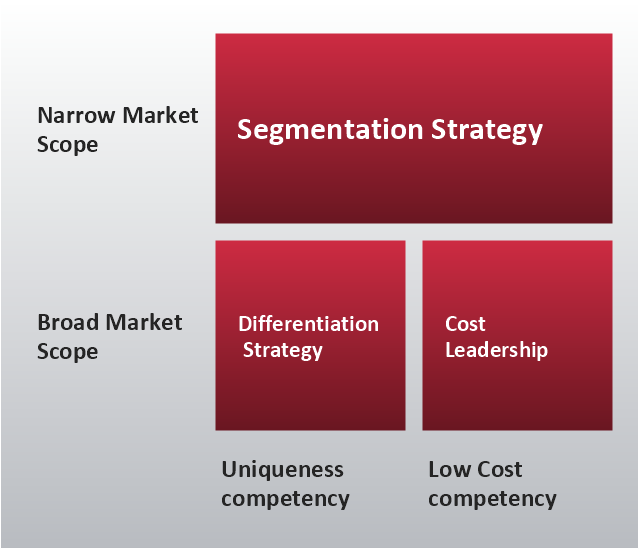
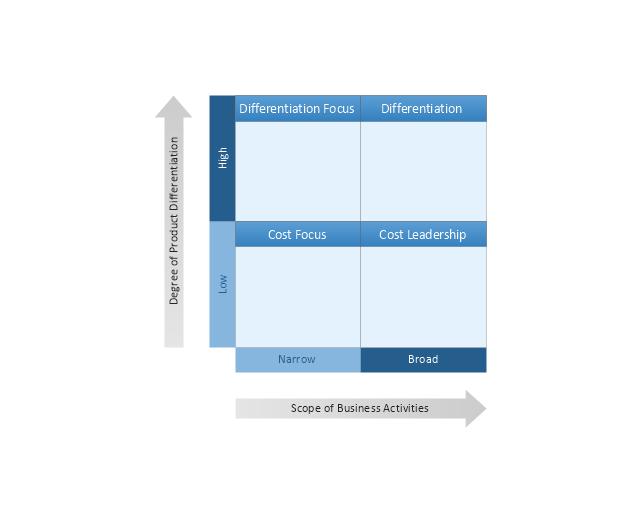
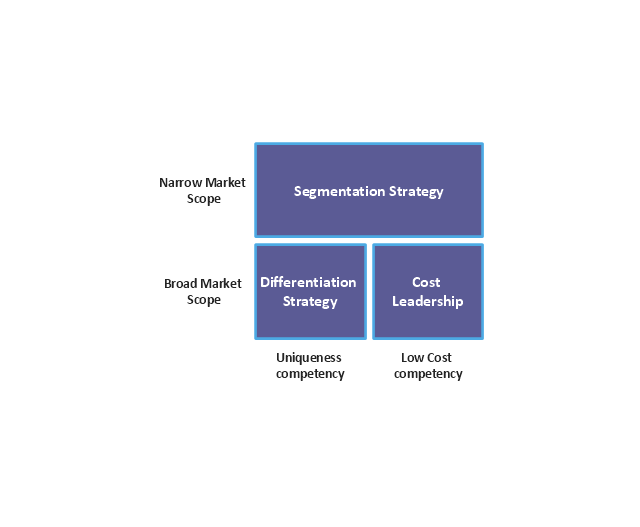
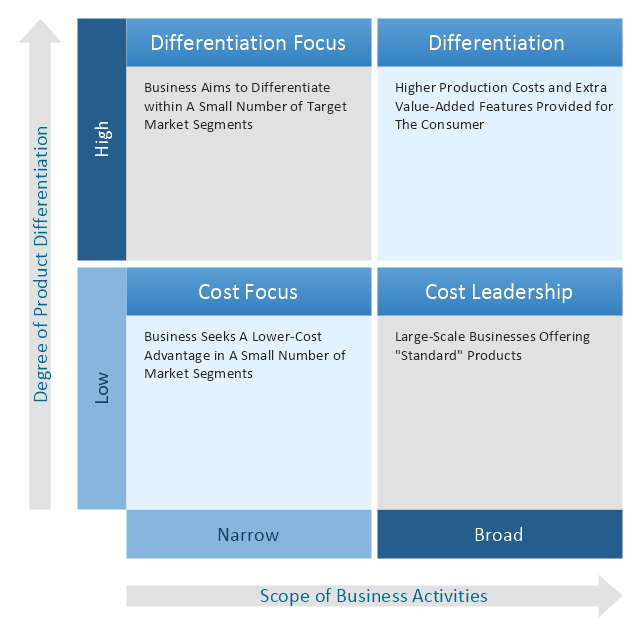
"Michael Porter has described a category scheme consisting of three general types of strategies that are commonly used by businesses to achieve and maintain competitive advantage. These three generic strategies are defined along two dimensions: strategic scope and strategic strength. Strategic scope is a demand-side dimension and looks at the size and composition of the market you intend to target. Strategic strength is a supply-side dimension and looks at the strength or core competency of the firm. In particular he identified two competencies that he felt were most important: product differentiation and product cost (efficiency)." [Porter's generic strategies. Wikipedia]
This Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram was redesigned from Wikipedia file PorterGenericStrategies.png. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:PorterGenericStrategies.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
This Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram example was created by the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram was redesigned from Wikipedia file PorterGenericStrategies.png. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:PorterGenericStrategies.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
This Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram example was created by the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
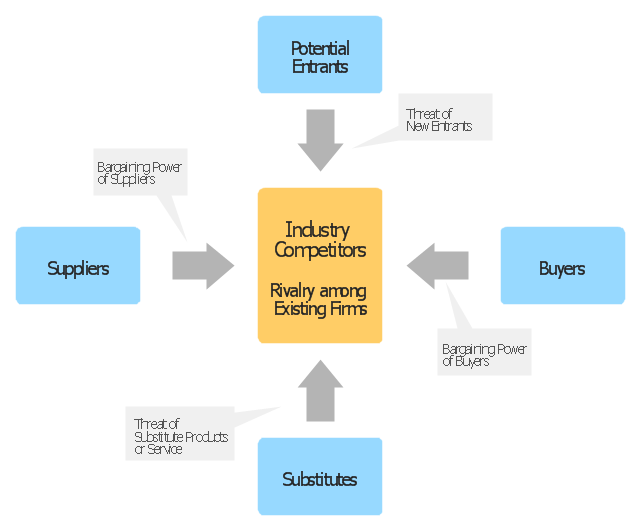
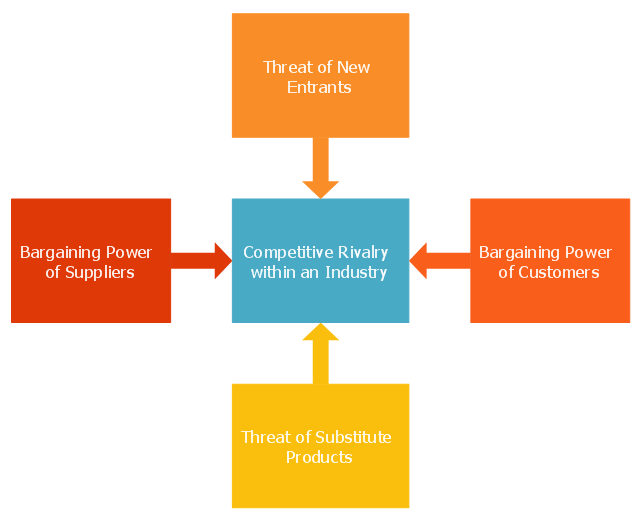
"Porter five forces analysis is a framework for industry analysis and business strategy development. It draws upon industrial organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and therefore attractiveness of a market. Attractiveness in this context refers to the overall industry profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the combination of these five forces acts to drive down overall profitability. A very unattractive industry would be one approaching "pure competition", in which available profits for all firms are driven to normal profit.
Three of Porter's five forces refer to competition from external sources. The remainder are internal threats.
