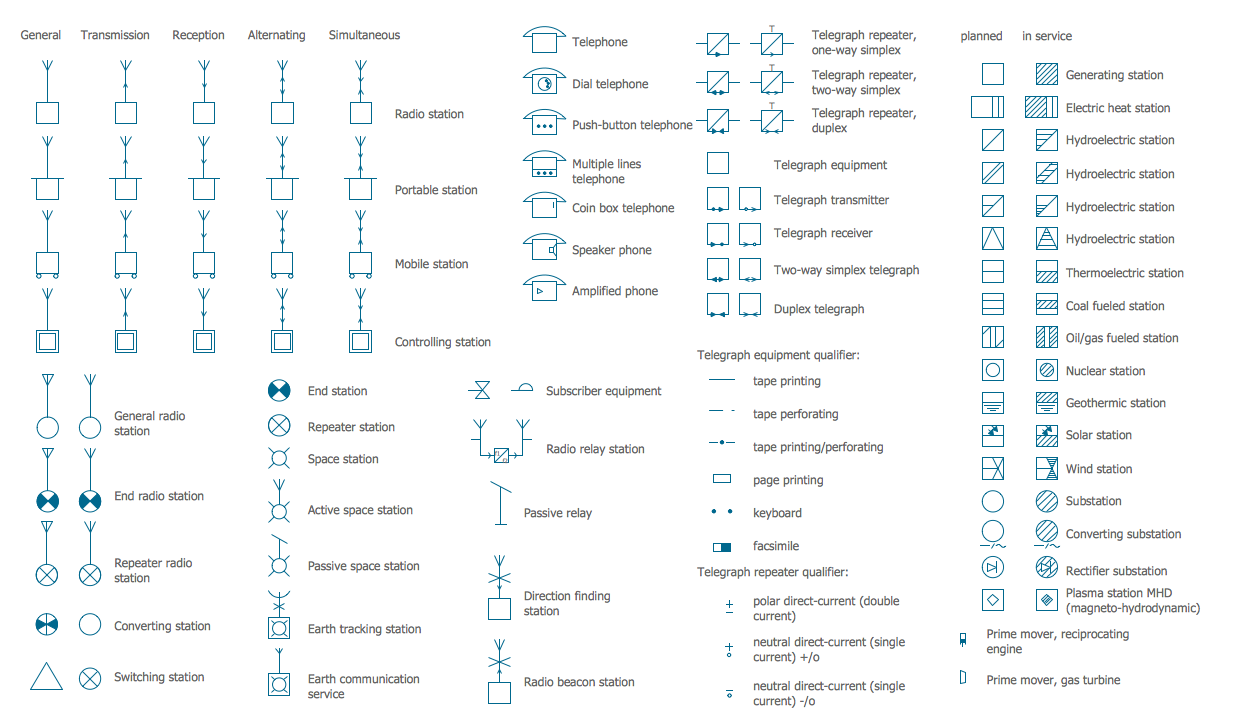
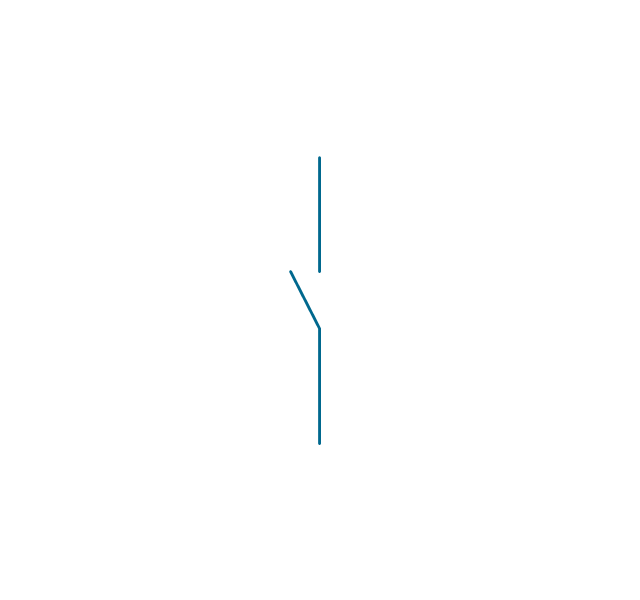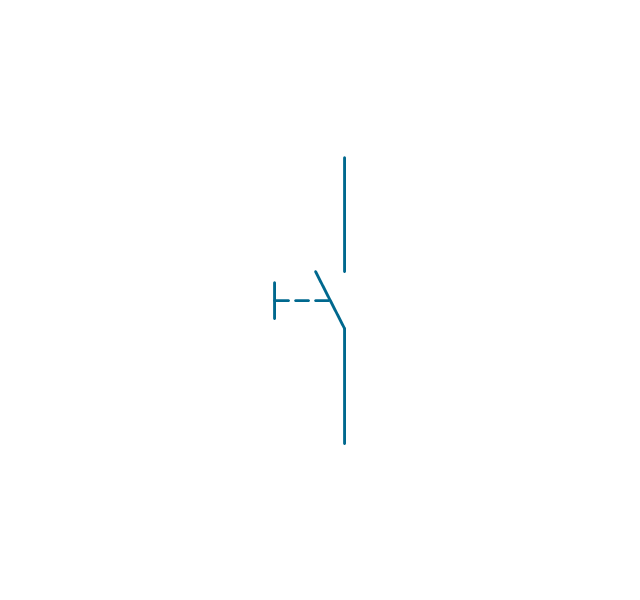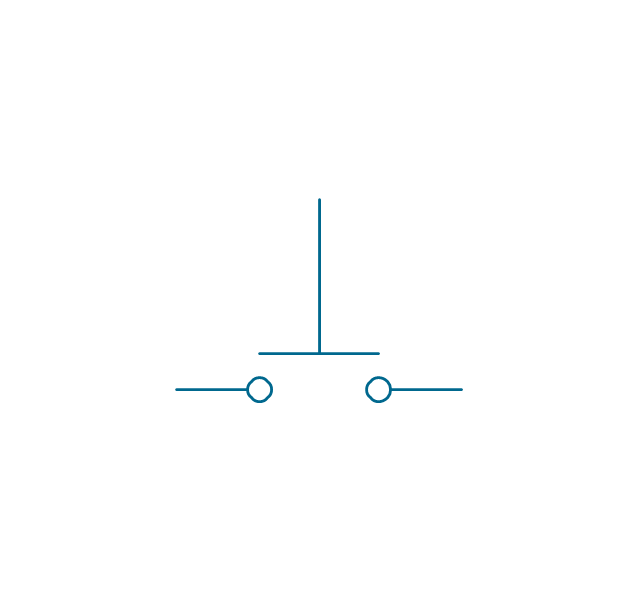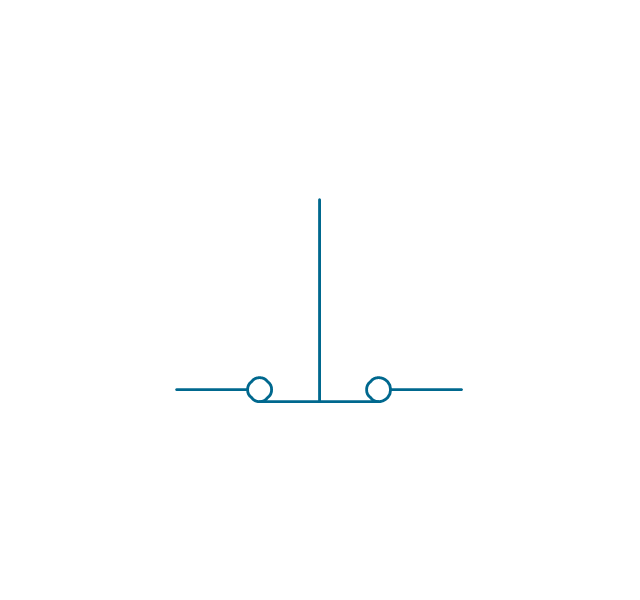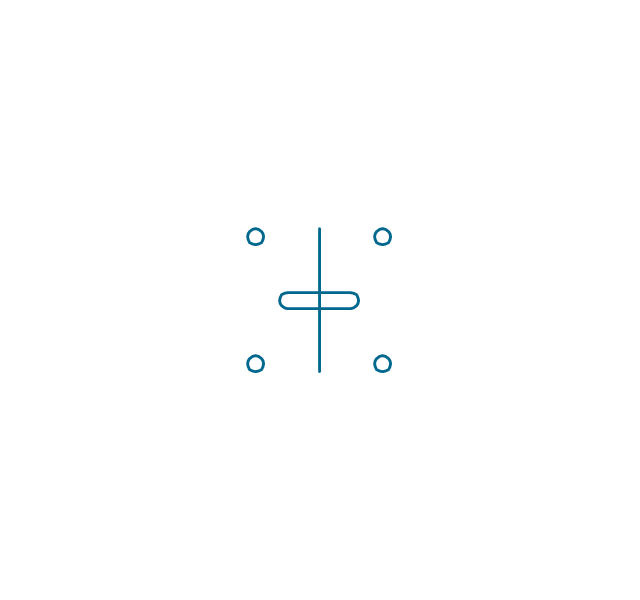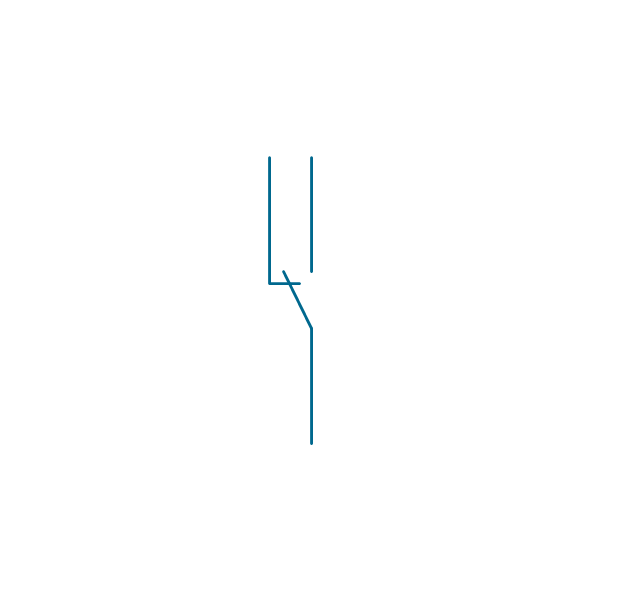Electrical Symbols — Stations
