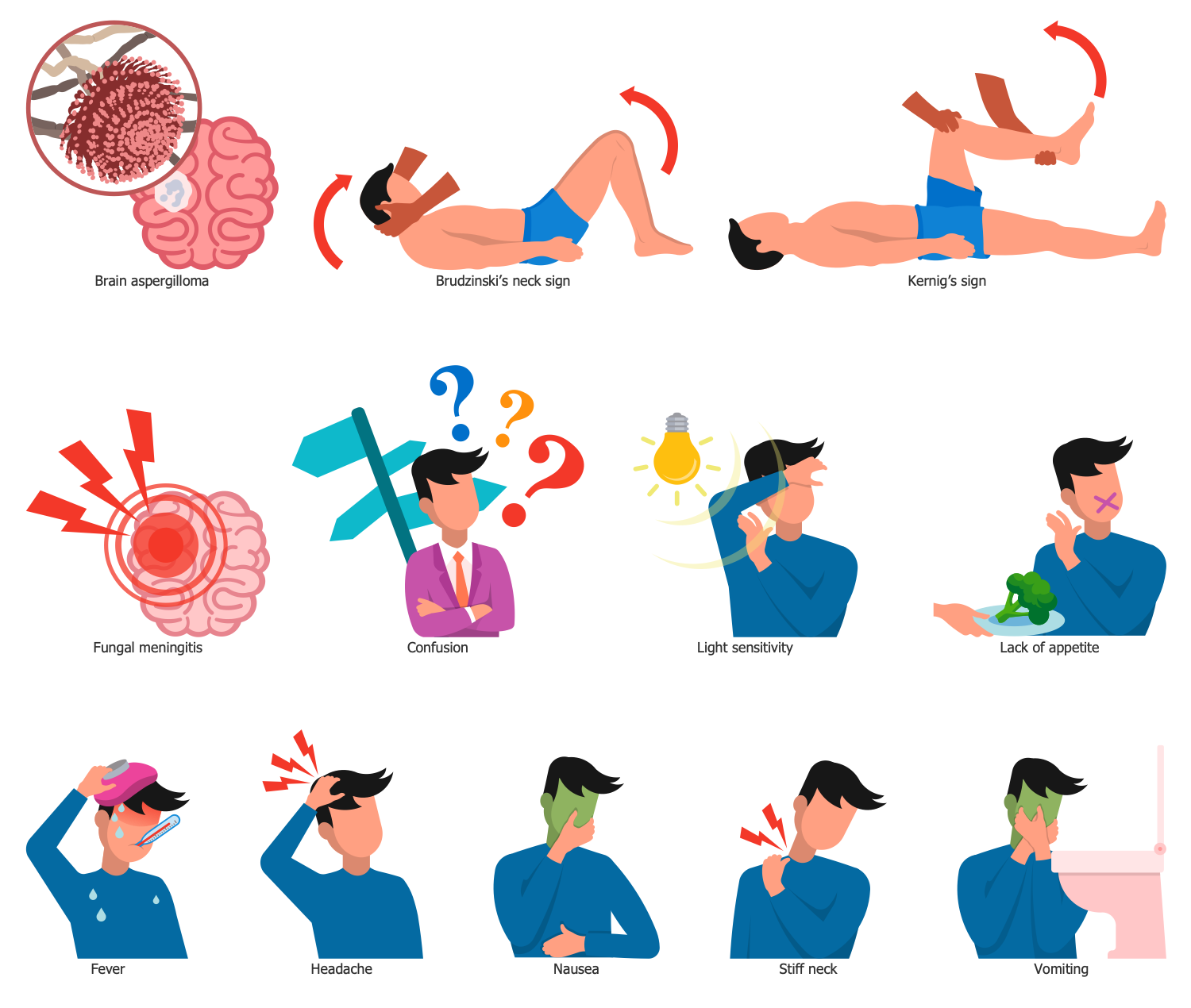
Fungal Meningitis
Fungal meningitis is meningitis caused by fungal infections like Histoplasma, Blastomyces, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus. Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membrane surrounding the central nervous system known as the meninges. It is a serious condition in which the meninges become swollen for the reason of entering germs and infecting the fluid around the central nervous system including the brain and spinal cord.
