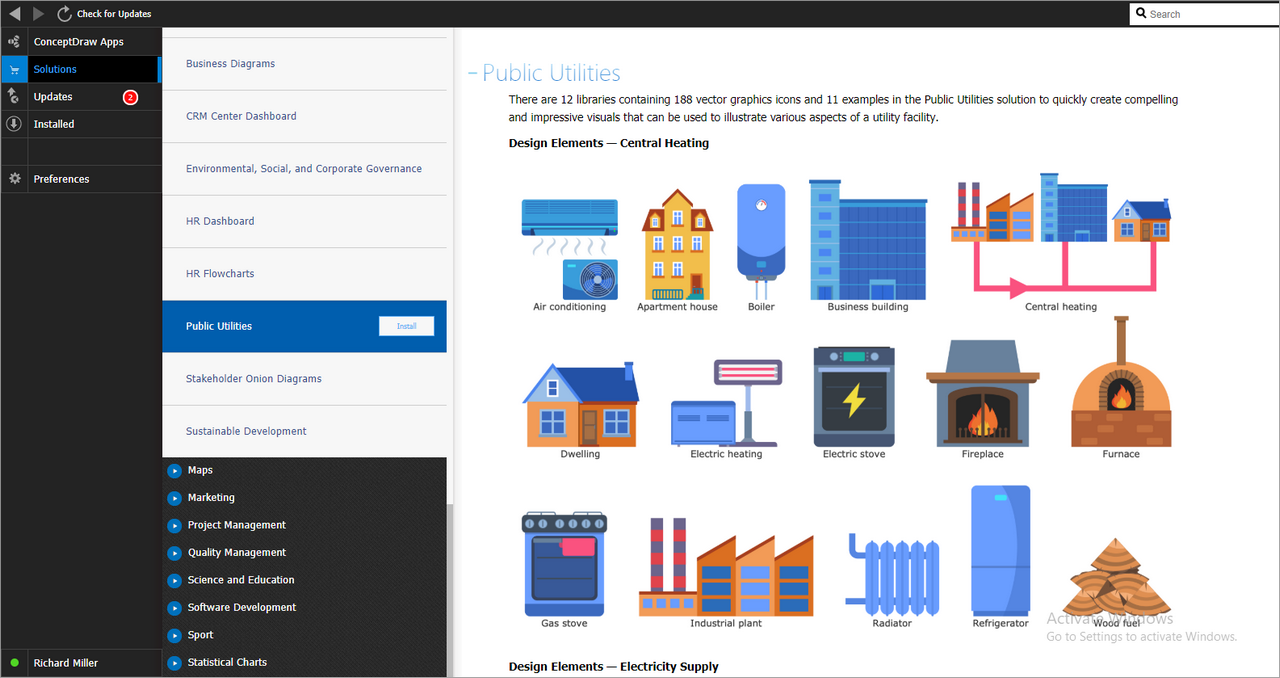
There are 12 libraries containing 188 vector graphics icons and 11 examples in the Public Utilities solution to quickly create compelling and impressive visuals that can be used to illustrate various aspects of a utility facility.
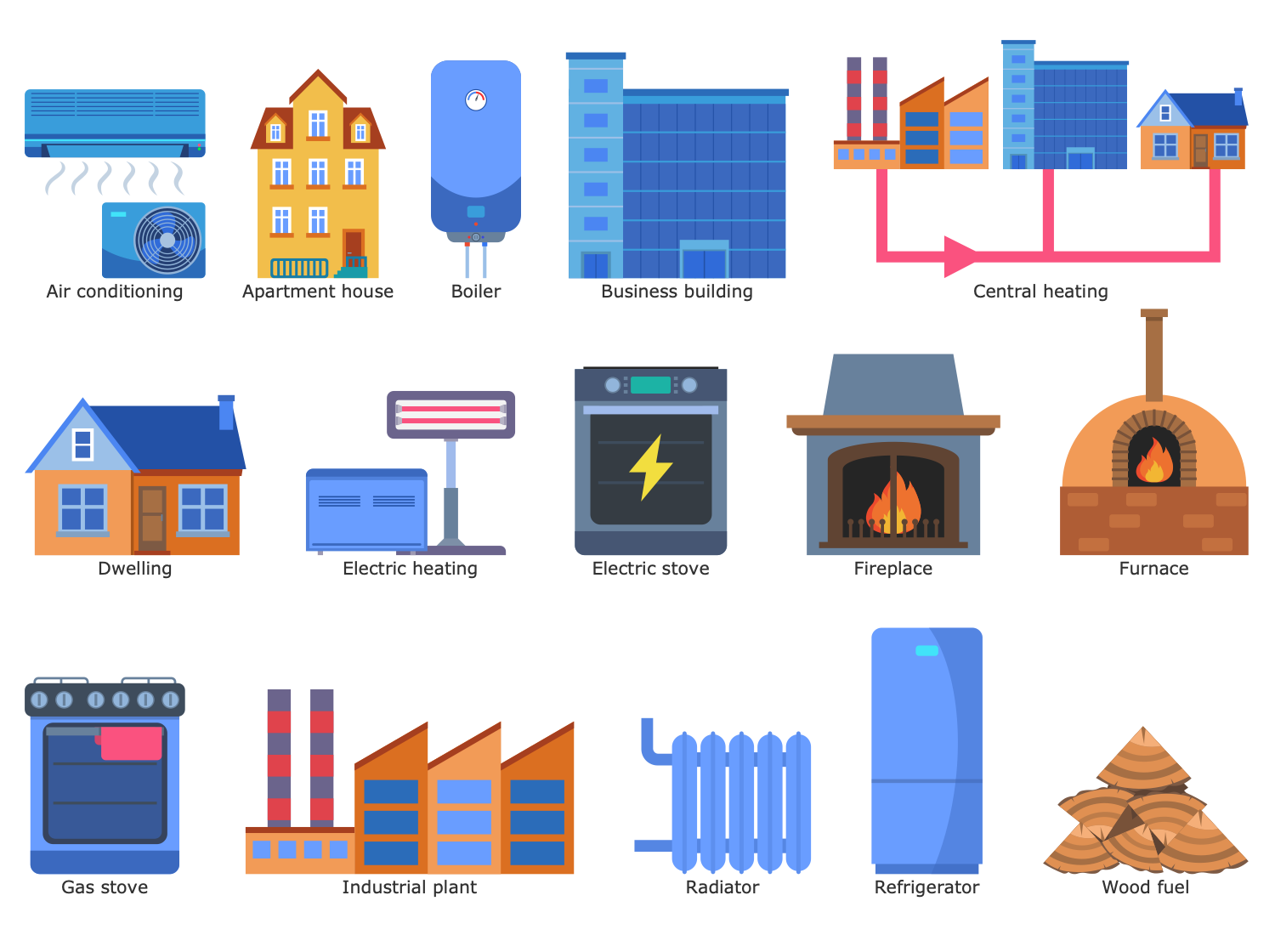
Design Elements — Central Heating
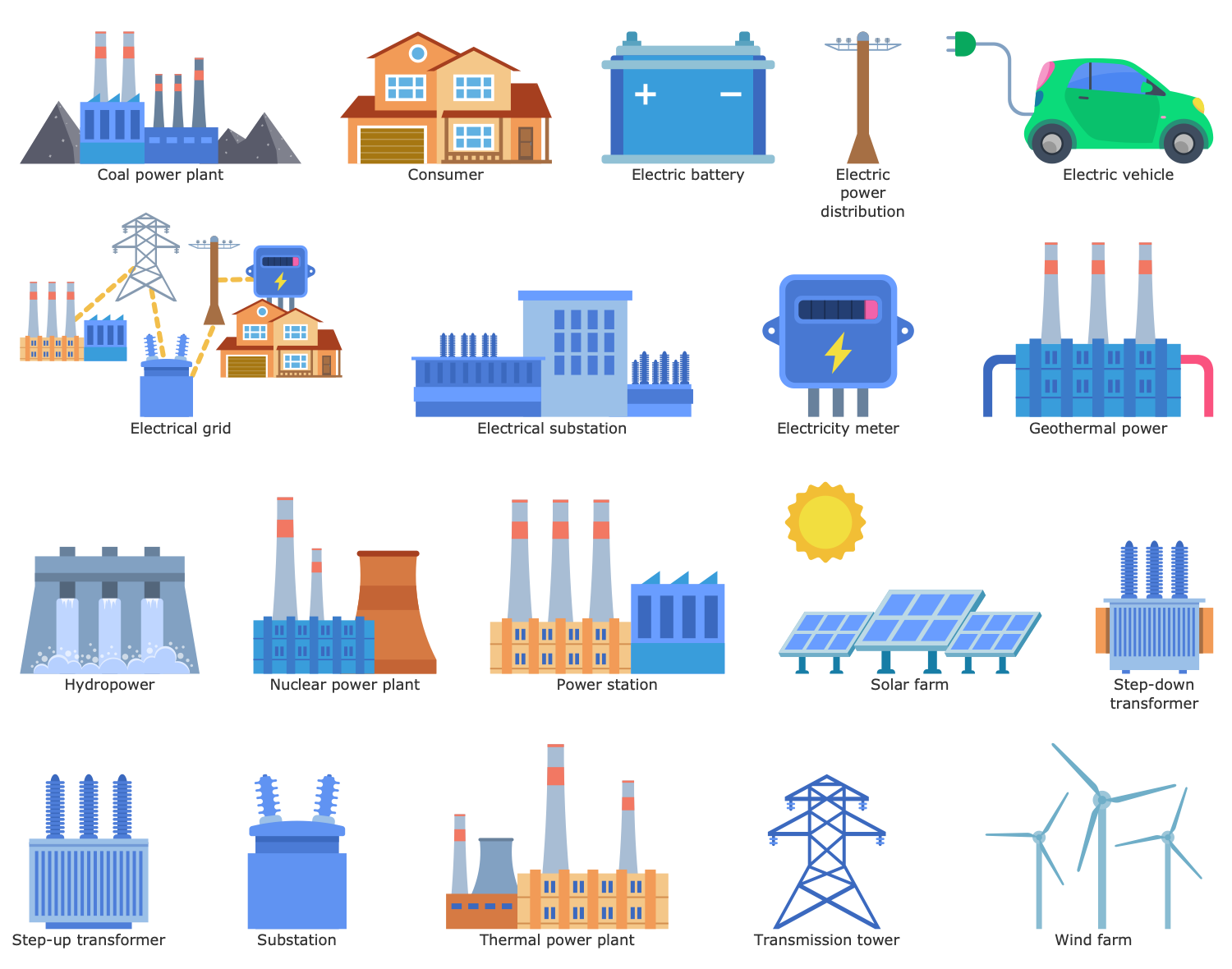
Design Elements — Electricity Supply
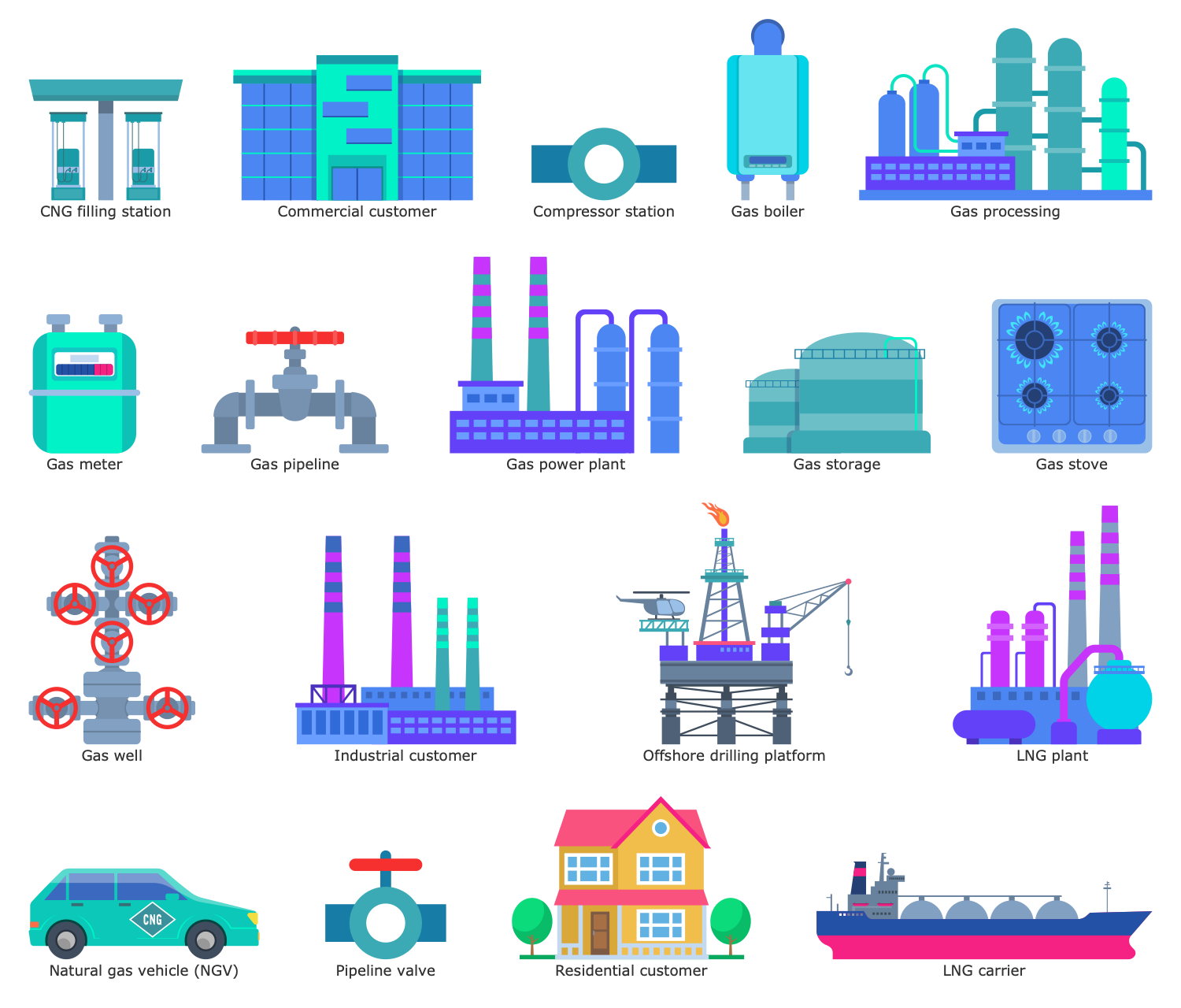
Design Elements — Gas Service
Design Elements — Public Education

Design Elements — Public Healthcare

Design Elements — Public Security
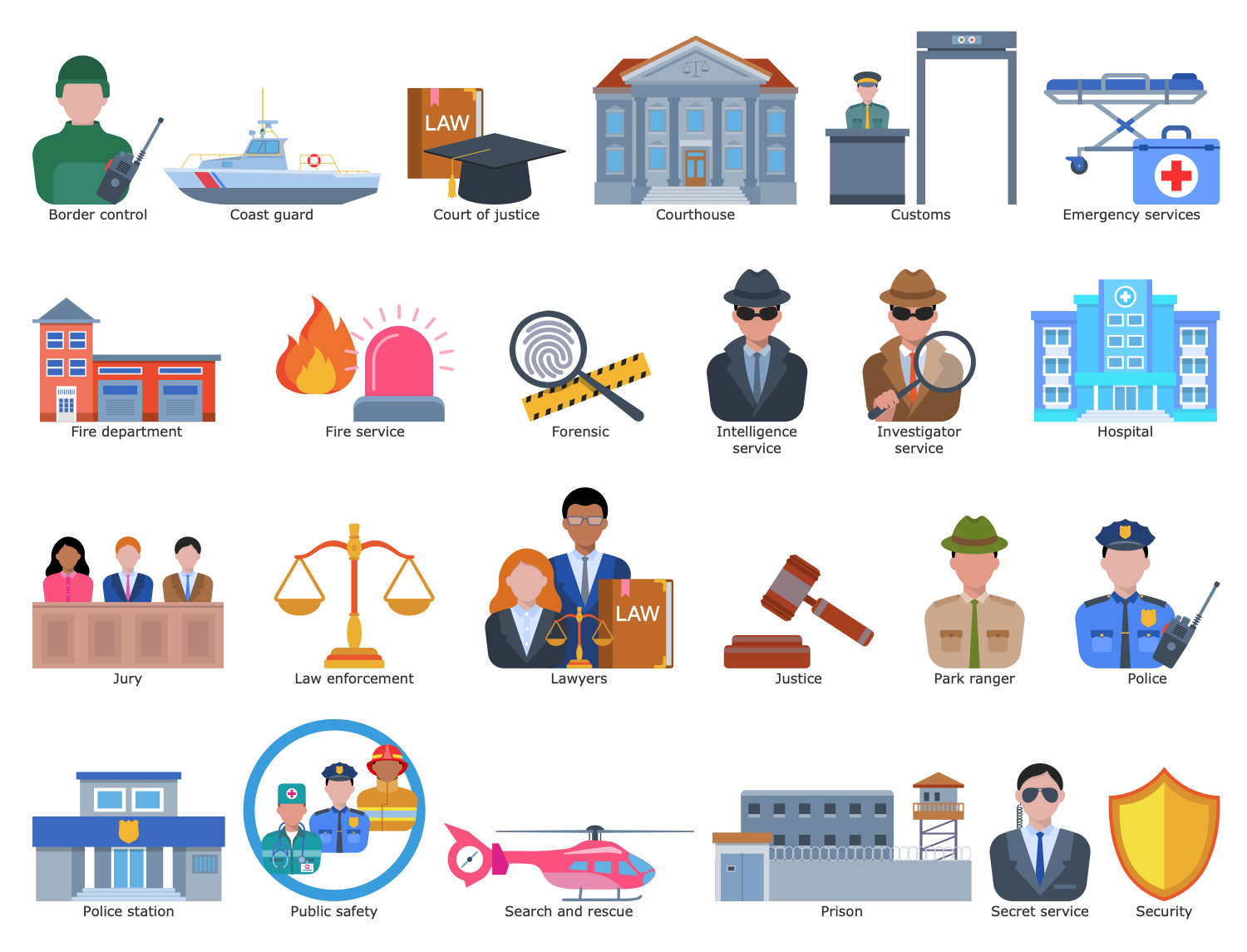

Design Elements — Public Spaces
Design Elements — Public Transit
Design Elements — Public Works

Design Elements — Traffic Management
Design Elements — Transport Asset Management
Design Elements — Water and Sewage
Related News:
Public Utilities Examples
There are a few samples that you see on this page which were created in the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM application by using the Public Utilities solution. Some of the solution's capabilities as well as the professional results which you can achieve are all demonstrated here on this page.
All source documents are vector graphic documents which are always available for modifying, reviewing and/or converting to many different formats, such as MS PowerPoint, PDF file, MS Visio, and many other graphic ones from the ConceptDraw Solution Park or ConceptDraw STORE. The Public Utilities solutions are available to all ConceptDraw DIAGRAM users to install and use it for working in diagramming and drawing.
