IDEF4 Standard
|
The development of the object-oriented programming significantly facilitated the process of software development. Nevertheless the development of software with good design, reliability, modularity and usability is still problematic. IDEF4 standard was developed for correct usage of object-oriented technologies. Accordingly to IDEF4 standard, the object-oriented process is represented with the help of diagrams, which helps to analyze this process and to discover its key points. The particularity of IDEF4 standard is the representation possibility of the influence of classes’ heredity, objects composition, functional decomposition and polymorphism on the object projecting.
The process of object-oriented projecting by IDEF4 method is divided into separate blocks.Each subrun has notations, which indicate which decision should be accepted during the projecting process and how it will influence on other subruns. By IDEF4 standard the common diagram, describing the whole project, is not developed. This allows to avoid confusion and quickly find the necessary information on the project. IDEF4 standard lets the planner easily find compromises between classes’ heredity, objects composition, functional decomposition and polymorphism in the project.
IDEF4 model consists of 2 submodels: model of classes and model of methods. These submodels are connected between each other with the help of a distribution scheme and contain the whole information on the project. Because of classes’ subruns sizes and methods the planner never uses them as a whole, using a set of simpler diagrams and specifications which contain the part of information.
A submodel of classes consists of the following diagram types: -
Diagrams of heredity, which define the heredity of classes;
- Diagrams of types, which define the composition of classes;
- Diagrams of protocols, which define protocols of methods call;
- Diagrams of objects creation (Instantiation), which describes the process of creation of exemplars of the preset classes’ objects.
A submodel of classes consists of following diagrams: -
Diagrams of methods systematization (Method taxonomy), which classify methods by behavior similarity;
- Diagrams of clients, which represent clients and operations suppliers, so that to define the functional decomposition.
|

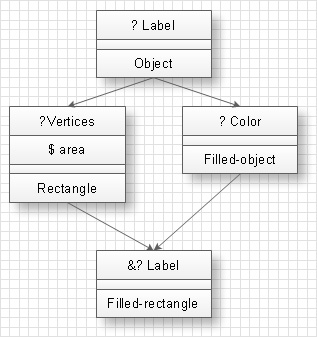
The diagram of heredity represents hereditary ties between classes. For example, at the picture below the structure of heredity and Filled Rectangle class behavior is shown.
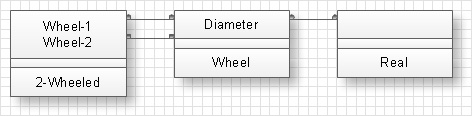
Diagrams of protocols define arguments of classes for protocols call. At the picture below the diagram of a protocol for Fill-closed-object is shown.
It is obvious from the diagram that Fill-closed-object gets requests from Polygon object (primary argument) and Color object (secondary argument) and returns the request to Polygon object.

Diagrams of objects creation come into diagrams of types and describe possible situations at composition of ties between created objects..
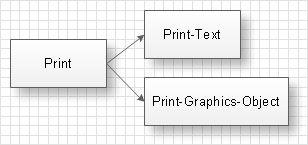
The diagram of methods systematization describes specific type of system behavior at the influence on the set of methods. Arrows on the diagram point at additional influences, done at the sets of methods. The sets of methods are grouped accordingly to additional obligatory conditions. At the example given below the set of methods ‘Print’ has an obligatory condition that the object must be printed and the set of methods ‘Print-Text’ – that the printed object must be a text.
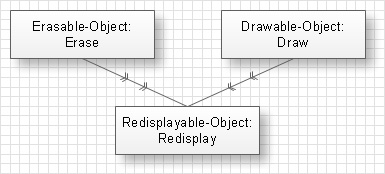
Diagrams of clients represent clients and operations suppliers. Double arrows on the diagram point from the called operation to the calling operation. At the example given below a diagram of clients is shown. On this diagram the Redisplay operation which belongs to Redisplayable-object class calls the Erase operation of the Erasable-object class and the Draw operation of the Drawable-object class.
