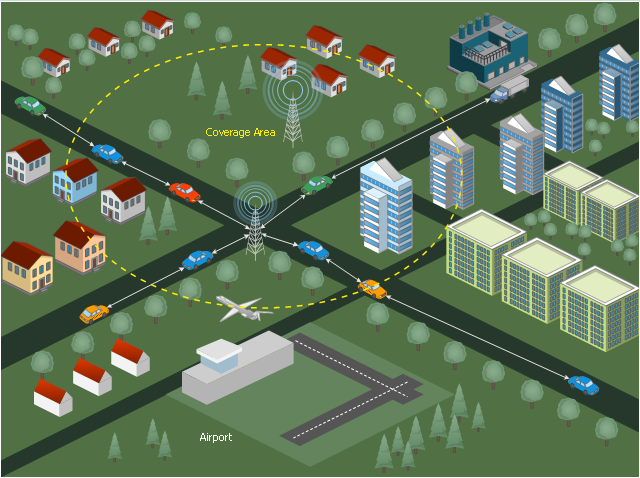
This diagram sample illustrates the cooperative vehicular delay-tolerant network operation.
"Delay-tolerant networking (DTN) is an approach to computer network architecture that seeks to address the technical issues in heterogeneous networks that may lack continuous network connectivity. Examples of such networks are those operating in mobile or extreme terrestrial environments, or planned networks in space.
Recently, the term disruption-tolerant networking has gained currency in the United States due to support from DARPA, which has funded many DTN projects. Disruption may occur because of the limits of wireless radio range, sparsity of mobile nodes, energy resources, attack, and noise." [Delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
"Routing in delay-tolerant networking concerns itself with the ability to transport, or route, data from a source to a destination, which is a fundamental ability all communication networks must have. Delay- and disruption-tolerant networks (DTNs) are characterized by their lack of connectivity, resulting in a lack of instantaneous end-to-end paths. In these challenging environments, popular ad hoc routing protocols such as AODV and DSR fail to establish routes. This is due to these protocols trying to first establish a complete route and then, after the route has been established, forward the actual data. However, when instantaneous end-to-end paths are difficult or impossible to establish, routing protocols must take to a "store and forward" approach, where data is incrementally moved and stored throughout the network in hopes that it will eventually reach its destination. A common technique used to maximize the probability of a message being successfully transferred is to replicate many copies of the message in hopes that one will succeed in reaching its destination." [Routing in delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
The example "Cooperative vehicular delay-tolerant network diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Delay-tolerant networking (DTN) is an approach to computer network architecture that seeks to address the technical issues in heterogeneous networks that may lack continuous network connectivity. Examples of such networks are those operating in mobile or extreme terrestrial environments, or planned networks in space.
Recently, the term disruption-tolerant networking has gained currency in the United States due to support from DARPA, which has funded many DTN projects. Disruption may occur because of the limits of wireless radio range, sparsity of mobile nodes, energy resources, attack, and noise." [Delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
"Routing in delay-tolerant networking concerns itself with the ability to transport, or route, data from a source to a destination, which is a fundamental ability all communication networks must have. Delay- and disruption-tolerant networks (DTNs) are characterized by their lack of connectivity, resulting in a lack of instantaneous end-to-end paths. In these challenging environments, popular ad hoc routing protocols such as AODV and DSR fail to establish routes. This is due to these protocols trying to first establish a complete route and then, after the route has been established, forward the actual data. However, when instantaneous end-to-end paths are difficult or impossible to establish, routing protocols must take to a "store and forward" approach, where data is incrementally moved and stored throughout the network in hopes that it will eventually reach its destination. A common technique used to maximize the probability of a message being successfully transferred is to replicate many copies of the message in hopes that one will succeed in reaching its destination." [Routing in delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
The example "Cooperative vehicular delay-tolerant network diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Computer and Networks Area
Computer and Networks Area
The solutions from Computer and Networks Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park collect samples, templates and vector stencils libraries for drawing computer and network diagrams, schemes and technical drawings.