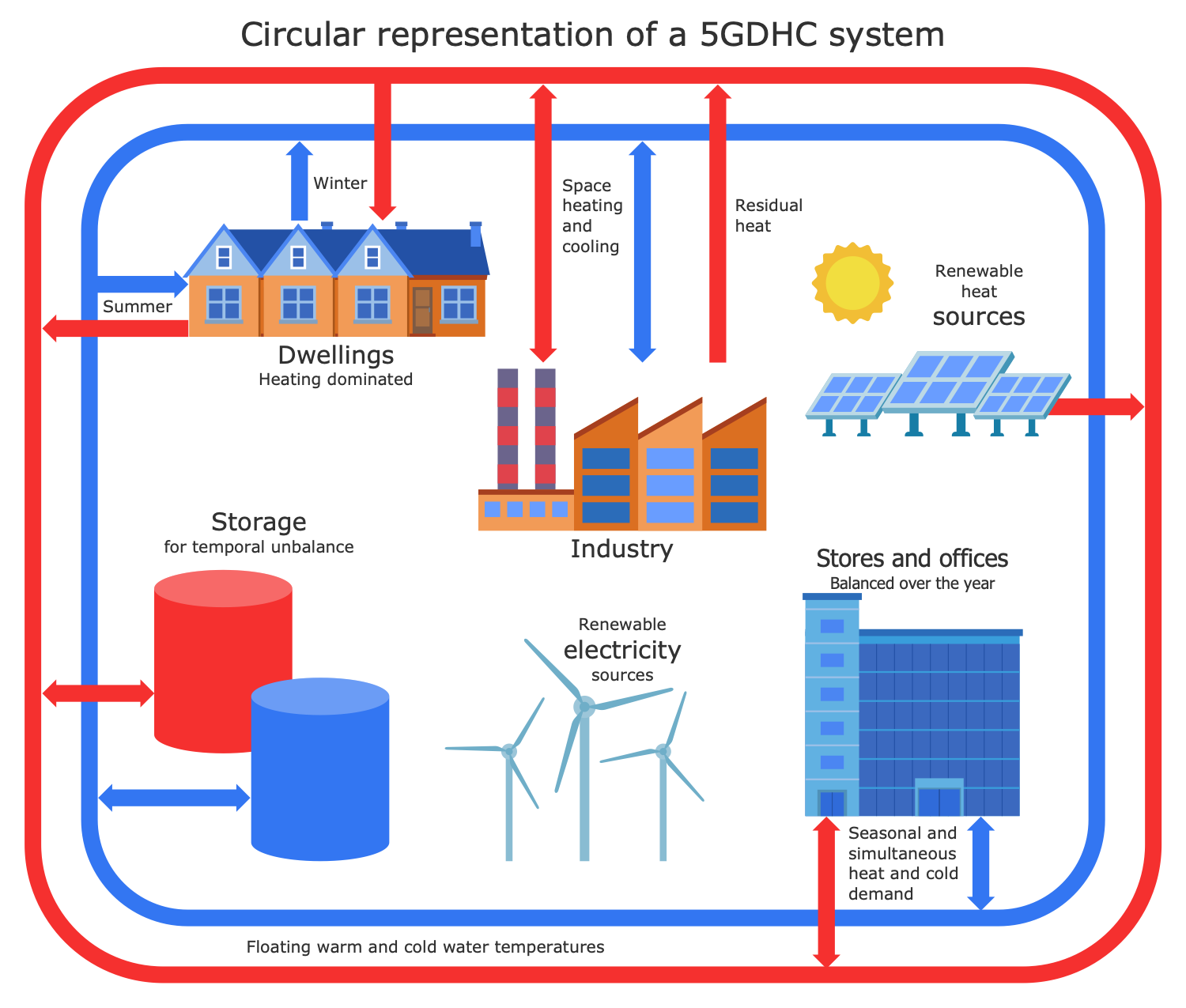
Example 1: Cold District Heating Network
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This technical drawing sample shows a Circular representation of a 5GDHC (5th generation district heating and cooling) system, which is a Cold District Heating (CHD) system referred also to as an Anergy network, District Heating and Cooling (LTDHC) or Low-temperature network (LTN). It is a type of district heating network that is a system of distributing heat through a system of insulated pipes, which is generated in a centralized location. Cold District Heating systems operate at low transmission temperatures (10 to 25°C) and ensure simultaneous and independent heating and cooling for different consumers. These systems provide zero emissions of CO2 and NO2 heat supply due to the active use of renewable energy or remote fossil-fuelled power stations. CHDs do not use combustion on-site and are the systems of the future as a way to transform and decarbonize the heat supply and mitigate climate change. Switching of Cold District Heating systems to 100% fed by renewable energy sources is planned in the future.
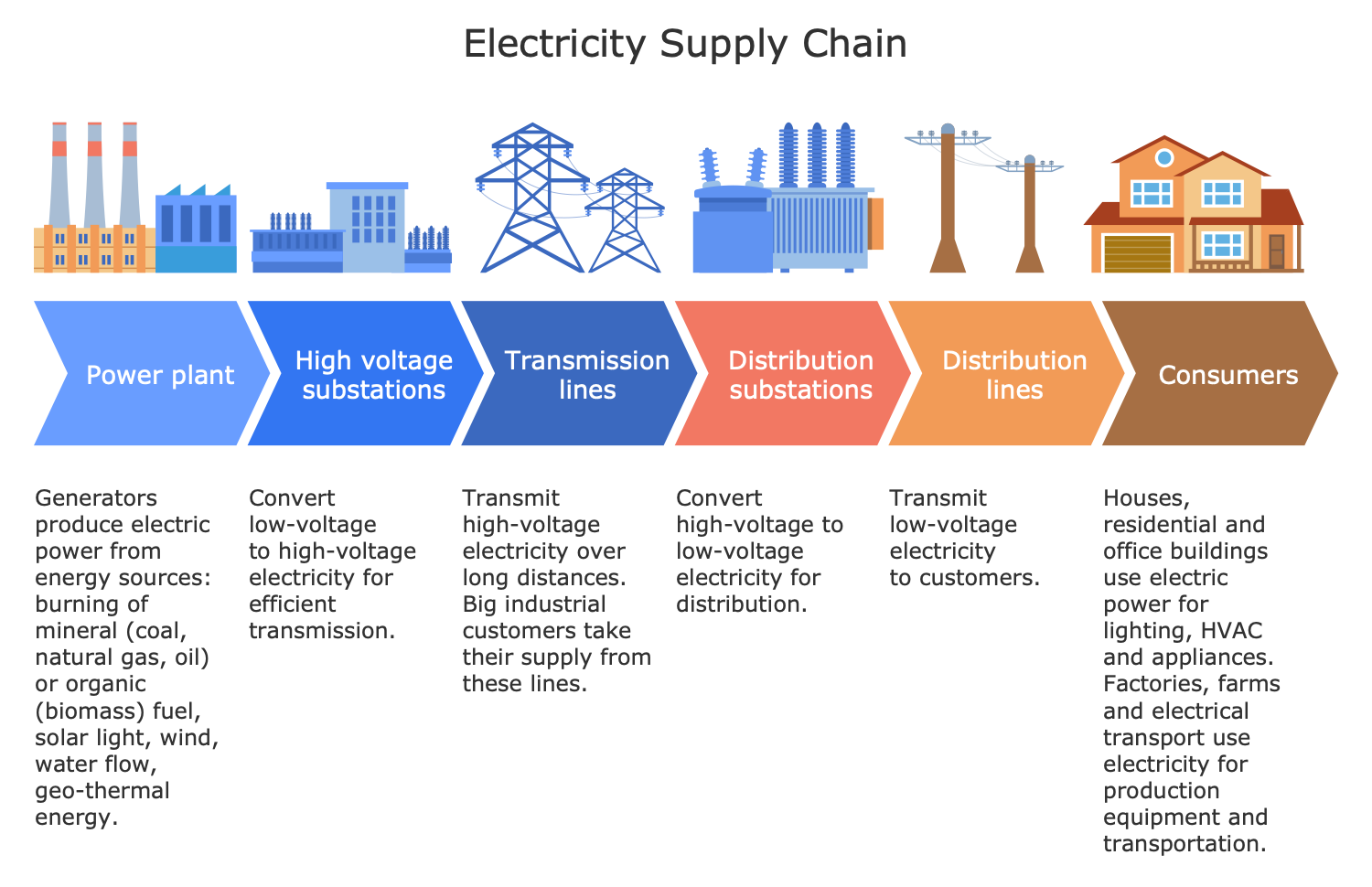
Example 2: Electricity Supply Chain
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This electrical diagram sample shows the electricity supply chain from the power plants to the end consumers through high-voltage substations, transmission lines, distribution substations, and distribution lines. All components of the electrical grid are interconnected to each other. The generators at the power plants produce electric power from mineral and organic energy sources including coal, natural gas, oil, and biomass, and renewable energy sources like solar light, water flow, wind, and geothermal energy. High-voltage substations are responsible for converting low-voltage electricity to high-voltage for efficient transmission. Transmission lines allow high-voltage electricity transmission over long distances. Distribution substations convert high-voltage electricity to low-voltage for mass distribution to consumers (residential and office buildings, private homes) through distribution lines. High-voltage electricity is directly supplied only to large industrial enterprises.
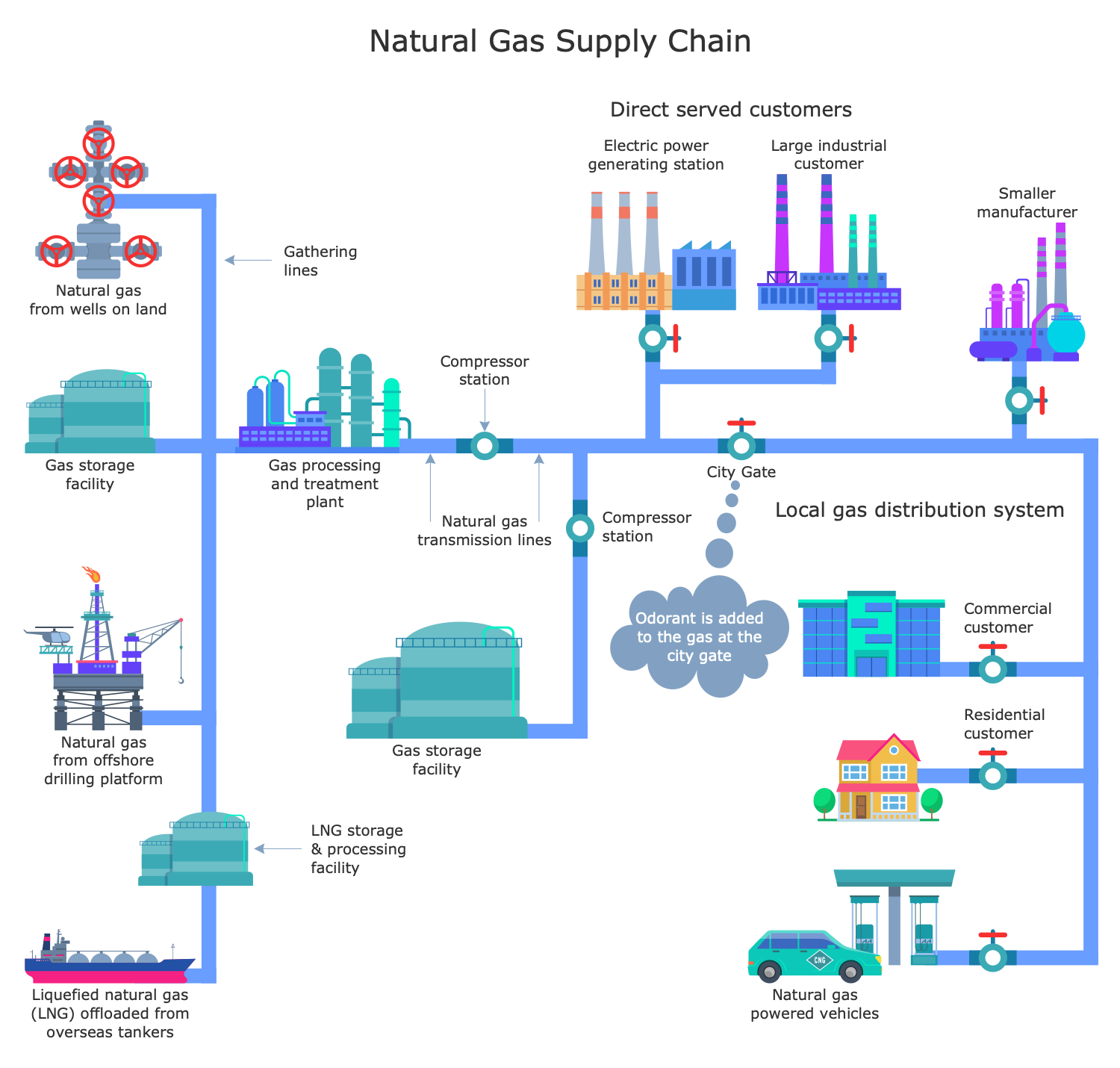
Example 3: Natural Gas Supply Chain
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 15 minutes creating this sample.