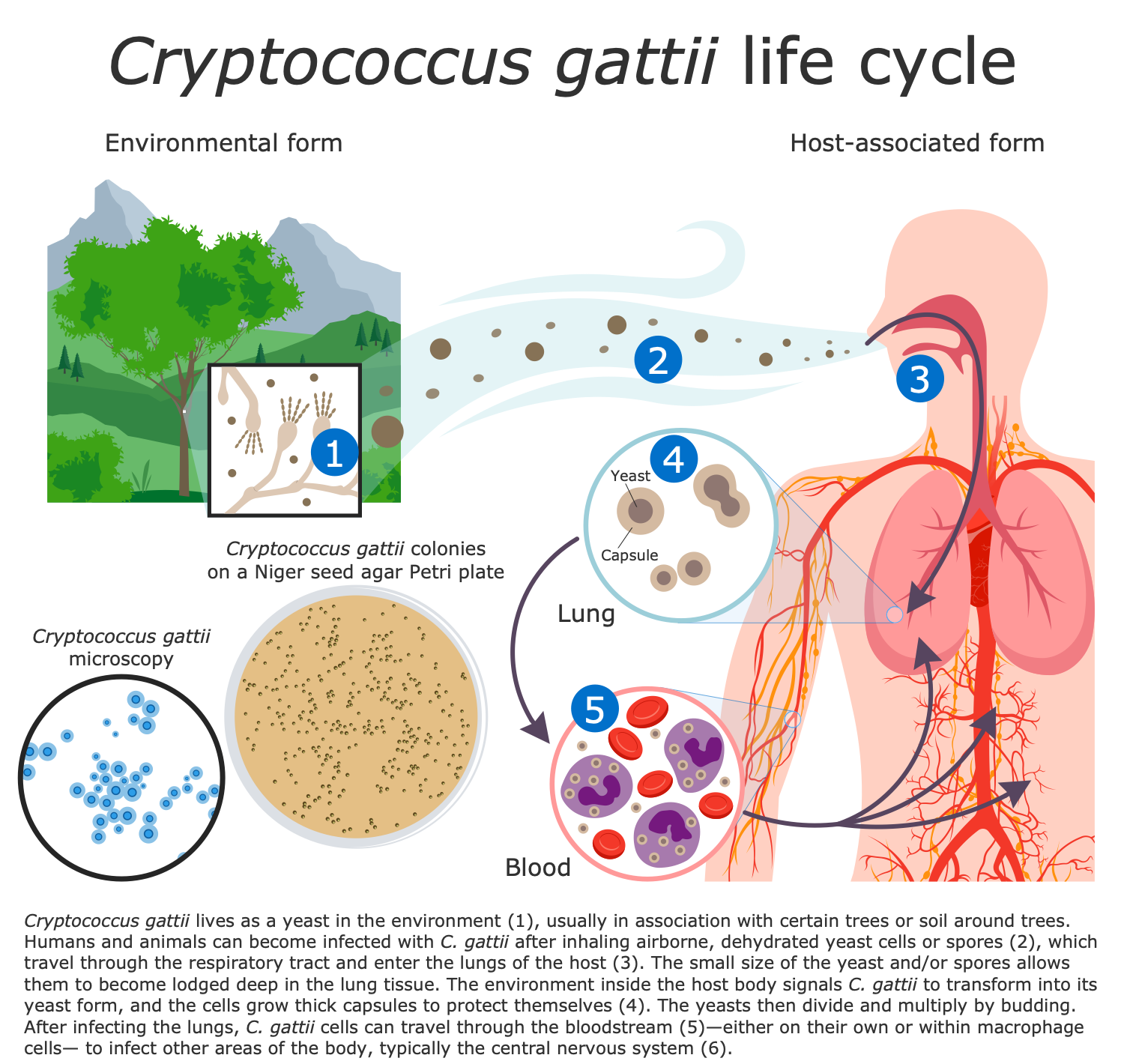
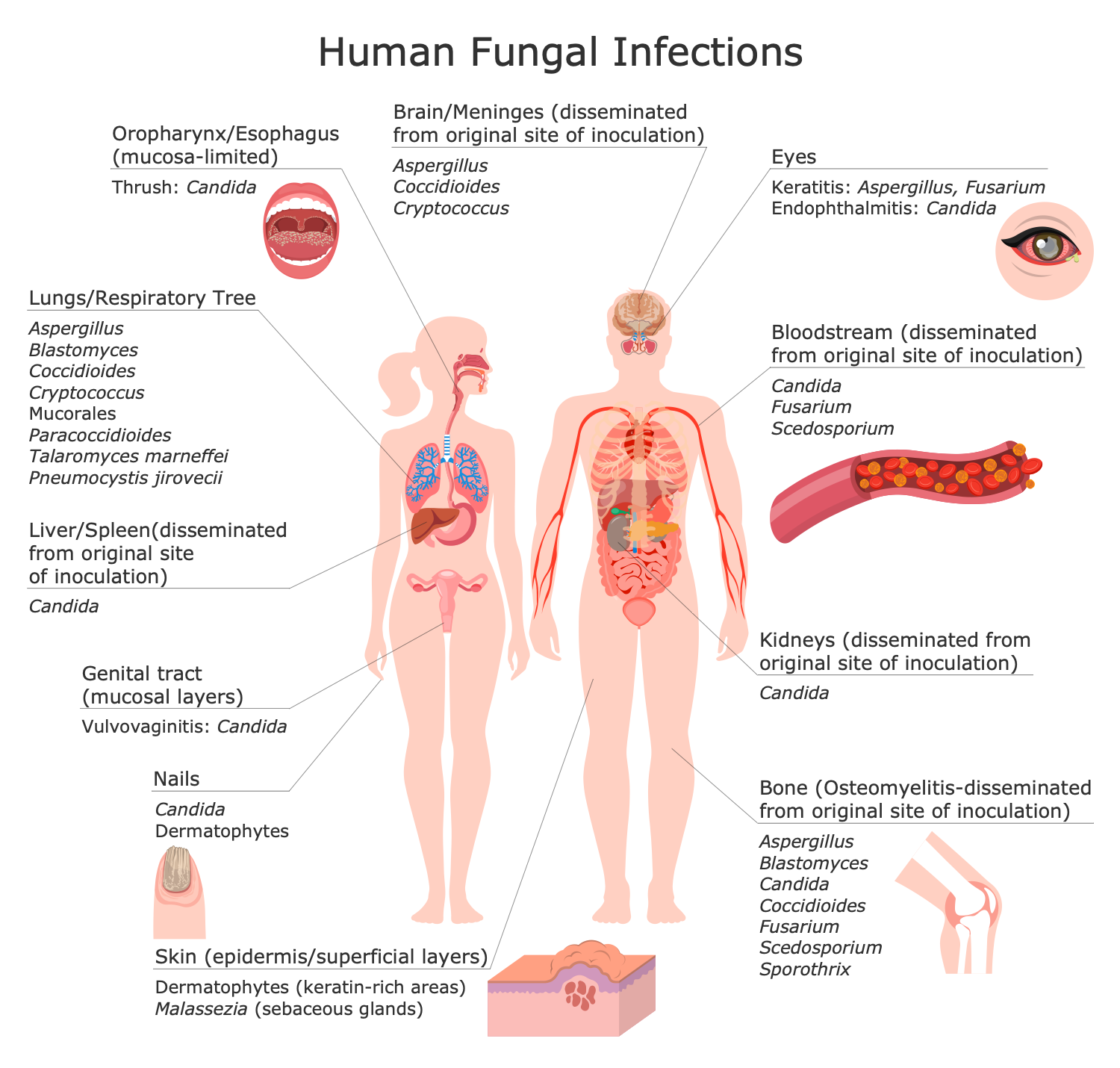
Fungal infections Candida, Aspergillus, Cryptococcus live in the environment throughout the world. Blastomyces and Coccidioides live in wet soil, decaying wood, and leaves. Histoplasma also lives mainly in soil, bird and bat droppings. The fungi that cause meningitis can infect anyone. However, individuals with a weak immune system like the elderly, HIV patients, cancer patients, after operations, taking immunosuppressive medication or steroids, and premature babies are most at risk. Living in certain areas may increase the risk of infection with fungi and respectively fungal meningitis.