IDEF4 standard implies not only graphical presentation but the additional information about diagrams of heredity, methods systematization and types which are contained in specifications. Accordingly to IDEF4 standard there are specifications of invariant classes and specifications of obligatory conditions.
Specifications of invariant classes are connected with diagrams of heredity and define influences which form properties of each concrete class of objects. For each class there exists a separate specification. For instance, the properties “Each square has four sides” and “All square sides are equal” are the properties of specification of the Square class.
Specifications of obligatory conditions are connected with sets of methods in diagrams of methods systematization and define obligatory conditions, which influence on methods and which methods should satisfy.
For each set of methods there is one specification of obligatory conditions. For example the set of methods ‘Pop’, which deletes values from the stack, as obligatory condition will have the absence of attempts to delete the value from the stack if the stack is empty.
IDEF 4 standard is developed by professional planners and programmers of the U.S. Air Force Armstrong Laboratory and is intended to facilitate the usage of object-oriented technologies at software development.
TEN RELATED HOW TO's:
Creating CCTV system diagrams is quick and easy with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming software enhanced with Audio, Video, Media solution from ConceptDraw Solution Park. It contains library of vector cliparts of video and TV devices and different digital gadgets for drawing this kind of diagrams.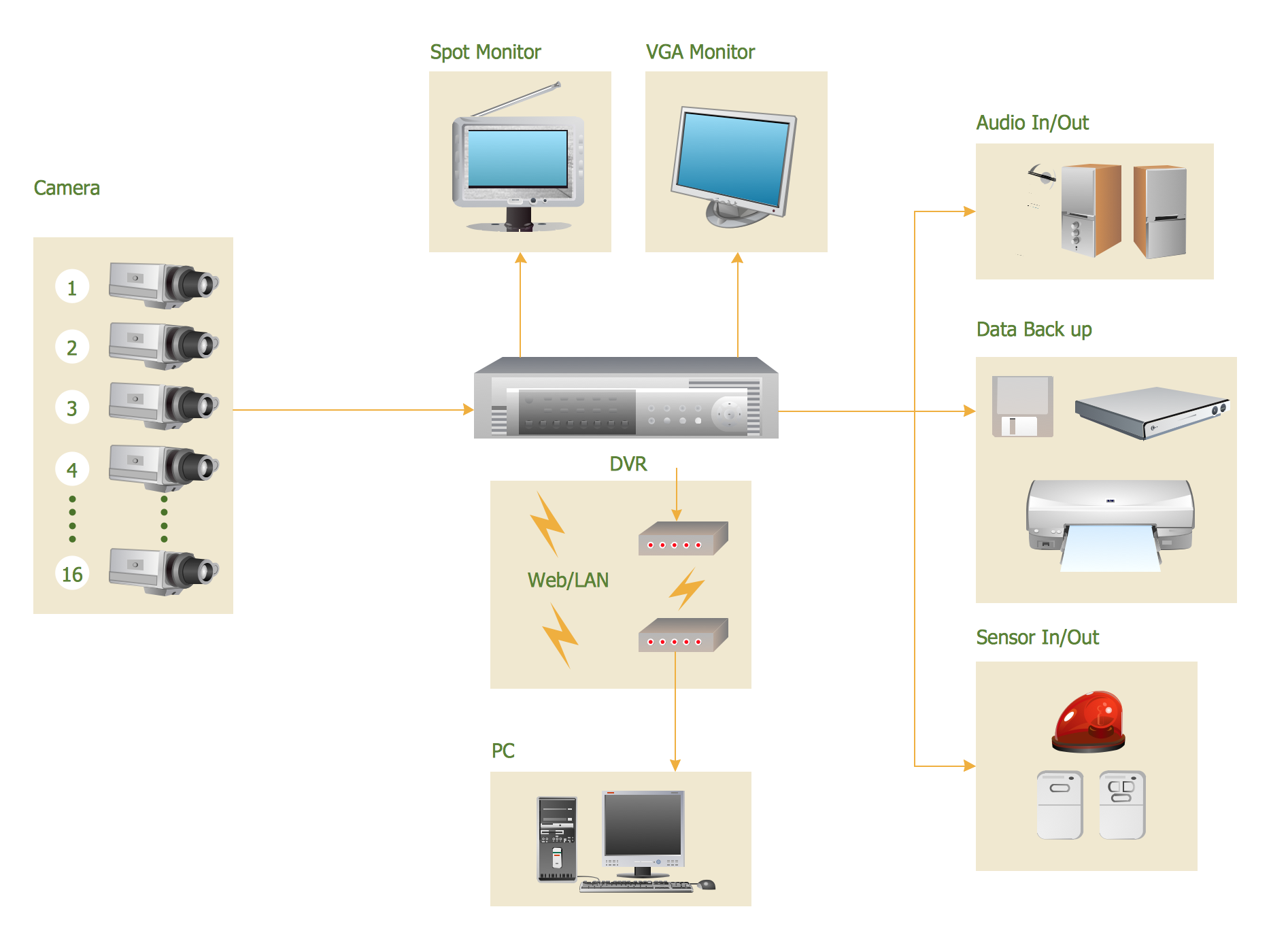