This sample shows the supply chain of natural gas, which is a fossil fuel and non-renewable resource, naturally occurring underground over millions of years as a result of the decomposition of organic matter under anaerobic conditions, intense heat, and pressure through biogenic or thermogenic processes. Natural gas is a mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons, mainly methane and low levels of higher alkanes and trace gases. It is used in household and manufacturing, it is burned for heating, cooking, electricity generation, etc. Methane is colorless and odorless, therefore for safety reasons unpleasant odorizers like mercaptan are added and help to detect leaks. The extraction and consumption of natural gas from underground geological formations on land and drilling underwater have great scopes. From the gas processing and treatment plant, it is transmitted through transmission lines to gas storage facility and electric power generation stations, industrial factories, and then is distributed to residential and commercial customers, including power stations for vehicles. Design easily supply chain, plumbing plan, and heating plan in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM with the Public Utilities solution.
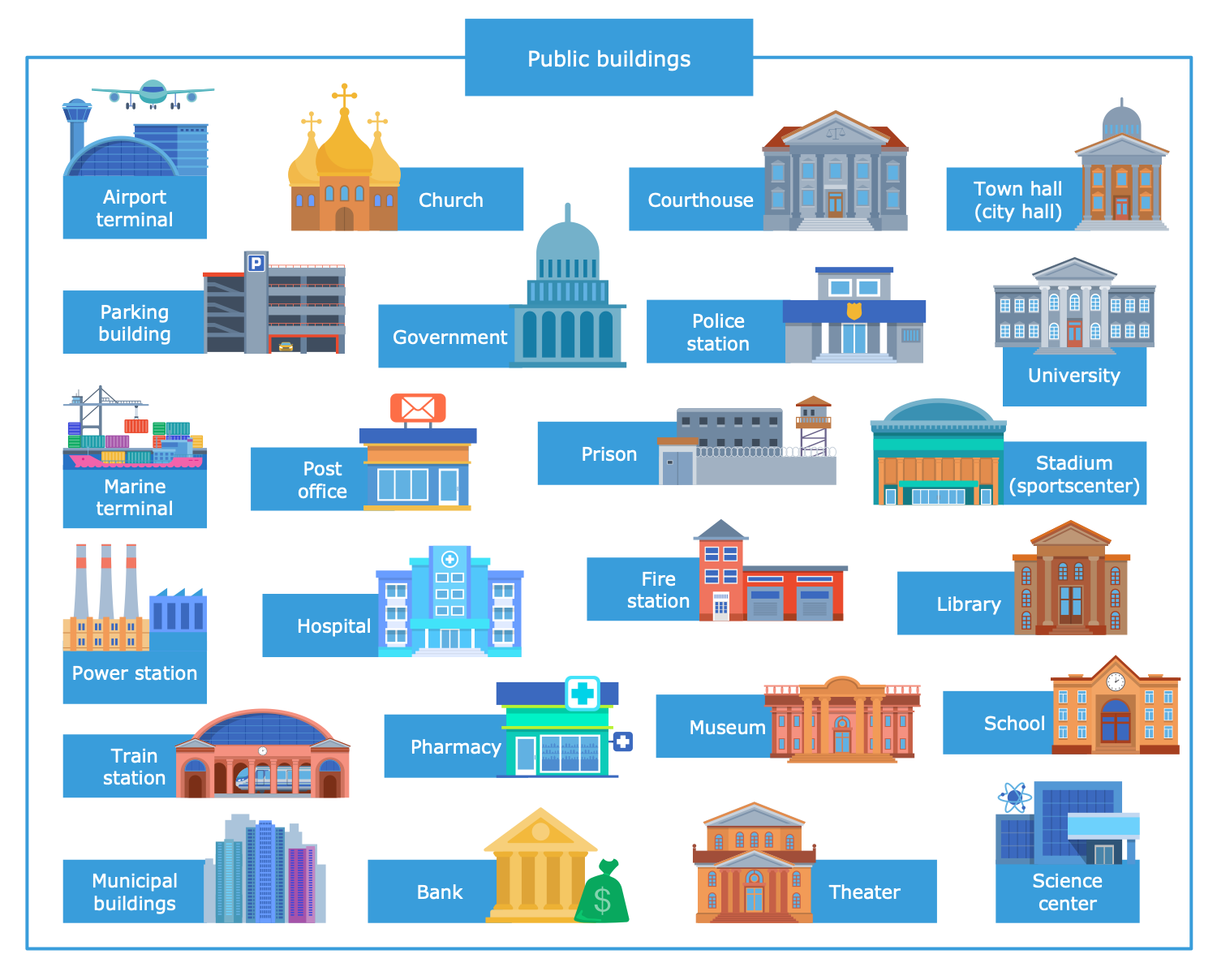
Example 4: Public Buildings
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This sample shows a variety of public buildings, which are part of public works and public infrastructure projects ensuring health, safety, recreation, employment, and other aims. Public buildings include hospitals, pharmacies, fire stations, schools and universities, science centers, churches, police stations, prisons, post offices, banks, government and municipal buildings, airport and marine terminals, train stations, libraries, theaters, museums, stadiums, courthouses, power stations, parking buildings, and town halls. They are built wholly or in part by public funds and