Porter referred to these forces as the micro environment, to contrast it with the more general term macro environment. They consist of those forces close to a company that affect its ability to serve its customers and make a profit. A change in any of the forces normally requires a business unit to re-assess the marketplace given the overall change in industry information. The overall industry attractiveness does not imply that every firm in the industry will return the same profitability. Firms are able to apply their core competencies, business model or network to achieve a profit above the industry average. A clear example of this is the airline industry. As an industry, profitability is low and yet individual companies, by applying unique business models, have been able to make a return in excess of the industry average.
Porter's five forces include - three forces from 'horizontal' competition: the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants; and two forces from 'vertical' competition: the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers.
This five forces analysis, is just one part of the complete Porter strategic models. The other elements are the value chain and the generic strategies." [Porter five forces analysis. Wikipedia]
The block diagram example "Porter's five forces model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Block Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Three of Porter's five forces refer to competition from external sources. The remainder are internal threats.
Porter referred to these forces as the micro environment, to contrast it with the more general term macro environment. They consist of those forces close to a company that affect its ability to serve its customers and make a profit. A change in any of the forces normally requires a business unit to re-assess the marketplace given the overall change in industry information. The overall industry attractiveness does not imply that every firm in the industry will return the same profitability. Firms are able to apply their core competencies, business model or network to achieve a profit above the industry average. A clear example of this is the airline industry. As an industry, profitability is low and yet individual companies, by applying unique business models, have been able to make a return in excess of the industry average.
Porter's five forces include - three forces from 'horizontal' competition: the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants; and two forces from 'vertical' competition: the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers.
