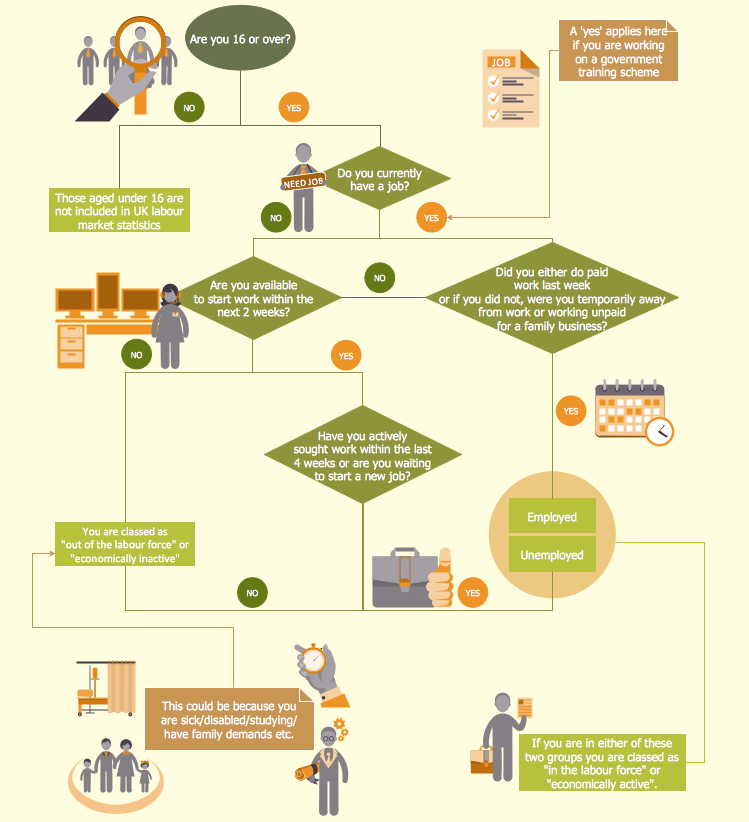
IDEF9 Standard
|
IDEF9 method, as well as other IDEF methods, was developed in the framework of the BBC USA program on information integration for coordinated development (The Air Force Information Integration for Concurrent Engineering (IICE)). IDEF9 method is one of the methods, which constitute the technology of the work with existing information and knowledge. In particular, IDEF9 method (Business Constraint Discovery) is developed for calculation and analysis of conditions and limitations in business-systems. The main motivation for development of such method was the perception of the fact, that conditions and limitations, influenced on the enterprise structure, usually are poorly defined and studied. An organization can normally function (which frequently happens) without knowledge about conditions and limitations, which acts in its system, in other words, without knowledge about requirements of this system.Nevertheless, if there is a task to improve the functioning of the production system, to increase its effectiveness and adapt the enterprise to new market conditions, the knowledge about the enterprise system requirements is critically significant. Each object of the production system has its own requirements, and their fulfillment affect the execution of the production task in general. Accordingly, if there is a necessity to change the system behavior (to increase the effectiveness or production) it is necessary to know which requirements of the system objects must be satisfied for this. As a result of using IDEF9 method, system requirements are specified and cataloged. Thus, it is always possible to check easily how much system requirements are satisfied and correspondingly to change work conditions for gaining the necessary result. By knowing the system requirements it is also possible to explain why at the moment the system works this way and how to improve its work. IDEF9 method is an indispensable tool of a business-engineer, as with its help is it possible to define how the system will work and which requirements will have to be satisfied for the system work accordingly to the project. Accordingly to IDEF9 method, requirement is a kind of a connection between system parts, which must obligatory exist at the given conditions set (context). The condition is considered as fulfilled if all conditions of its existence in the given context are fulfilled. Requirement is a connection type, which can be established between system objects, between processes, between objects and processes, between processes and objects properties, etc. Requirements are described by statements. An example of the requirement statement to objects: “Only heads of departments are authorized to sign waybills.” An example of the requirement statement of the process to objects: “Transportations are only allowed in the presence of a signed waybill” or “Credit giving out is only possible at monthly paying off the percents on the credit.” An example of the requirement statement of the process to object properties: “Maximum carrying capacity of the elevator is 500 kg.”