Picture: CCTV Surveillance System Diagram. CCTV Network Diagram Example
Related Solutions:
Working with personnel might be difficult if you are not prepared enough. To explain your workers all the details of communication with customers, you can draw an order process flowchart which will describe every step of the process and answer all the questions that might appear. You can view a lot of business process mapping diagram examples here, in ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This business process flow chart is created to illustrate the sample work order process. Before an organization can make some work for a person, the customer work order request must be completed. It is needed for tracking and accountability objectives. We used this business process flowchart to show a certain tasks and actions assumed by an organization. This flowchart depicts the outside inputs that are needed to launch a process, and ways the organization delivers its outputs. This business process flowchart was created with a help of ConceptDraw Business Process Mapping solution.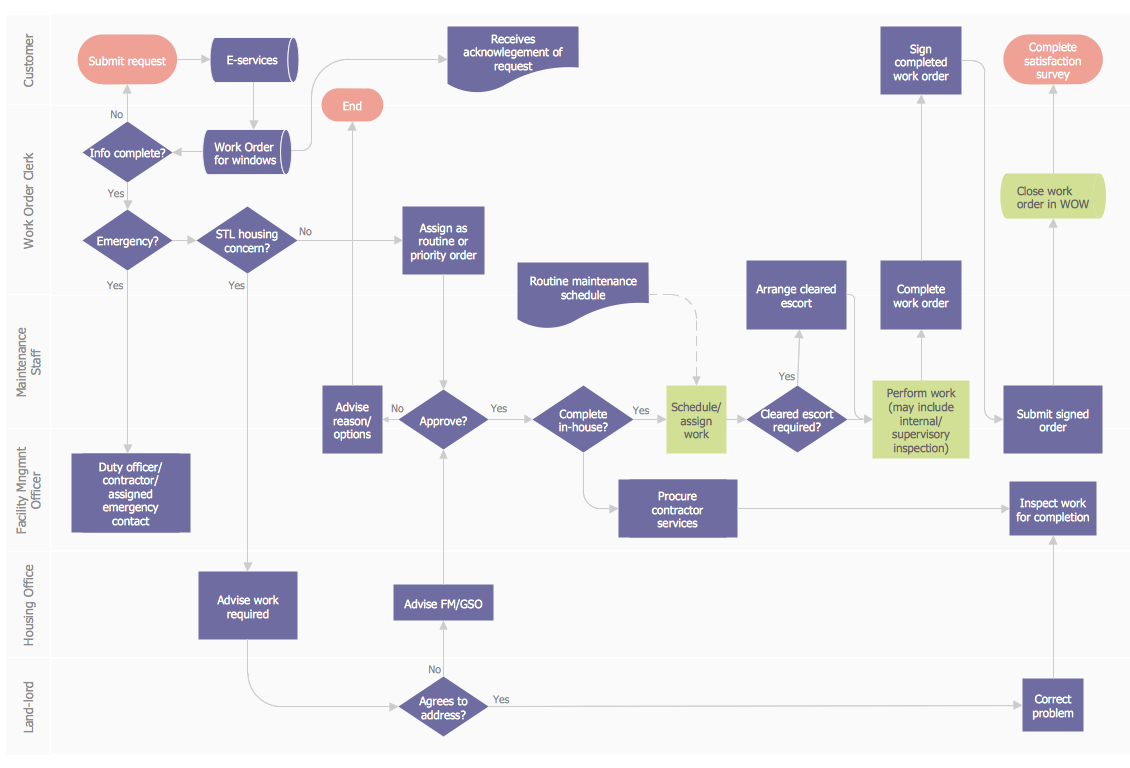
Picture: Work Order Process Flowchart. Business Process Mapping Examples
Related Solution:
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Physics solution from the Science and Education area is a powerful software for creating various physics diagrams.