are important for the entire society. Public buildings provide public services, connect people, and are accessible to the public for assembly, education, treatment, entertainment, economic activity, support community, and other goals. Public buildings reflect the priorities of the people and governments, culture, and era when they were built, and should be structurally sound and reliable. Many of the public buildings built in previous centuries are architecturally significant and create a great impression nowadays. The public utility icons included in the libraries of the Public Utilities solutions serve for easy designing your diagrams.
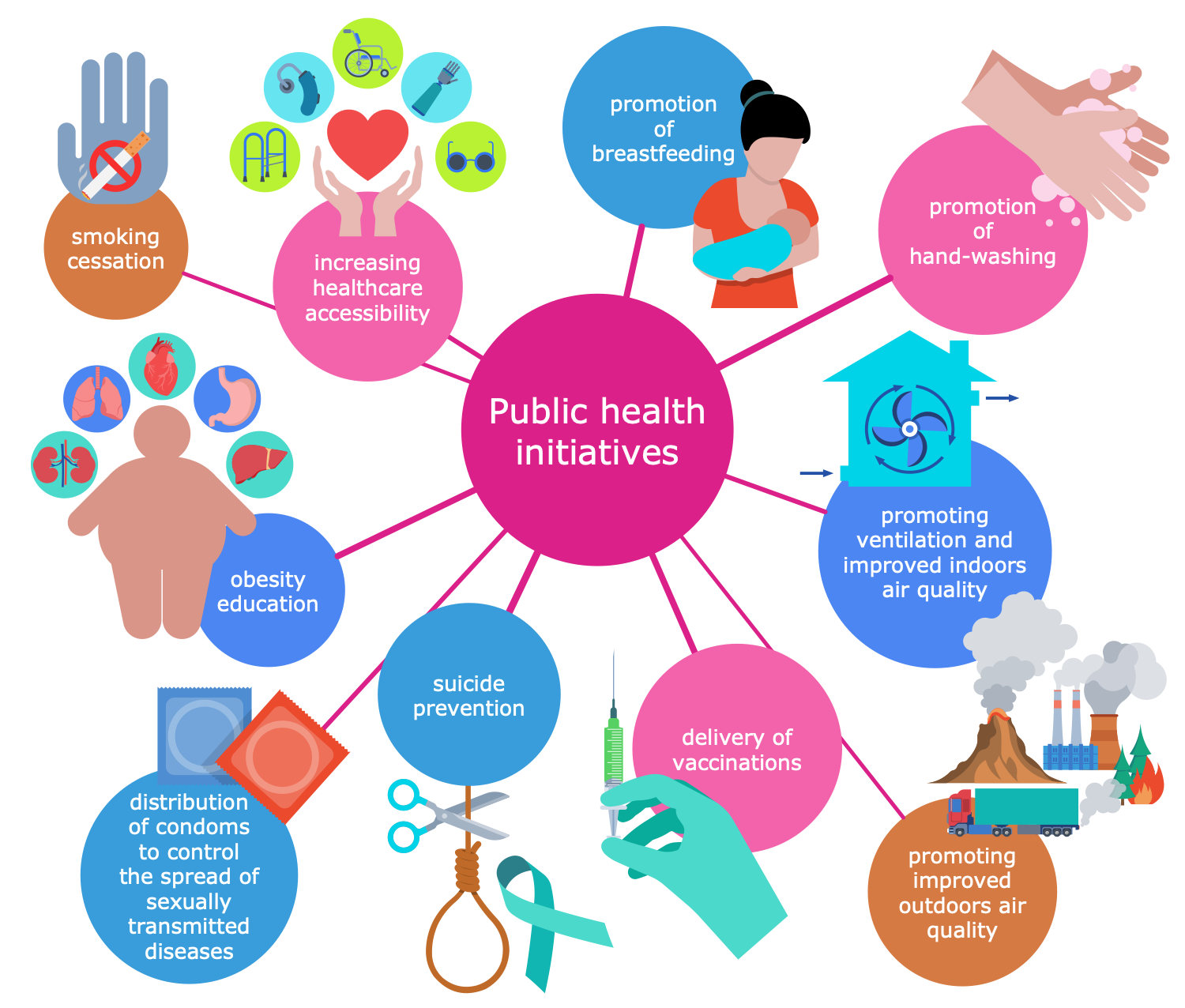
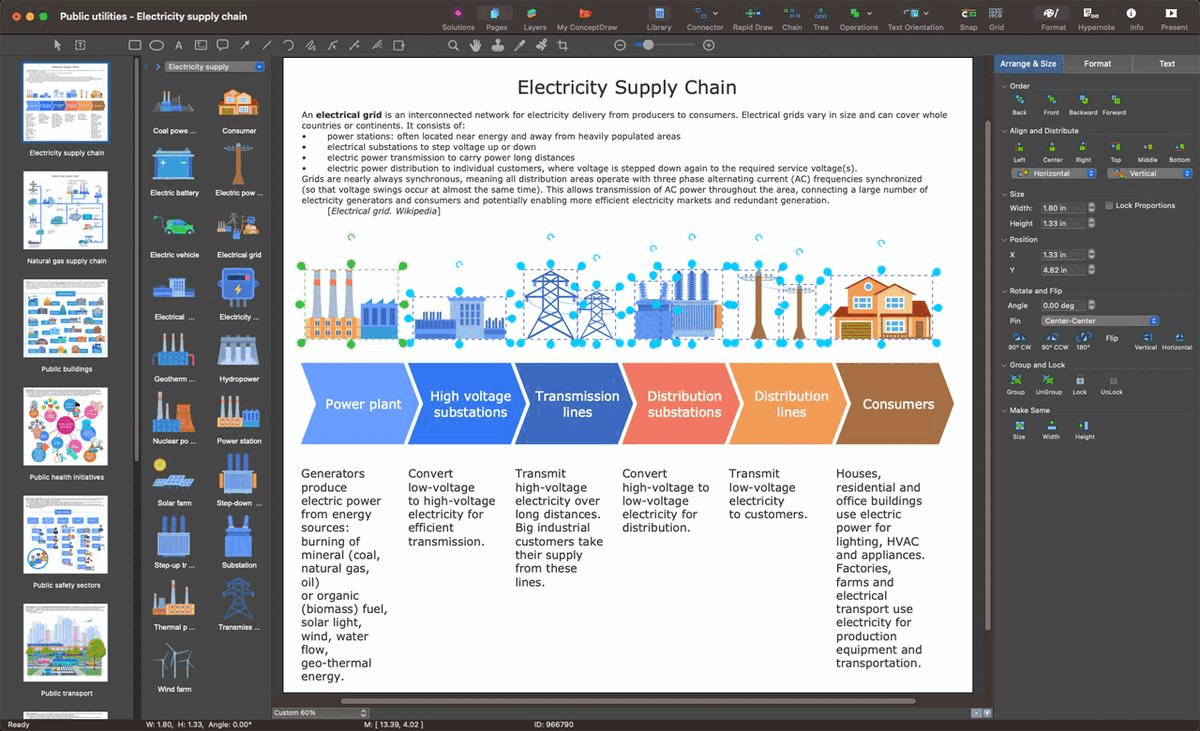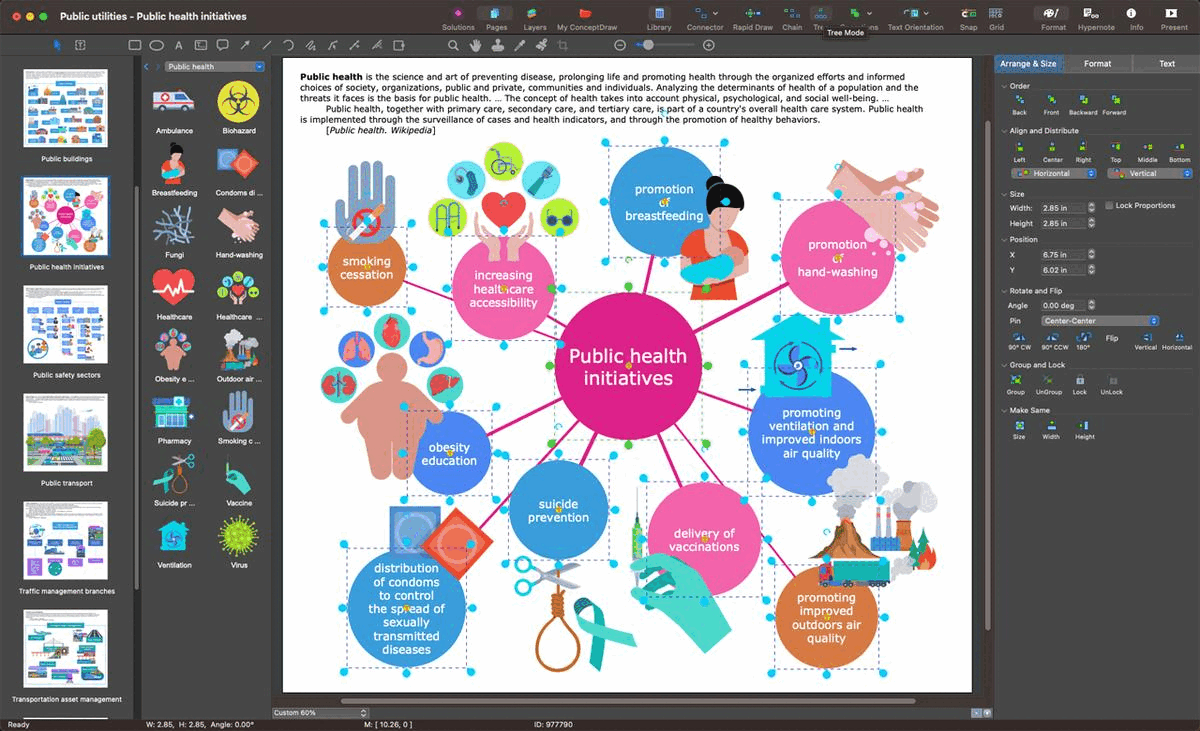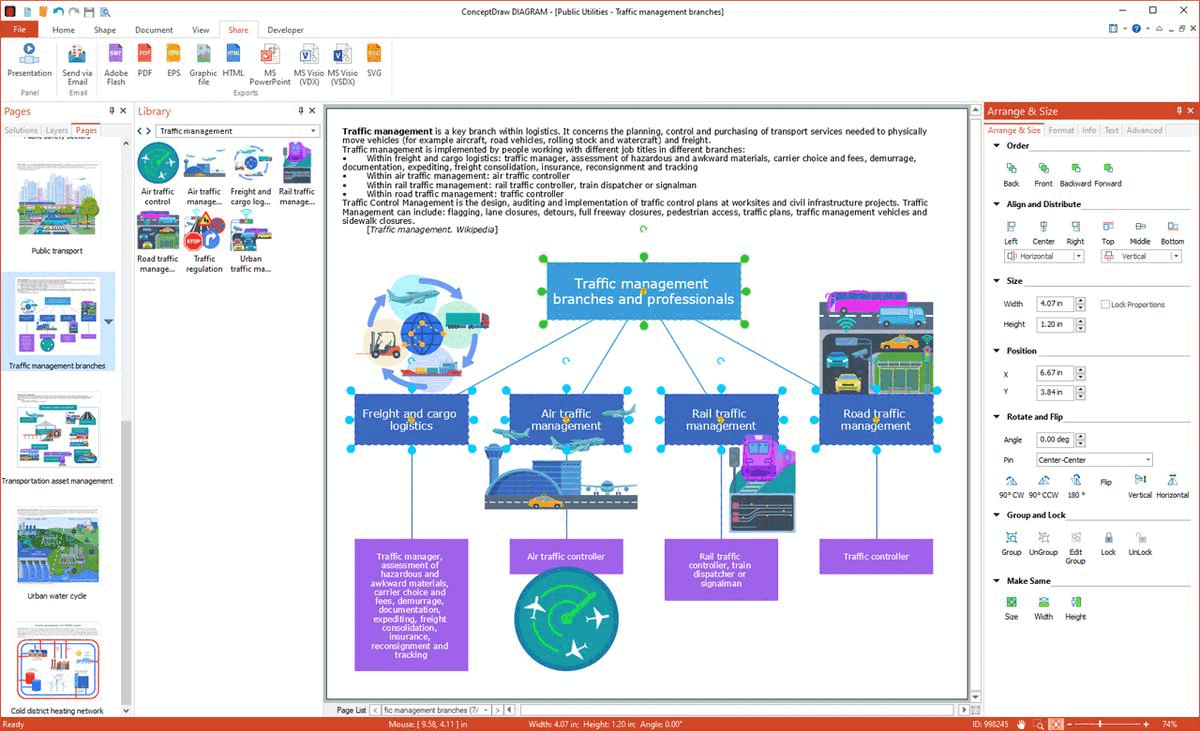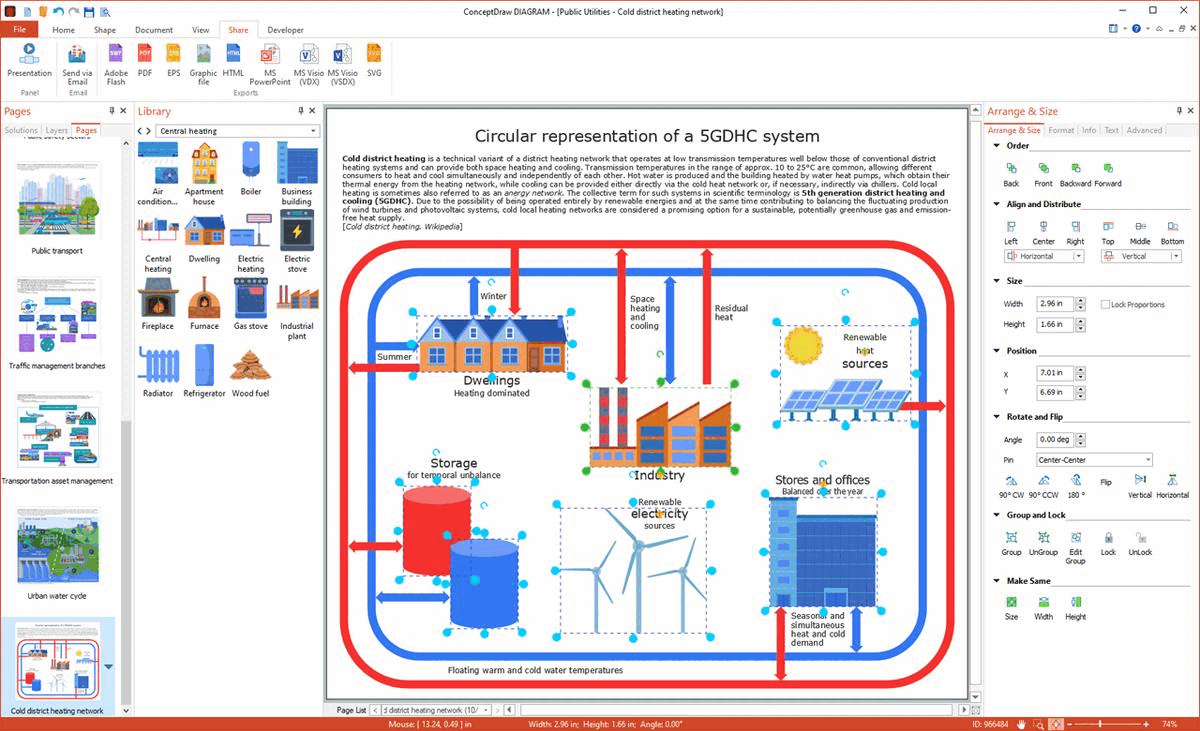
Example 5: Public Health Initiatives
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This sample provides the public health initiatives, which are a basis for preventing diseases, promoting health, reducing the incidence of disease and disability, and increasing the life expectancy of society due to the organized efforts, collective actions of medical and other public organizations, government and international organizations, public communities and private individuals. Public health initiatives suppose wide-ranging improvement of health, physical and mental, and also social well-being, analyzing the determinants and threats of population health. Public health initiatives are a part of the overall country's healthcare system. Common public health initiatives promoted to health and fought diseases include increasing healthcare accessibility, delivery of vaccinations, hand-washing, ventilation, improvement indoor and outdoor air quality, promotion of breastfeeding, obesity education, smoking cessation, suicide prevention, and ways to control the spread of diseases including sexually transmitted.