This five forces analysis, is just one part of the complete Porter strategic models. The other elements are the value chain and the generic strategies." [Porter five forces analysis. Wikipedia]
The block diagram example "Porter's five forces model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Block Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Matrices" contains 10 templates of marketing matrix diagrams and charts.
Use these templates to create your marketing matrices in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these templates to create your marketing matrices in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This marketing diagram sample illustrates Porter five forces model. It was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Porters five forces.PNG.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Porters_ five_ forces.PNG]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Porter five forces analysis is a framework for industry analysis and business strategy development. It draws upon industrial organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and therefore attractiveness of a market. Attractiveness in this context refers to the overall industry profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the combination of these five forces acts to drive down overall profitability. A very unattractive industry would be one approaching "pure competition", in which available profits for all firms are driven to normal profit. This analysis is associated with its principal innovator Michael E. Porter of Harvard University (as of 2014).
Three of Porter's five forces refer to competition from external sources. The remainder are internal threats.
Porter referred to these forces as the micro environment, to contrast it with the more general term macro environment. They consist of those forces close to a company that affect its ability to serve its customers and make a profit. A change in any of the forces normally requires a business unit to re-assess the marketplace given the overall change in industry information. The overall industry attractiveness does not imply that every firm in the industry will return the same profitability. Firms are able to apply their core competencies, business model or network to achieve a profit above the industry average. A clear example of this is the airline industry. As an industry, profitability is low and yet individual companies, by applying unique business models, have been able to make a return in excess of the industry average.
Porter's five forces include - three forces from 'horizontal' competition: the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants; and two forces from 'vertical' competition: the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers.
This five forces analysis, is just one part of the complete Porter strategic models. The other elements are the value chain and the generic strategies." [Porter five forces analysis. Wikipedia]