Physics solution provides all tools that you can need for physics diagrams designing. It includes 3 libraries with predesigned vector physics symbols: Optics Library, Mechanics Library and Nuclear Physics Library.
Picture: Physics Symbols
Related Solution:
Set of vector cliparts, samples, templates and libraries helps you to create all sorts of new imagesthe for Money Illustrations.
Various styles of money design elements (currency symbols, clipart, money symbols) can be found in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM Business and Finance Solution.
Picture: Money - Design Elements
Related Solution:
The Rapid UML solution provides diagram examples, templates and vector stencils libraries for quick and easy drawing all types of UML 2.x and 1.x diagrams
Picture: UML Business Process
Related Solution:
There are numerous articles about the advantages of flowcharting, creating business graphics and developing different charts. Nevertheless, these articles are almost useless without the main component - the examples of flowcharts, org charts and without a fine example, it is difficult to get all the conveniences of creating diagrams. You can find tons of templates and vivid examples on Solution Park.
This illustration shows a variety of business diagrams that can be created using ConceptDraw DIAGRAM. It comprises a different fields of business activities: management, marketing, networking, software and database development along with design of infographics and business illustrations. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM provides a huge set of sample drawings including business process modeling diagrams,, network diagrams, UML diagrams, orgcharts, DFD, flowcharts, ERD, geographical maps and more.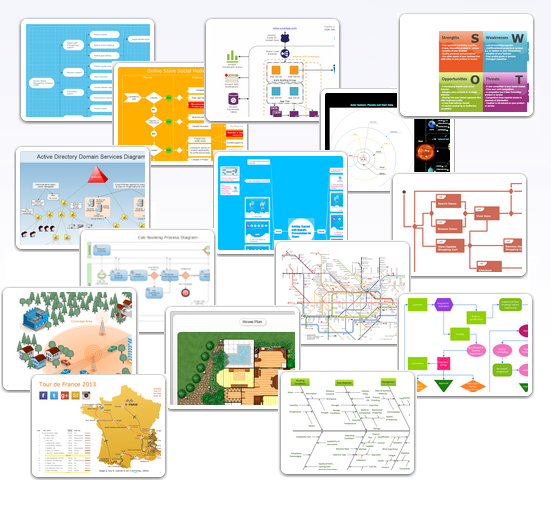
Picture: Examples of Flowcharts, Org Charts and More
Related Solution:
Network community structure is a network which nodes can be easily grouped into the sets of nodes with dense internally connections.