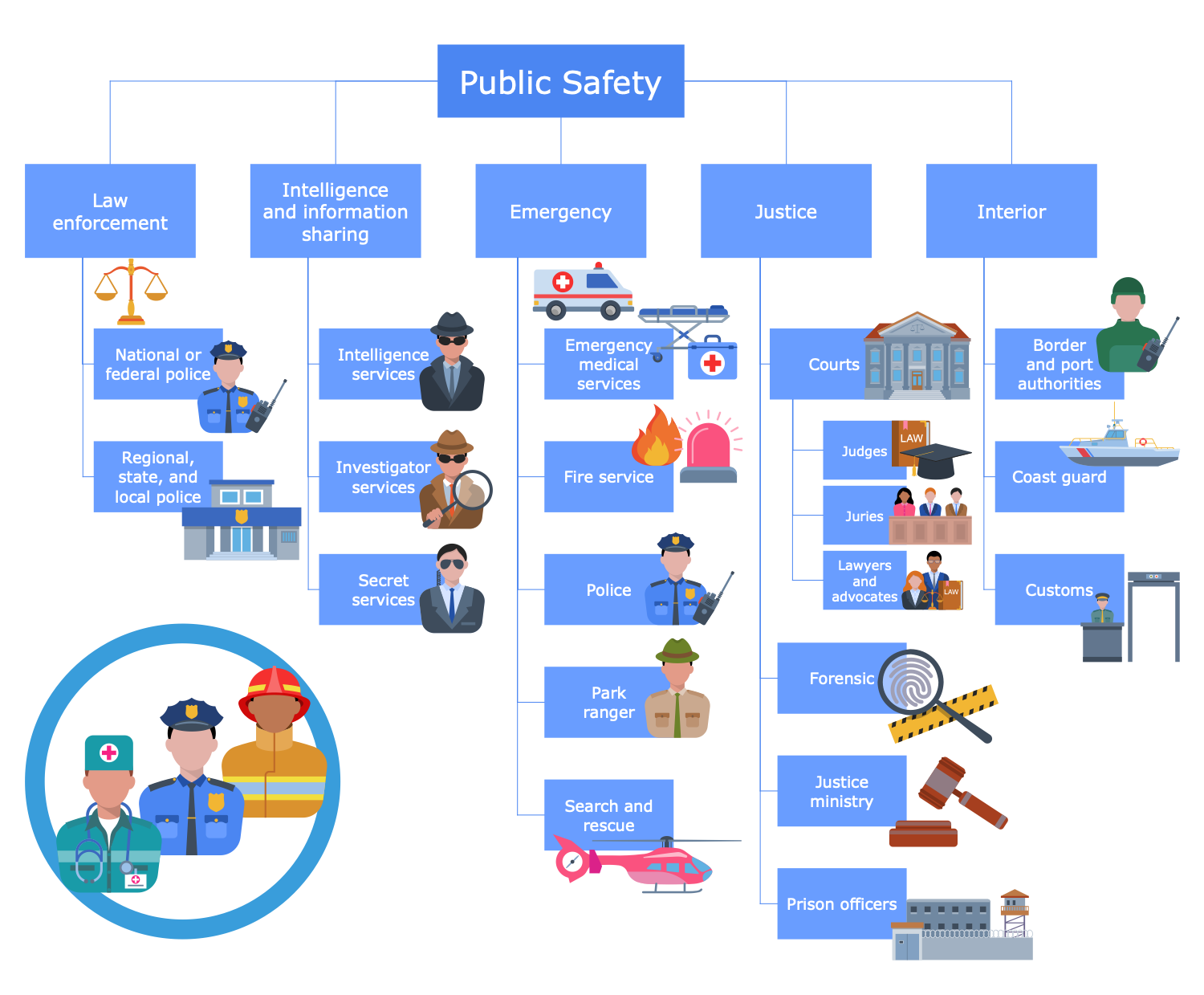
Example 6: Public Safety Sectors
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This sample shows 5 sectors of public safety: law enforcement, intelligence and information sharing, emergency, justice, and interior sector. Public safety is the protection and prevention of events that may cause danger to the security and safety of the public, order, health, and well-being of people in a certain territory. It includes the prevention of crimes and property damages, provision of medical emergencies, firefighting, and help in disasters. Public security is an important political and economic issue at both national and international levels. It contributes to economic success, increasing human living standards and productivity, and the attractiveness of a certain location. Public safety organizations are distributed between the sectors and include police (national, federal, regional, state, and local), intelligent services, investigator services, secret services, emergency medical services, fire services, park rangers, search and rescue, courts, forensics, justice ministries, prisons, border and port authorities, coast guard, and customs.
Example 7: Public Transport
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This sample is dedicated to public transport, which is a system of transport available for use by the general public. In common, public transport follows a schedule and fixed routes with set embarkation and disembarkation points, is centrally managed, and a set fee is charged for each trip. Public transport is exploited within cities and also links different cities, countries, and distant parts of the world. It is equally popular in low and high-wealth cities. Public transport includes land transport, road transport, buses, minibusses, trams, trolleybuses, taxis, rail transport, intercity bus and rail service, light rail, suspension railway, cable railway, maritime transport, ferries, and air transport. Each kind of transport has its own advantages. Some transport like, for example, the metro helps to save time at peak times, aircrafts overcome great distances in a relatively short time, the taxis offer individual on-demand services. The use of electrical public transport gains popularity in many countries because ensures environmental protection by reducing emissions.

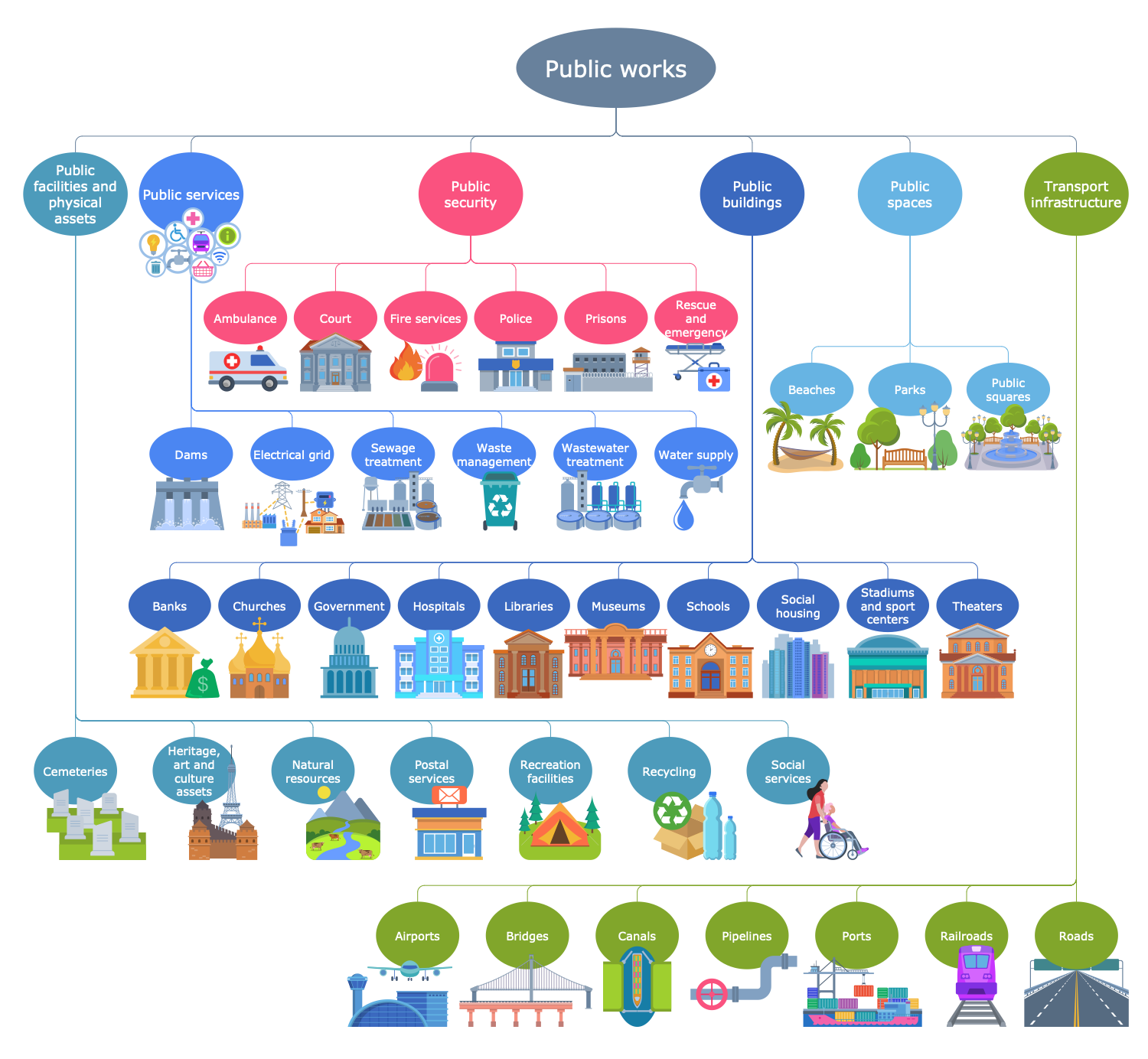
Example 8: Public Works
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This sample shows a variety of public works, which are all infrastructure objects, services, and public goods financed by the government for health, safety, employment, and recreation of the population. They include five common categories: public services, public security, public facilities and physical assets, public spaces, and transport infrastructure. Governmental investing in public works projects has many benefits for the country and society, key of them are stimulating of country's economy, environment protection, reducing unemployment, and increasing people's well-being, level and quality of life. Digital public infrastructure projects are also included. Public works have been encouraged since antiquity and touch all spheres of economics, politics, and social life including recreation, law, education, transport infrastructure, medical services, insurance, public services including water supply and electrical grid, physical assets and facilities, aesthetics, public spaces like public squares, parks, beaches, and many more.