The chart example "Five forces model diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Marketing Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Porters_ five_ forces.PNG]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Porter five forces analysis is a framework for industry analysis and business strategy development. It draws upon industrial organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and therefore attractiveness of a market. Attractiveness in this context refers to the overall industry profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the combination of these five forces acts to drive down overall profitability. A very unattractive industry would be one approaching "pure competition", in which available profits for all firms are driven to normal profit. This analysis is associated with its principal innovator Michael E. Porter of Harvard University (as of 2014).
Three of Porter's five forces refer to competition from external sources. The remainder are internal threats.
Porter referred to these forces as the micro environment, to contrast it with the more general term macro environment. They consist of those forces close to a company that affect its ability to serve its customers and make a profit. A change in any of the forces normally requires a business unit to re-assess the marketplace given the overall change in industry information. The overall industry attractiveness does not imply that every firm in the industry will return the same profitability. Firms are able to apply their core competencies, business model or network to achieve a profit above the industry average. A clear example of this is the airline industry. As an industry, profitability is low and yet individual companies, by applying unique business models, have been able to make a return in excess of the industry average.
Porter's five forces include - three forces from 'horizontal' competition: the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants; and two forces from 'vertical' competition: the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers.
This five forces analysis, is just one part of the complete Porter strategic models. The other elements are the value chain and the generic strategies." [Porter five forces analysis. Wikipedia]
The chart example "Five forces model diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Marketing Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Matrices
Matrices
This solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with samples, templates and library of design elements for drawing the business matrix diagrams.
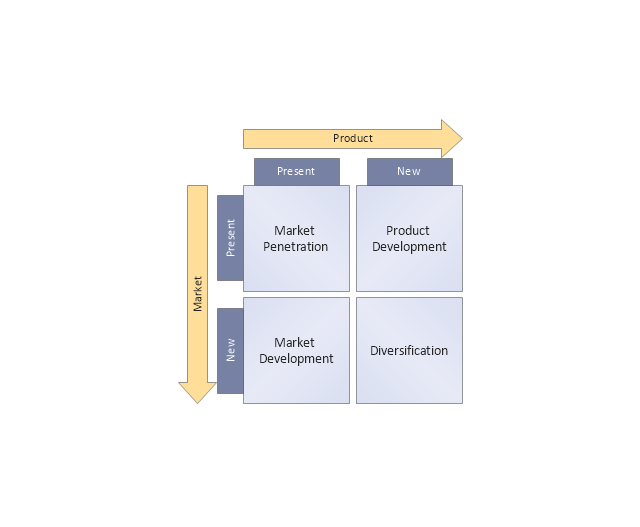
Ansoff Matrix
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software extended with Matrices Solution from the Marketing Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park offers you the possibility to develop the Ansoff Matrix of any complexity.Competitor Analysis
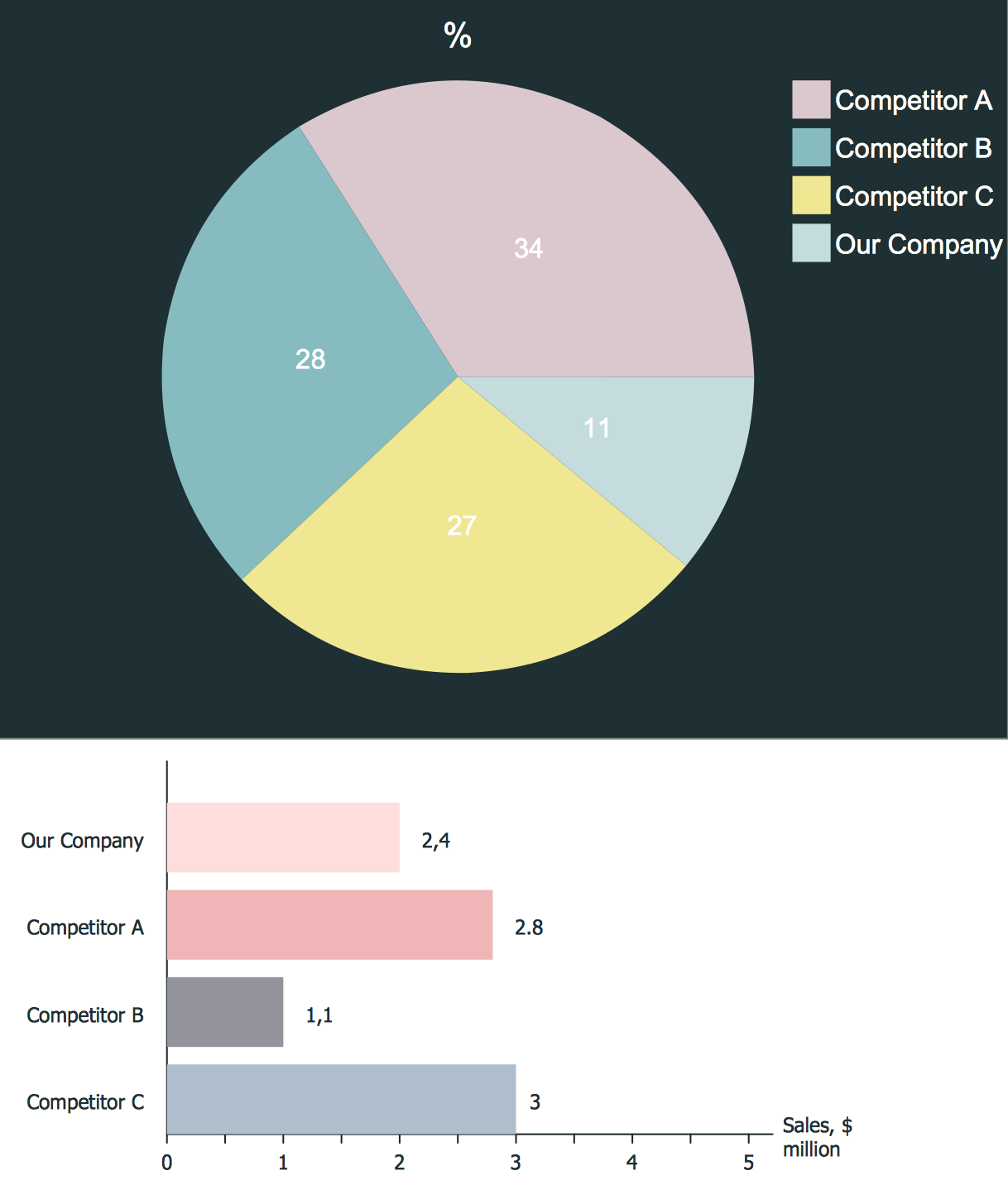
Competitor analysis is a first and obligatory step in elaboration the proper corporate marketing strategy and creating sustainable competitive advantage. Use powerful opportunities of numerous solutions from ConceptDraw Solution Park for designing illustrative diagrams, charts, matrices which are necessary for effective competitor analysis.Porter's Value Chain