This example shows a network that displays the community structure with three groups of nodes with dense internal connections and sparser connections between the groups.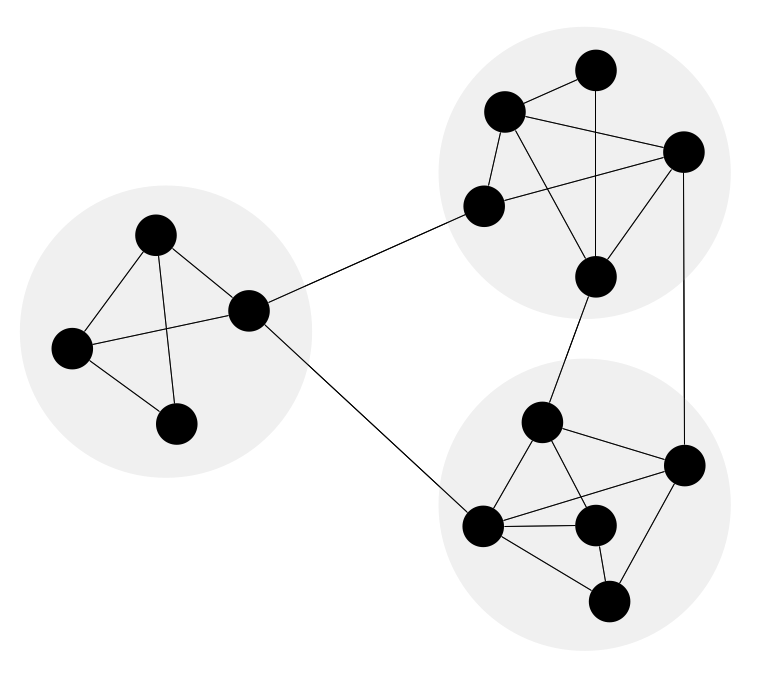
Picture: Network Community Structure. Computer and Network Examples
Related Solution:
Use ConceptDraw DIAGRAM enhanced with solutions from ConceptDraw Solution Park to create diagrams to present and explain structures, process flows, logical relationships and networks.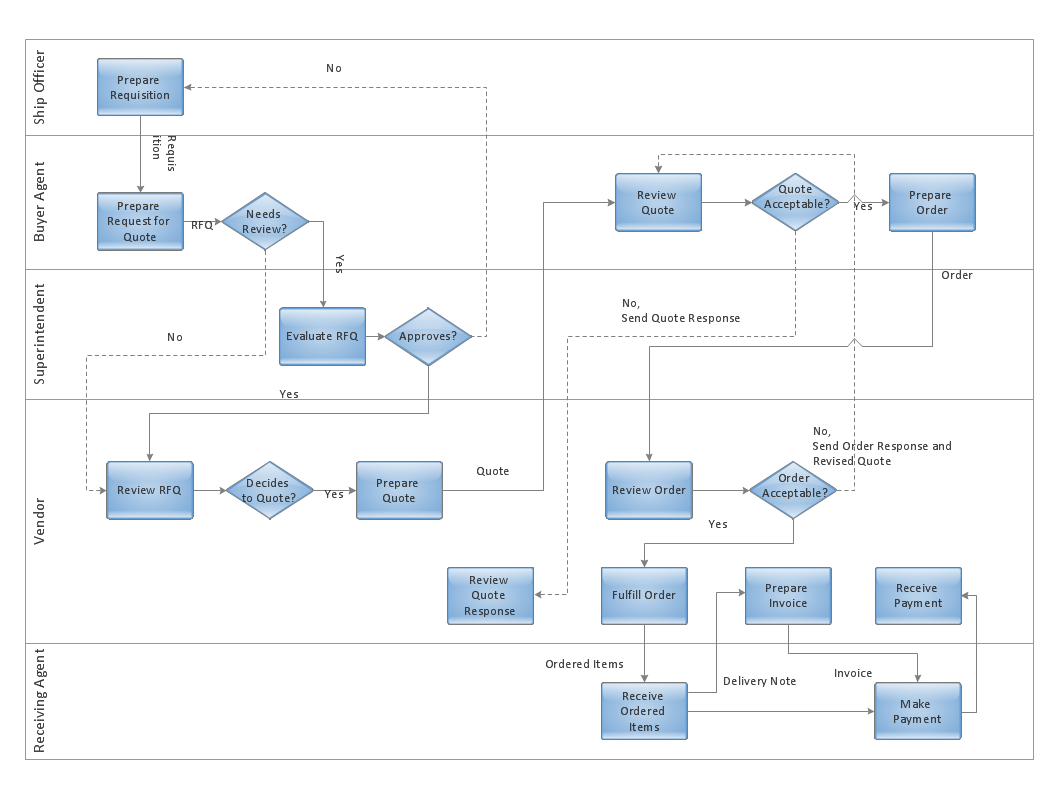