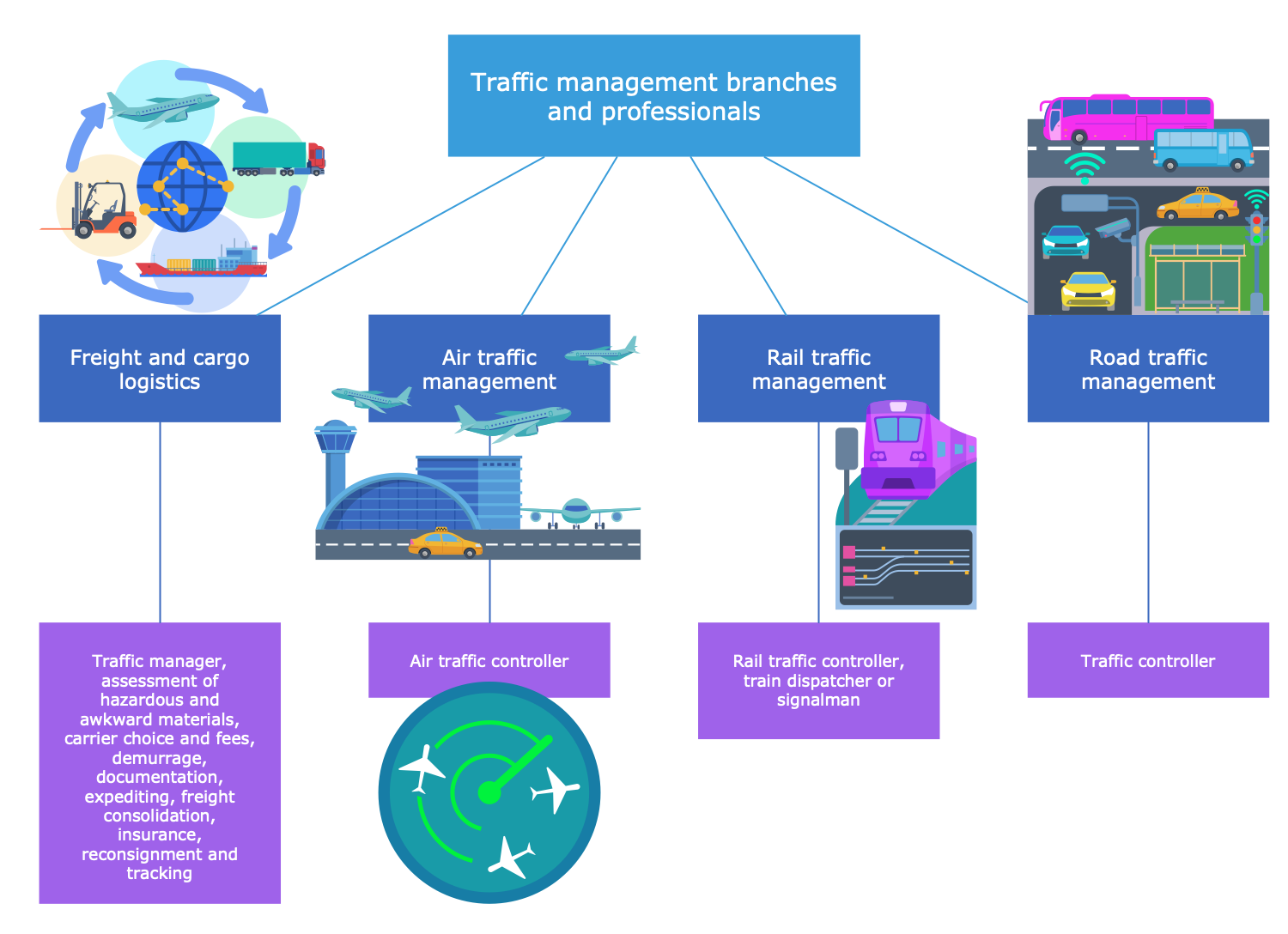
Example 9: Traffic Management Branches
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This sample shows the key traffic management branches and the professionals responsible for each of them. Traffic management is a key logistics branch, which includes freight and cargo logistics, air traffic management, rail traffic management, and road traffic management. It comprises a variety of activities: design, auditing and implementation of traffic control plans, control, purchasing of transport services, and planning. People of different job titles are employed in different branches. Traffic managers are responsible for freight and cargo logistics, they provide an assessment of hazardous and awkward materials, expediting, documentation, insurance, tracking, carrier choice and fees, demurrage, freight consolidation, and reconsignment. Rail traffic controllers, train dispatchers, and signalmen are employed in rail traffic management, traffic controllers in road traffic management, and air traffic controllers in air traffic management correspondingly. The use of pre-made vector icons is the easiest and fastest way to design exceptionally looking diagrams and infographics.
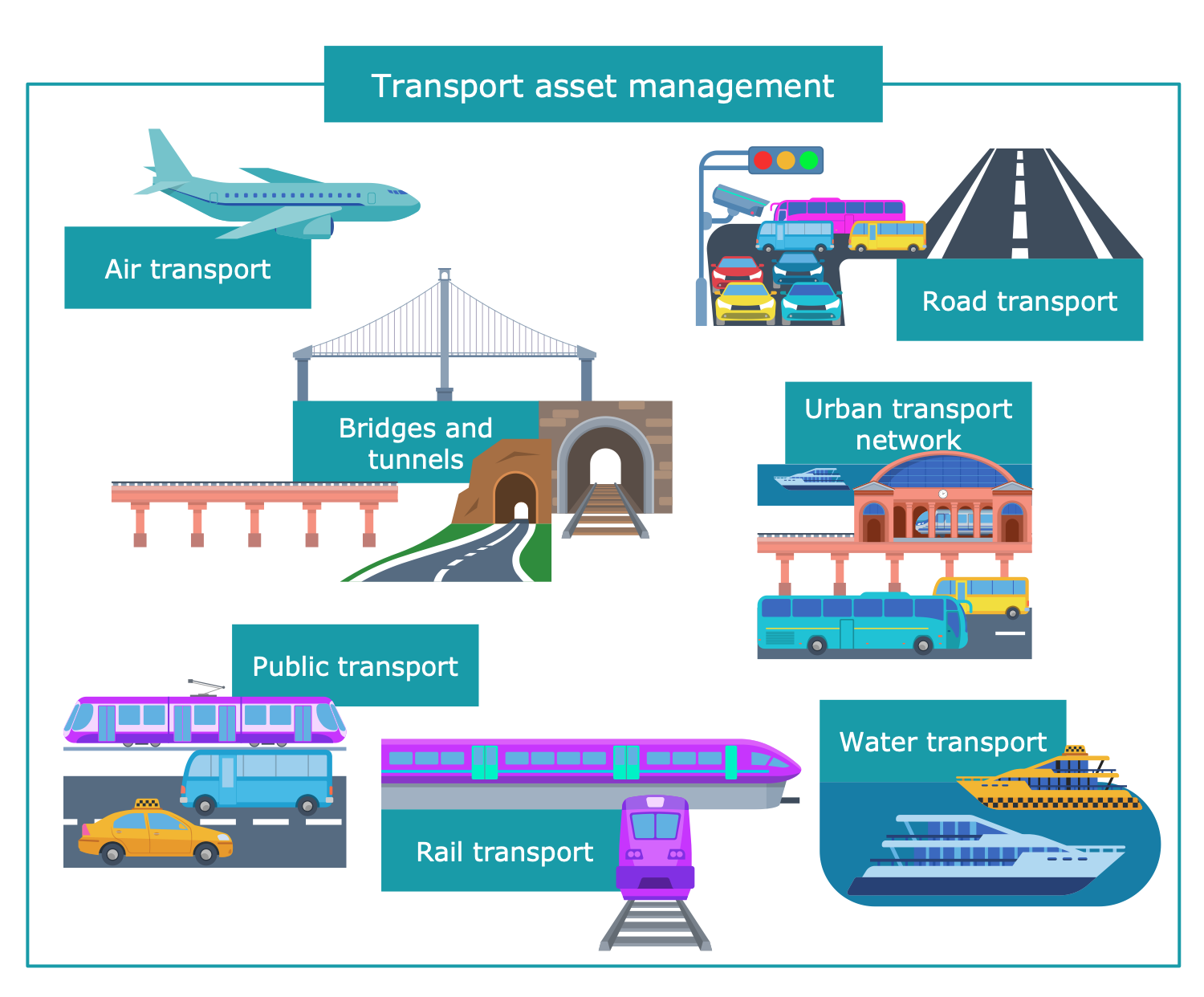
Example 10: Transportation Asset Management
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This sample is dedicated to transport asset management. It is a strategic business process aimed at the optimization of performance and cost-effectiveness of public transport infrastructure. Transport asset management is a comprehensive approach focused on physical assets. It is implemented through scheduled maintenance, sustaining, repair, rehabilitation, and in-time replacement of unusable parts. Essential infrastructure asset management processes and activities also include systematic accounting, implementing and managing information systems and management strategies directed at systems' support and improvement efficiency. The primary goals are to preserve and extend the service life and performance of infrastructure assets, improve economics and quality of life in society. Public transport infrastructure assets include public transport lines, roads, railways, transport interchanges, bridges, tunnels, stops, depots, stations, fuel and charging stations, sea ports, river piers, airports, etc.