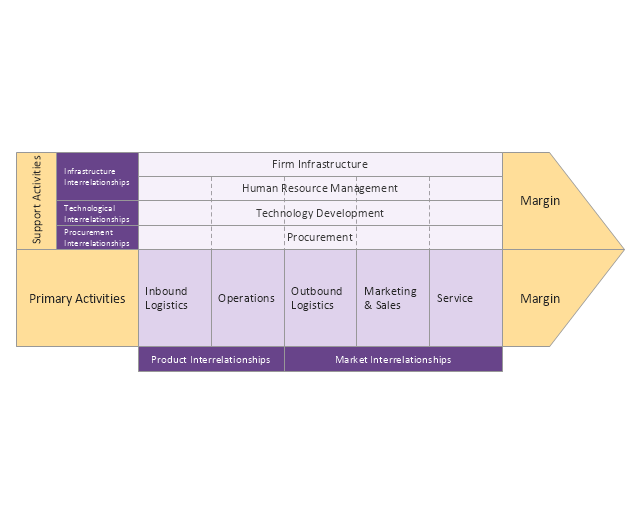
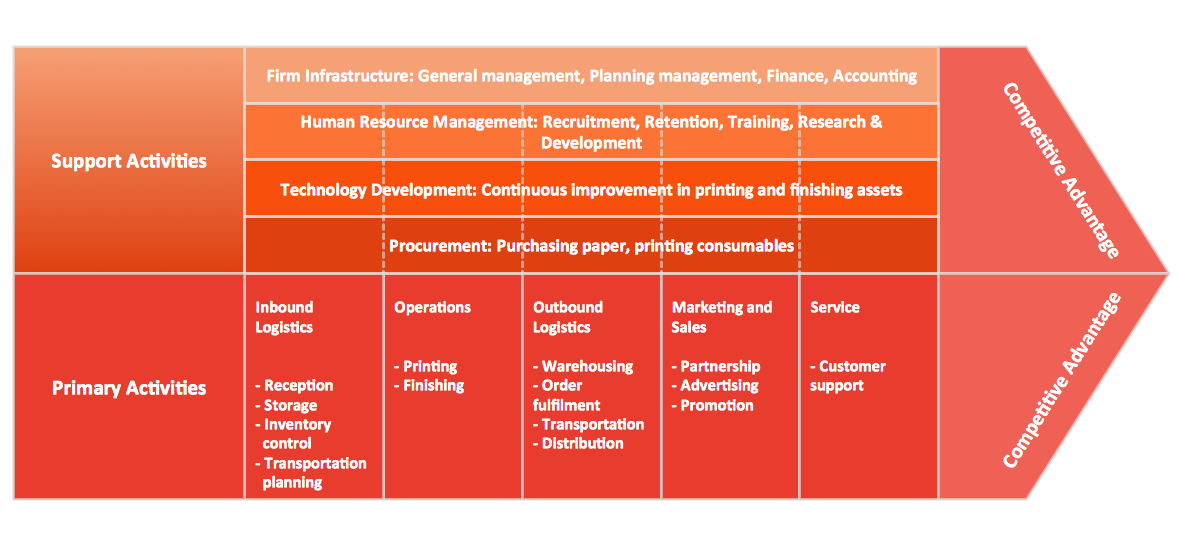
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software offers you the Matrices Solution from the Marketing Area with extensive drawing tools for creating the Porter's Value Chain diagrams.The vector stencils library "Matrices" contains 10 templates of marketing matrix diagrams and charts.
Use these templates to create your marketing matrices in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these templates to create your marketing matrices in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Matrices
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM extended with Matrices Solution from the Marketing Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is a powerful software for drawing various types of Marketing Matrices: Ansoff Matrix, BCG Matrix, Deployment Chart, Feature Comparison Chart, Competitive Strategies Matrix, Flow Process Chart, Porter's Value Chain Diagram, Positioning Map, and many others.The vector stencils library "Matrices" contains 10 templates of marketing matrix diagrams and charts.
Use these templates to create your marketing matrices in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these templates to create your marketing matrices in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Matrices" contains 10 templates of marketing matrix diagrams and charts.
Use these templates to create your marketing matrices in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these templates to create your marketing matrices in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Creating a default presentation in ConceptDraw MINDMAP
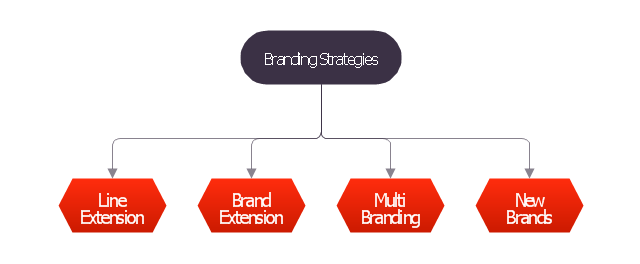
ConceptDraw MINDMAP a versatile, yet easy-to-use tool for organizing ideas and data. Creates mind maps that intuitively illustrate your thought process. Outputs a wide variety of document styles and formats. Delivers presentations from mind maps with built-in modes and MS PowerPoint export. Perfect for brainstorming, project planning, meeting management, note taking, and more."Branding strategies.
Company name.
Often, especially in the industrial sector, it is just the company's name which is promoted...
Individual branding.
Each brand has a separate name ..., which may compete against other brands from the same company...
Attitude branding and iconic brands.
Attitude branding is the choice to represent a larger feeling, which is not necessarily connected with the product or consumption of the product at all. ...
Iconic brands are defined as having aspects that contribute to consumer's self-expression and personal identity. ...
"No-brand" branding.
Recently a number of companies have successfully pursued "no-brand" strategies by creating packaging that imitates generic brand simplicity.
Derived brands.
In this case the supplier of a key component, used by a number of suppliers of the end-product, may wish to guarantee its own position by promoting that component as a brand in its own right.
Brand extension and brand dilution.
The existing strong brand name can be used as a vehicle for new or modified products ...