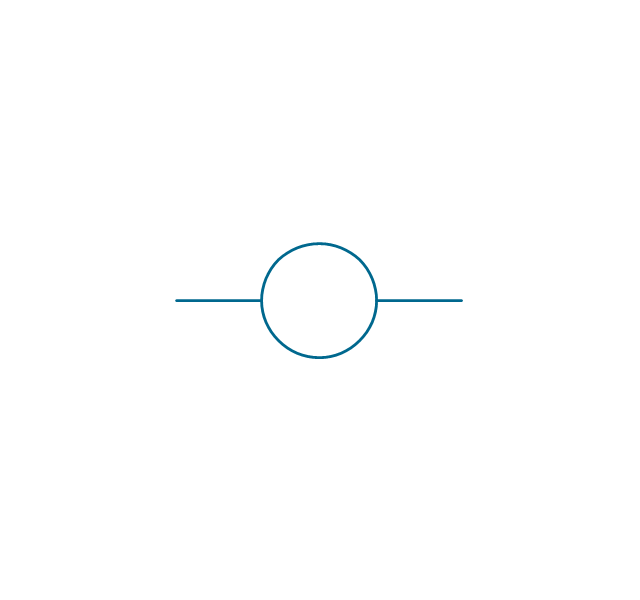
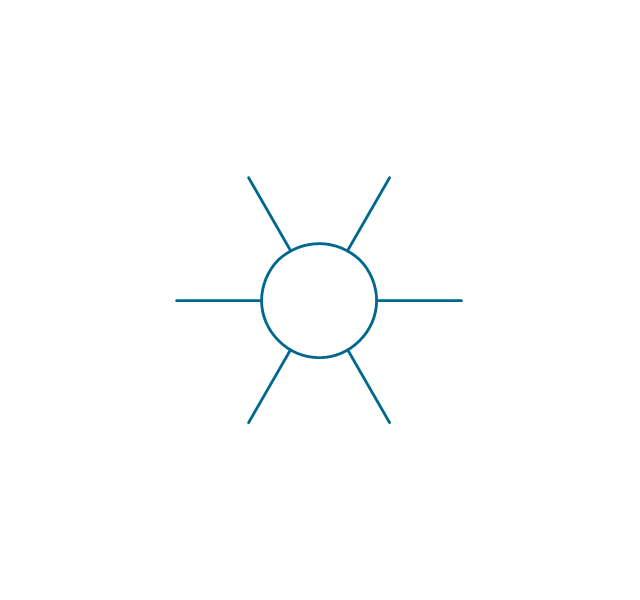
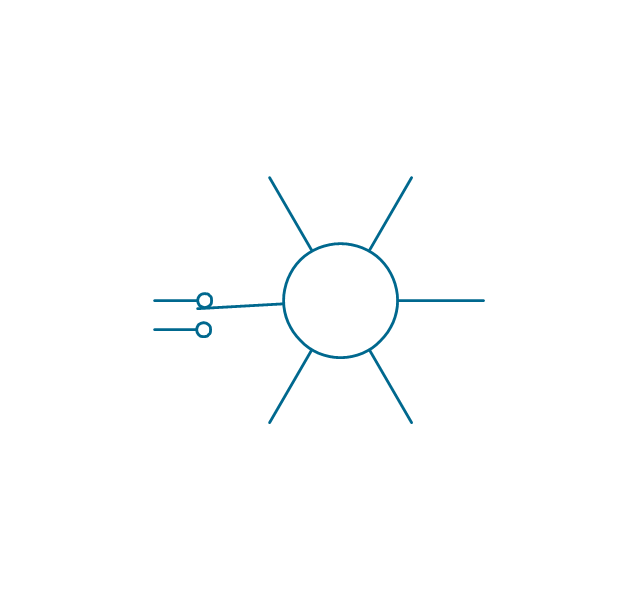
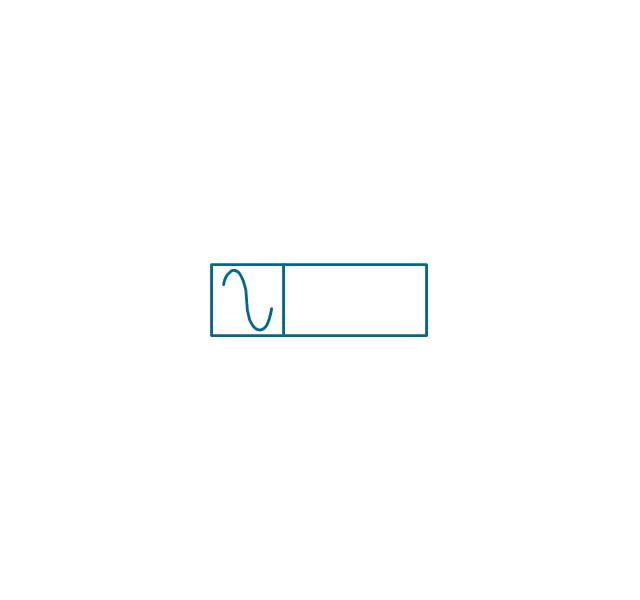
A power station is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Most power stations contain one or more generators, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into