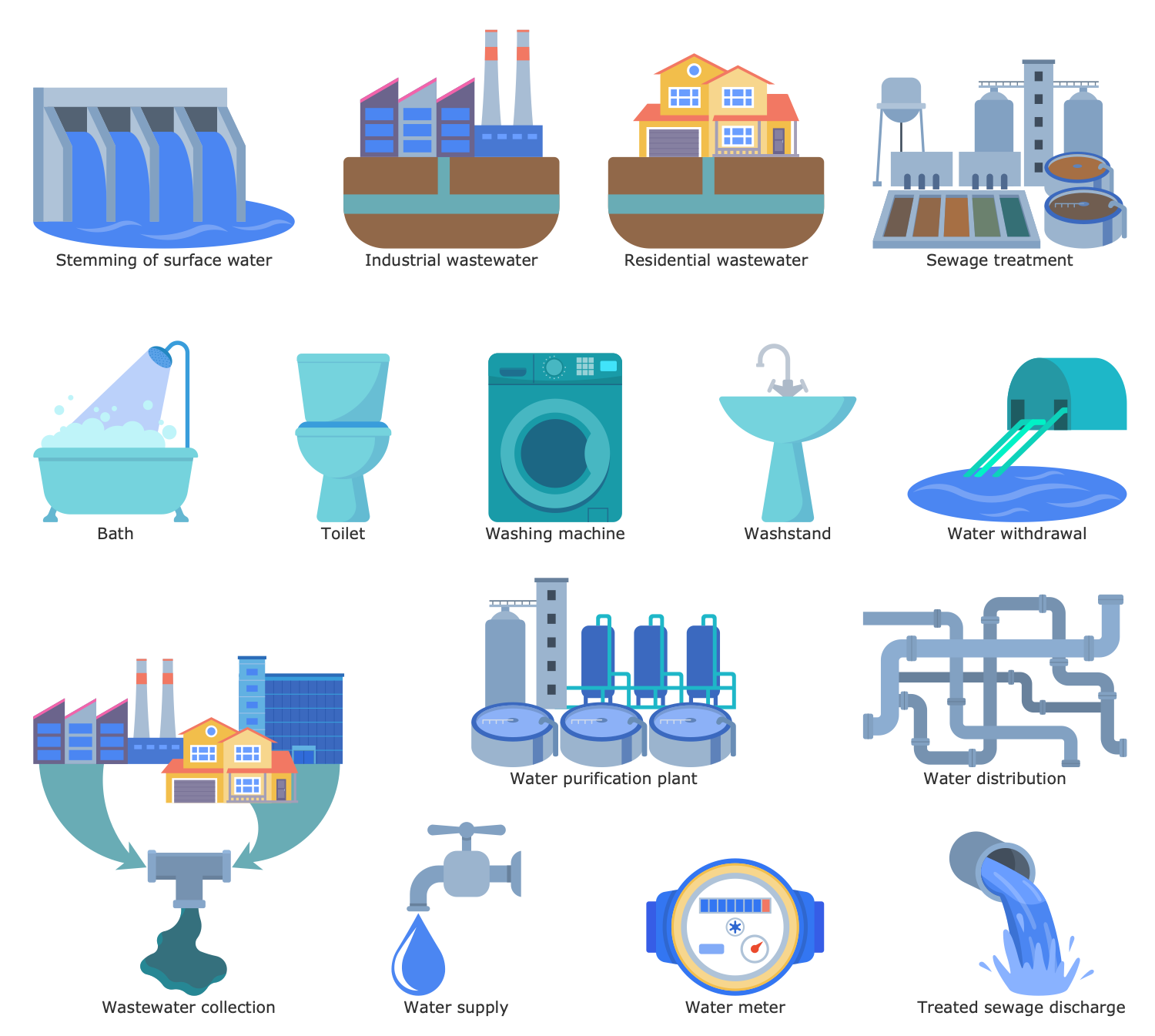
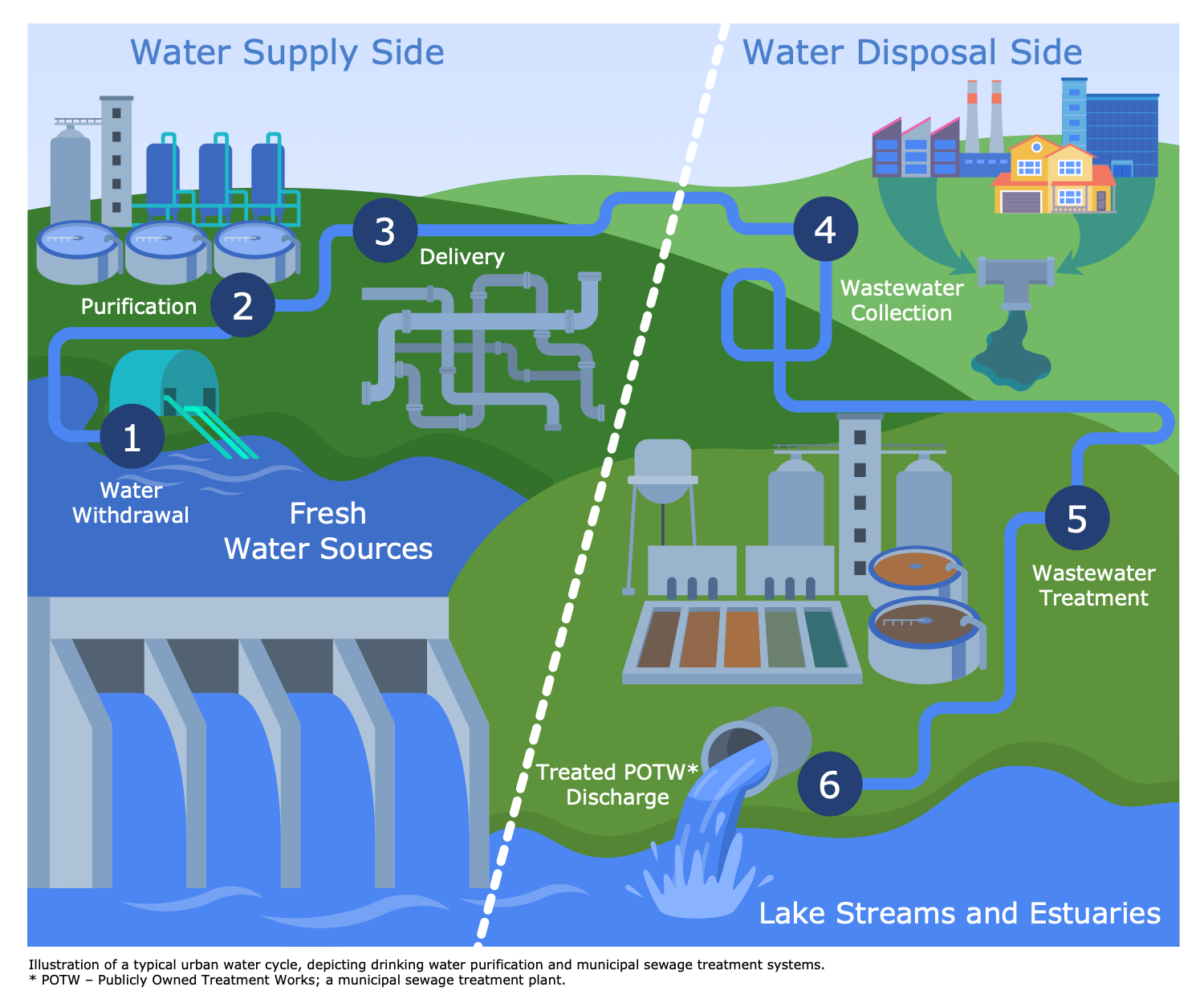
Example 11: Urban Water Cycle
This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the combination of libraries from the Public Utilities Solution. An experienced user spent 10 minutes creating this sample.
This sample shows a typical urban water cycle, which involves water supply and water disposal steps. Water supply includes water withdrawal from freshwater sources, its purification, and delivery to the population. At the same time, water disposal contains wastewater collection, treatment, and discharge of treated POTW. Integrated urban water management (IUWM) is incredibly important in this process. It is the method of managing freshwater, wastewater, and stormwater within the urban cycle and the entire river basin. IUWM is a way to use water resources more efficiently without the impact on the natural water cycle, so it is a path of improvement environmental, social, and economic outcomes. It helps to improve water supply and wastewater treatment, enhance drinking water quality and consumption efficiency, increase investments in water, wastewater, and stormwater management, and enhance the efficiency of their operations. IUWM includes evaluation and analysis performance assessment of the operation of sewage treatment systems, new technologies and strategies, system sustainability and safety.
Inside
What I Need to Get Started
After ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is installed, the Public Utilities solution can be purchased either from the Management area of ConceptDraw STORE itself or from our online store. Thus, you will be able to use the Stakeholder Onion Diagrams solution straight after.
How to install
First of all, make sure that both ConceptDraw STORE and ConceptDraw DIAGRAM applications are downloaded and installed on your computer. Next, install the Public Utilities solution from the ConceptDraw STORE to use it in the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM application.
Start using
Start using the Public Utilities solution to make the professionally looking business planning diagrams by adding the design elements taken from the stencil libraries and editing the pre-made examples that can be found there.