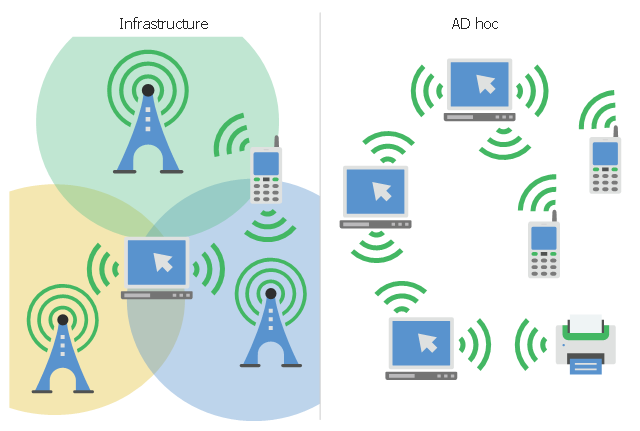
This infographic sample visualizes the Conventional and wireless ad hoc network. It was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Běžná bezdrátová síť a ad hoc síť.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:B%C4%9B%C5%BEn%C3%A1_ bezdr%C3%A1tov%C3%A1_ s%C3%AD%C5%A5_ a_ ad_ hoc_ s%C3%AD%C5%A5.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 4.0/ deed.en]
"A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre existing infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points in managed (infrastructure) wireless networks. Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes, so the determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity. In addition to the classic routing, ad hoc networks can use flooding for forwarding data.
Wireless mobile ad hoc networks are self-configuring, dynamic networks in which nodes are free to move. Wireless networks lack the complexities of infrastructure setup and administration, enabling devices to create and join networks "on the fly" – anywhere, anytime." [Wireless ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The infographic example "Conventional and wireless ad hoc network" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computers and Communications solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:B%C4%9B%C5%BEn%C3%A1_ bezdr%C3%A1tov%C3%A1_ s%C3%AD%C5%A5_ a_ ad_ hoc_ s%C3%AD%C5%A5.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 4.0/ deed.en]
"A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre existing infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points in managed (infrastructure) wireless networks. Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes, so the determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity. In addition to the classic routing, ad hoc networks can use flooding for forwarding data.
Wireless mobile ad hoc networks are self-configuring, dynamic networks in which nodes are free to move. Wireless networks lack the complexities of infrastructure setup and administration, enabling devices to create and join networks "on the fly" – anywhere, anytime." [Wireless ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The infographic example "Conventional and wireless ad hoc network" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computers and Communications solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Network Security Diagrams
Network Security Diagrams
The Network Security Diagrams solution presents a large collection of predesigned cybersecurity vector stencils, cliparts, shapes, icons and connectors to help you succeed in designing professional and accurate Network Security Diagrams, Network Security Infographics to share knowledge about effective ways of networks protection with help of software and network security devices of different cyber security degrees, Network Plans for secure wireless network, Computer Security Diagrams to visually tell about amazing possibilities of IT security solutions. The samples and examples reflect the power of ConceptDraw PRO software in drawing Network Security Diagrams, give the representation about variety of existing types of attacks and threats, help to realize their seriousness and the methods to deal with them.
 Interactive Voice Response Diagrams
Interactive Voice Response Diagrams
Interactive Voice Response Diagrams solution extends ConceptDraw PRO v10 software with samples, templates and libraries of ready-to-use vector stencils that help create Interactive Voice Response (IVR) diagrams illustrating in details a work of interactive voice response system, the IVR system’s logical and physical structure, Voice-over-Internet Protocol (VoIP) diagrams, and Action VoIP diagrams with representing voice actions on them, to visualize how the computers interact with callers through voice recognition and dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) keypad inputs.
- Network Diagram Software LAN Network Diagrams & Diagrams for
- Network Diagram Software LAN Network Diagrams & Diagrams for
- Simple Locial Network Diagram
- A Simple Lan Network Diagram
- Basic Network Diagram | Network Protocols | Network Configuration ...
- Network Diagram Software LAN Network Diagrams & Diagrams for ...
- Network Diagram Software LAN Network Diagrams & Diagrams for
- Active Directory Diagram | Network Protocols | IDEF4 Standard ...
- Basic Network Diagram | Network Diagram Software LAN Network ...
- Satellite telecom network diagram | Local area network (LAN ...
- Network Protocols | Logical network topology diagram | Network ...
- Physical Layout Of A Computer Network
- Network Layout Floor Plans | Design elements - Network layout ...
- Network Diagram Software LAN Network Diagrams & Diagrams for
- Physical Layout Of Network
- Simple Diagram Of Lan Network
- Physical LAN topology diagram | Network Diagram Software LAN ...
- Physical And Logical Network Layout
- Network Layout | ConceptDraw PRO Network Diagram Tool ...
- Network Diagram Software LAN Network Diagrams & Diagrams for ...