Social media brands.
social media brands may be the most evolved version of the brand form, because they focus not on themselves but on their users. ...
Multi-brands.
Alternatively, in a market that is fragmented amongst a number of brands a supplier can choose deliberately to launch totally new brands in apparent competition with its own existing strong brand ...
Private labels.
Private label brands, also called own brands, or store brands have become popular. Where the retailer has a particularly strong identity this "own brand" may be able to compete against even the strongest brand leaders ...
Individual and organizational brands.
There are kinds of branding that treat individuals and organizations as the products to be branded. Personal branding treats persons and their careers as brands. ... Faith branding treats religious figures and organizations as brands. ... Nation branding works with the perception and reputation of countries as brands. ...
Crowd sourcing branding.
These are brands that are created by "the public" for the business, which is opposite to the traditional method where the business create a brand. ...
Nation branding (place branding and public diplomacy).
Nation branding is a field of theory and practice which aims to measure, build and manage the reputation of countries ...
Destination Branding.
Destination Branding is the work of cities, states, and other localities to promote to themselves." [Brand. Wikipedia]
The block diagram example "Branding strategies" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Block Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Company name.
Often, especially in the industrial sector, it is just the company's name which is promoted...
Individual branding.
Each brand has a separate name ..., which may compete against other brands from the same company...
Attitude branding and iconic brands.
Attitude branding is the choice to represent a larger feeling, which is not necessarily connected with the product or consumption of the product at all. ...
Iconic brands are defined as having aspects that contribute to consumer's self-expression and personal identity. ...
"No-brand" branding.
Recently a number of companies have successfully pursued "no-brand" strategies by creating packaging that imitates generic brand simplicity.
Derived brands.
In this case the supplier of a key component, used by a number of suppliers of the end-product, may wish to guarantee its own position by promoting that component as a brand in its own right.
Brand extension and brand dilution.
The existing strong brand name can be used as a vehicle for new or modified products ...
Social media brands.
social media brands may be the most evolved version of the brand form, because they focus not on themselves but on their users. ...
Multi-brands.
Alternatively, in a market that is fragmented amongst a number of brands a supplier can choose deliberately to launch totally new brands in apparent competition with its own existing strong brand ...
Private labels.
Private label brands, also called own brands, or store brands have become popular. Where the retailer has a particularly strong identity this "own brand" may be able to compete against even the strongest brand leaders ...
Individual and organizational brands.