Fungal spores enter to lungs with breathed air and from there are spread through the blood to various organs, including the central nervous system, spinal cord, brain, and meninges. When the fungal infection gets into the central nervous system, fungal meningitis can occur.
Symptoms of fungal meningitis are similar to those of other types of meningitis. They include fever, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, severe headache, photophobia, drowsiness, altered mental state, confusion, hallucinations, and more. Usually, the symptoms appear gradually, not suddenly as in other types of meningitis.
Currently, the incidence of fungal meningitis rises worldwide due to the increasing number of immunosuppressed patients. However, it is not contagious, people can get it only from a fungal infection, not from a sick person.
Fungal meningitis is diagnosed by examining blood and cerebrospinal fluid for fungi. Depending on the type of pathogen, its concentration, and degree of infection, appropriate treatment is prescribed and the prognosis is made. In common, high doses of antifungal medications are prescribed, often IV medications, and then therapy continues with oral antifungals. The treatment is realized by long courses, sometimes repeated. The success of treatment depends on many factors, including the kind of pathogen, the strength of the patient's immune system, and his ability to stave off the infection. Overall mortality for fungal meningitis differs from about 10-20% for candidal infection to mostly unfavorable prognosis for Coccidioidal and Aspergillus infections.
As a rule, echinocandins, fluconazole, flucytosine, amphotericin B, and itraconazole are used to treat fungal meningitis infection. In severe cases, long-term maintenance therapy or lifelong treatment antifungal medication may be prescribed. Most people recover without any consequences or long-term effects. Only sometimes, meningitis can cause temporary or permanent effects including headache, difficulties with coordination or loss of balance, weakness, spasms, memory loss, difficulty concentrating, vision problems, hearing issues, seizures, and speech problems. Therefore, it is extremely important to diagnose the problem timely and start treatment as soon as possible.
Example 1. Fungal Diseases - Fungal Meningitis
The Medical Mycology solution for ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software includes 17 libraries with a huge collection of pre-made vector design elements for the effective design of medical mycology infographics, illustrations, and diagrams:
- Fungal Diseases
- Fungal Meningitis
- Fungi Microscopy
- Fungi Hosts
- Fungi Biology
- Fungi Culture
- Antifungal
- Mycoses Diagnosis
- Mycoses Epidemiology
- Mycoses Prevention
- Mycoses Symptoms
- Mycoses Transmission
- Mold
- Eye Mycoses
- Skin and Nail Mycoses
- Personal Hygiene
- Cleaning and Disinfecting
Example 2. Fungal Meningitis Library Design Elements
Use the colorful vector clipart from the Medical Mycology solution libraries to compile an overview of fungi pathogens and diseases they cause, symptoms of human fungal diseases and effects including the most severe like fungal meningitis when the fungal infection gets into the central nervous system, spinal cord, brain, and meninges. Outline the ways to prevent fungal infections and alarming symptoms to consult a doctor as soon as possible if they are detected and avoid dangerous complications.
Example 3. Cryptococcus Gattii Life Cycle
The mycology infographics you see on this page were created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software using the Medical Mycology Solution. They successfully demonstrate the solution's capabilities and the professional results you can achieve. An experienced user spent 10-15 minutes creating each of these samples.
Use the powerful tools of the Medical Mycology Solution for ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software to create your own infographics and diagrams of any complexity fast and easy, and then successfully use them in your work activity.
All source documents are vector graphic documents. They are available for reviewing, modifying, or converting to a variety of formats (PDF file, MS PowerPoint, MS Visio, and many more graphic formats) from the ConceptDraw STORE. The Medical Mycology Solution is available for all ConceptDraw DIAGRAM users.