Picture: Cross-Functional Flowcharts in ConceptDraw
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software provides vector shapes and connector tools for quick and easy drawing diagrams for business, technology, science and education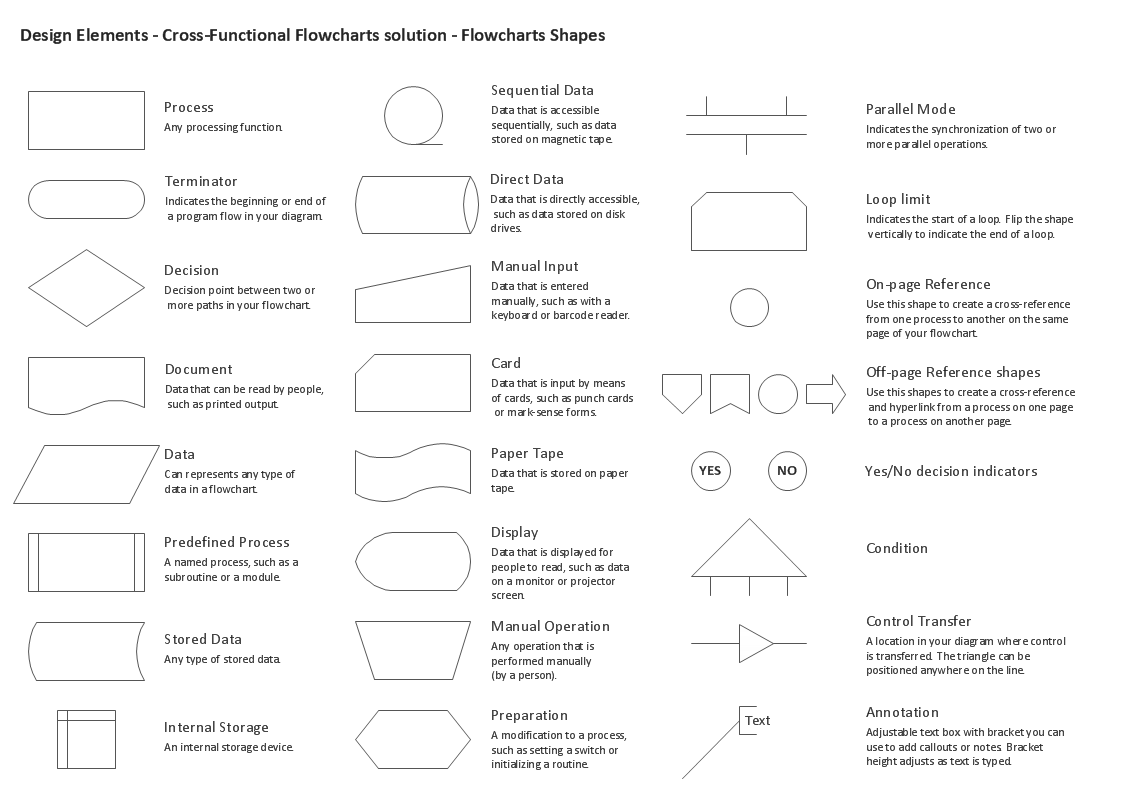
Picture: Cross Functional Flowchart Shapes Stencil
Program Structure Diagram is a visual representation of a program's organization, showing its components and their relationships.
Picture: Program Structure Diagram