There are kinds of branding that treat individuals and organizations as the products to be branded. Personal branding treats persons and their careers as brands. ... Faith branding treats religious figures and organizations as brands. ... Nation branding works with the perception and reputation of countries as brands. ...
Crowd sourcing branding.
These are brands that are created by "the public" for the business, which is opposite to the traditional method where the business create a brand. ...
Nation branding (place branding and public diplomacy).
Nation branding is a field of theory and practice which aims to measure, build and manage the reputation of countries ...
Destination Branding.
Destination Branding is the work of cities, states, and other localities to promote to themselves." [Brand. Wikipedia]
The block diagram example "Branding strategies" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Block Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
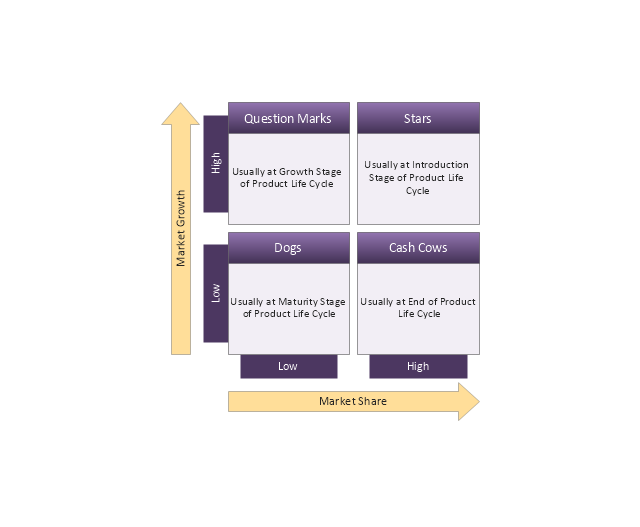
BCG Matrix
The growth–share matrix (BCG Matrix) was created by Bruce D. Henderson for the Boston Consulting Group in 1970 to help corporations to analyze their business units and to help the company allocate resources. How is it easy design the BCG Matrices in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software supplied with unique Matrices Solution from the Marketing Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.Prioritization Matrix
You can design the Prioritization Matrix by hand on the paper, but we offer you the most easier way - to use the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Seven Management and Planning Tools Solution from the Management Area.Marketing Analysis Diagram
An example of marketing analysis diagram, can be used to analyse product market and define marketing strategy. This types of charts used by small business project management for making presentations on market shares, it used by marketing project management software and project management tracking tools for reporting results and statuses.Deployment Chart Software
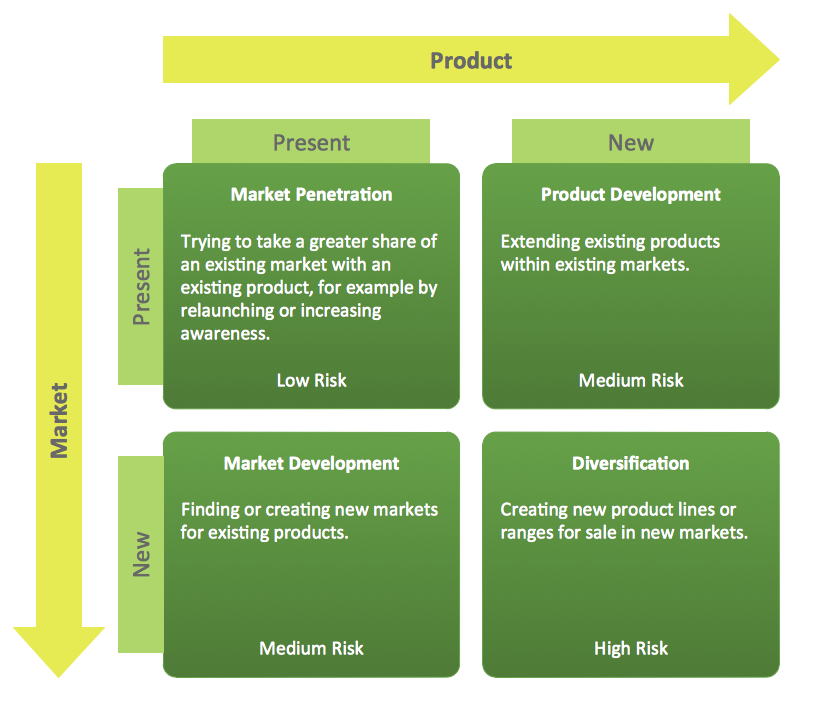
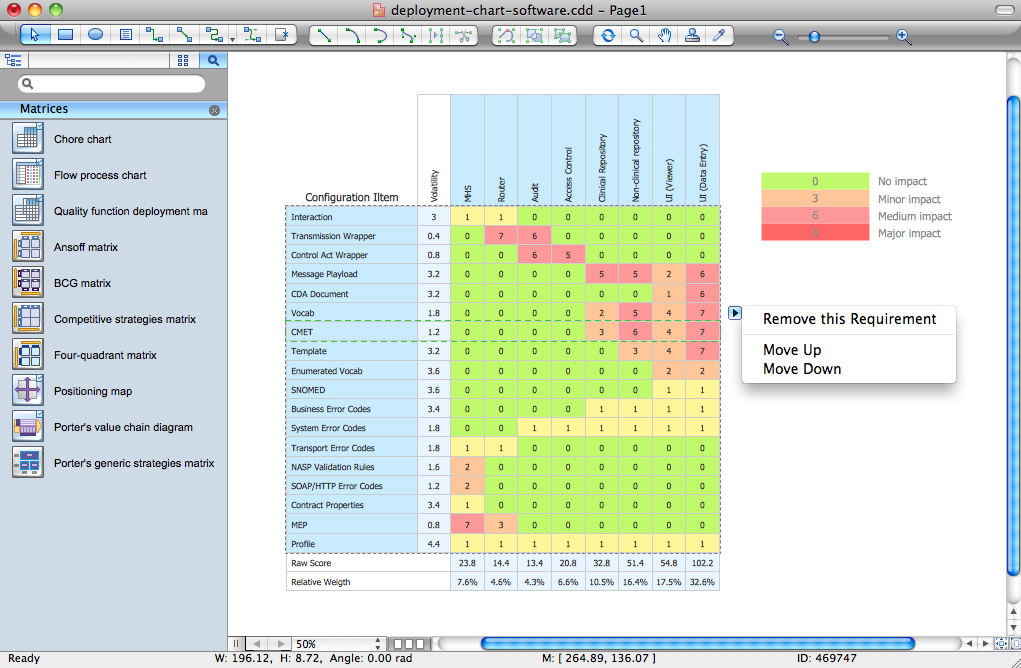
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM extended with Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is the best Deployment Chart Software. The Matrices solution offers you the useful tools for creating Deployment Charts in just minutes. The Deployment Charts designed with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM are vector graphic documents and are available for reviewing, modifying, converting to a variety of formats (image, HTML, PDF file, MS PowerPoint Presentation, Adobe Flash or MS Visio XML), printing and send via e-mail in one moment."Michael Porter has described a category scheme consisting of three general types of strategies that are commonly used by businesses to achieve and maintain competitive advantage. These three generic strategies are defined along two dimensions: strategic scope and strategic strength. Strategic scope is a demand-side dimension and looks at the size and composition of the market you intend to target. Strategic strength is a supply-side dimension and looks at the strength or core competency of the firm. In particular he identified two competencies that he felt were most important: product differentiation and product cost (efficiency).