In that way, the system is represented in the view of a set of objects and processes, which have definite requirements for system functioning. Also into the system description the purpose of the work of this system is usually included. This is necessary for definition of only those requirements of objects and processes, which are important for execution of the considered task.At the system projecting the requirements define which rules, conditions, limitations and necessary connections the project must involve. The production system represents the set of objects, executing one or several functions under the influence of requirements for reaching the preset goal. Requirements are divided into:
Also the requirements are divided into enabling and limiting in the context of the considered conditions. Surely, limiting requirements are more obvious and become apparent in the form of following problem symptoms: excess costs, low quality, terms increase, etc. Such symptoms are called evidence of existing of the requirements in a system. The set of opinions, proving the necessity of definition and providing the requirement for system objects is called rationale for the requirement. The consequences of the influence of the requirement on the system are called effects of the requirements. Effects can be direct and indirect, intended and unintended, desirable and undesirable in the framework of the considered context. It is necessary the sufficient number of evidence of requirements existence, otherwise the requirement will remain undefined. The effective definition of requirements and their management lets quickly identify requirements and react upon the typical industrial problems of requirements, listed below:
Also systems overloaded with outdated or inappropriate requirements lose productivity and waste resources on execution of these requirements. Potential users of IDEF9 method are business owners, organization managers, system projecting and planning specialists and analysts. The knowledge of system requirements may help in Business Process Reengineering (BPR), Total Quality Management (TQM) and in strategic planning.. There is an example of the procedure of definition, confirmation and further improving of the requirement. The given procedure consists of following stages:
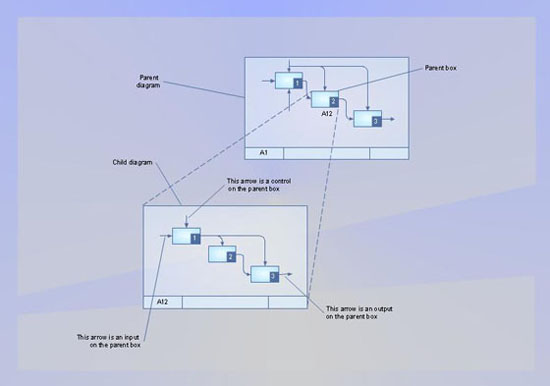
Accordingly to IDEF9 method requirements are displayed in the form of visual schemes. Requirements on the schemes are displayed by way of rounded rectangles, objects and processes in the form of rectangles. Connections between objects of the scheme are represented by way of lines. The connection, indicating at obliging circumstances, is represented in the form of a line with the black little circle at the end. There are also used junctions, which are shown on the scheme in the form of squares with the definition of the junction type: &, O, X.
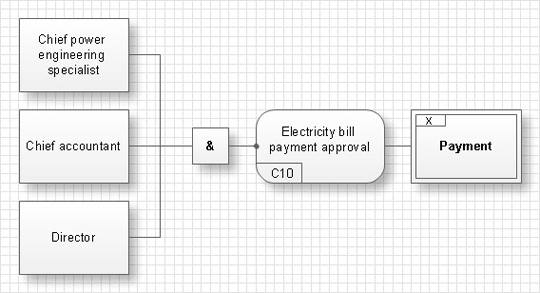
For example there is a following requirement: “An account for payment of consumed electricity must be signed by the head specialist of the power engineering, by the chief accountant and the head of the enterprise.” The corresponding scheme will have the following view:
Here the double-sided rectangle presents the context of a task, the rounded rectangle shows the requirement itself, and rectangles represent objects, which influence on the requirement execution. & junction shows that the requirement needs an influence of all objects, i.e. the account should be signed by each of the three faces. Analogously it is possible to compose a scheme of the selection of requirements-candidates, a scheme, reflecting requirement effects and a scheme showing which requirements should be executed for reaching the general goal. An effective management of changes is significantly facilitated by way of definition and documenting of business-requirements. The knowledge about the business-requirements which exist and how they interrelate between each other in the best way is insufficient sometimes. Nevertheless the requirements trigger, manage and bound the behavior of objects of the business-system and affect them so that the final goal is reached with more or less costs of resources and time. IDEF9 method is developed to help with definition and analysis of the requirements. |