In his 1980 classic Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors, Porter simplifies the scheme by reducing it down to the three best strategies. They are cost leadership, differentiation, and market segmentation (or focus). Market segmentation is narrow in scope while both cost leadership and differentiation are relatively broad in market scope." [Porter's generic strategies. Wikipedia]
This competitive strategy matrix diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
In his 1980 classic Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors, Porter simplifies the scheme by reducing it down to the three best strategies. They are cost leadership, differentiation, and market segmentation (or focus). Market segmentation is narrow in scope while both cost leadership and differentiation are relatively broad in market scope." [Porter's generic strategies. Wikipedia]
This competitive strategy matrix diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Matrices solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
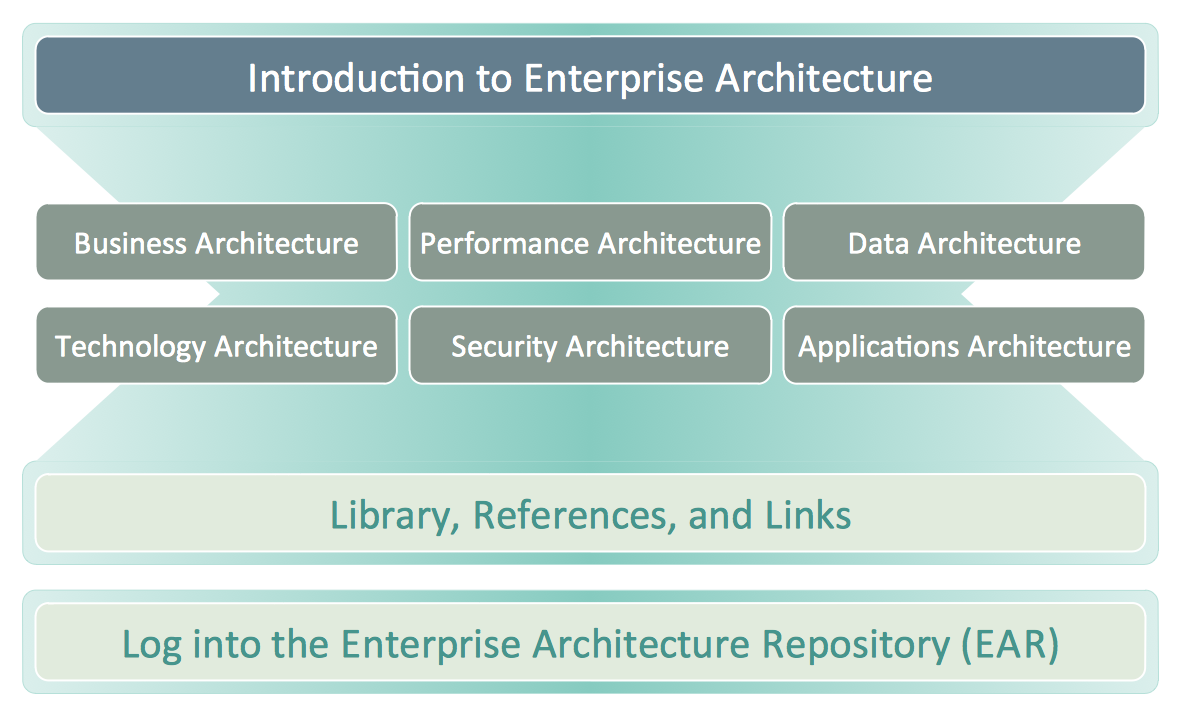
Business Architecture
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a powerful diagramming and vector drawing software. Supplied with Enterprise Architecture Diagrams Solution from the Management Area, ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is ideal for construction the Business Architecture Diagrams.- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram | Porter's Value Chain ...
- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram | Competitive strategy ...
- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram | Block diagram - Porter's ...
- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram | Competitor Analysis ...
- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram | Porter's value chain ...
- Block diagram - Porter's five forces model | Porter's Value Chain ...
- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram | Competitive strategy ...
- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram | Matrices - Vector stencils ...
- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram | Define Porters Matrix
- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram
- Matrices | Matrices - Vector stencils library | Porters Generic Strategy ...
- Competitive strategy matrix
- Porter's Value Chain | Block diagram - Porter's five forces model ...
- Business Process Elements: Activities | Porter's generic strategies ...
- Competitor Analysis | Porter's Value Chain | Business Productivity ...
- Porter's value chain matrix diagram
- Porter's Value Chain | Porter's value chain matrix diagram ...
- Strategic planning - Cycle diagram | Social strategy - Pyramid ...
- Authority Matrix Diagram Software | PROBLEM ANALYSIS ...
- Four-quadrant matrix template | Porters 2x2 Strategy Matrix Examples