electrical power. The relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor creates an electrical current. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity. Others use nuclear power, but there is an increasing use of cleaner renewable sources such as solar, wind, wave and hydroelectric. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — Transformers and Windings
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction produces an electromotive force within a conductor which is exposed to time varying magnetic fields. Transformers are used to increase or decrease the alternating voltages in electric power applications. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — Inductors
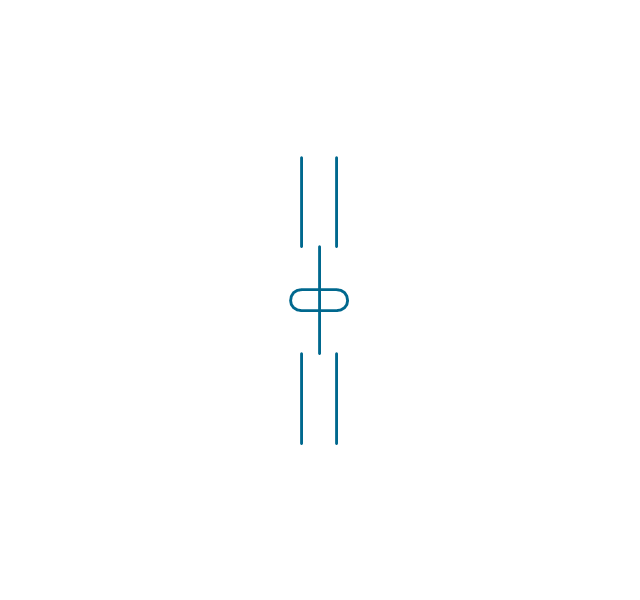
An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. Energy is stored in a magnetic field in the coil as long as current flows. When the current flowing through an inductor changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — Switches and Relays
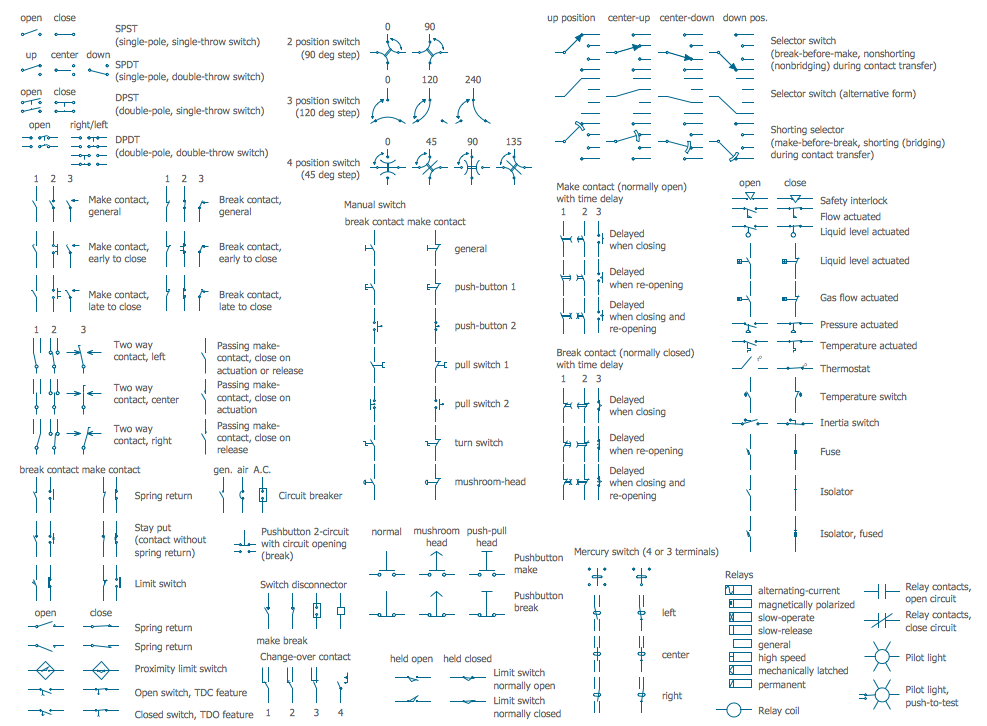
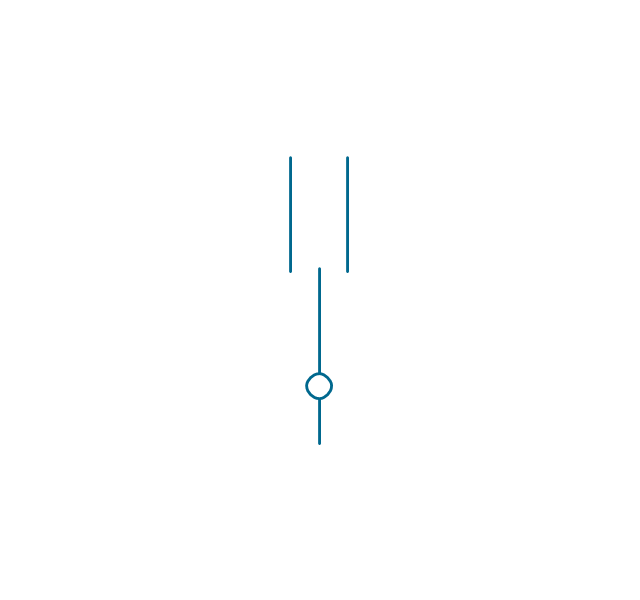
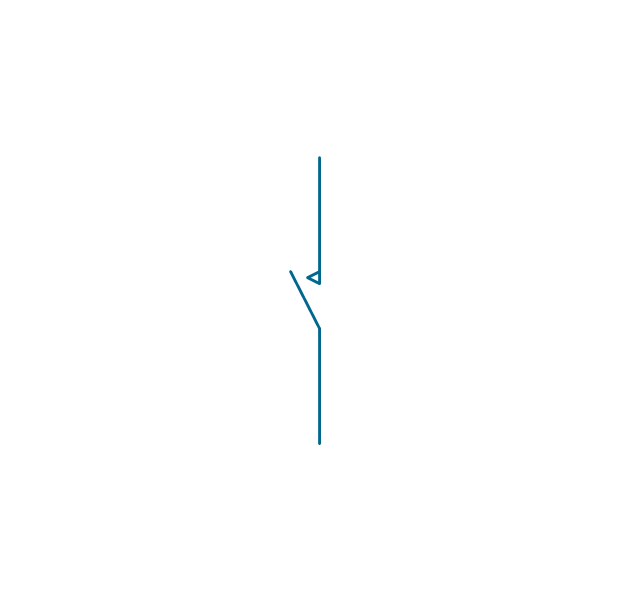
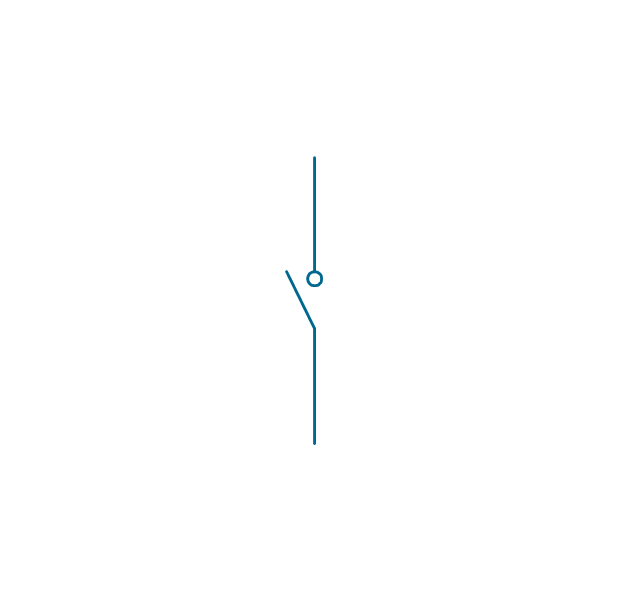
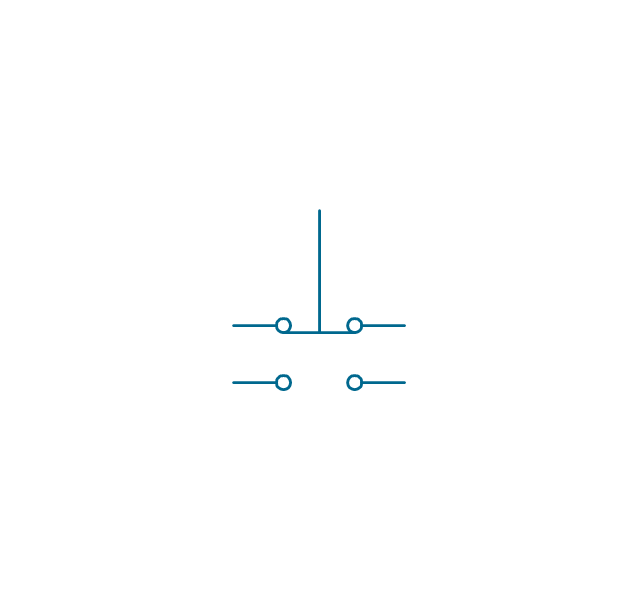
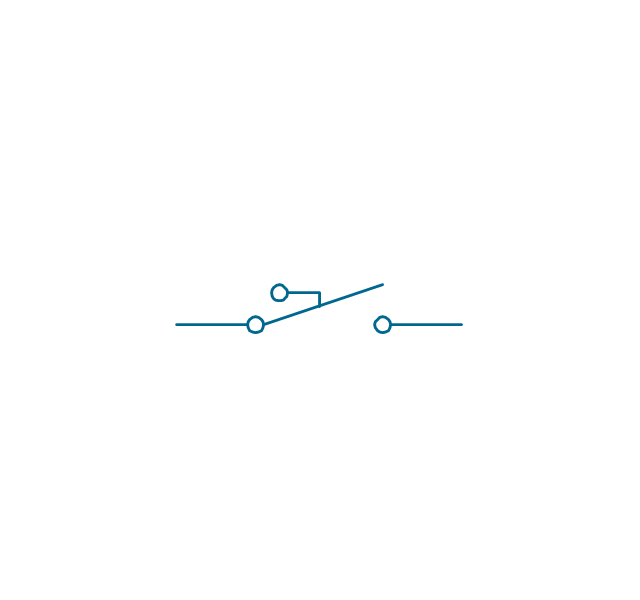
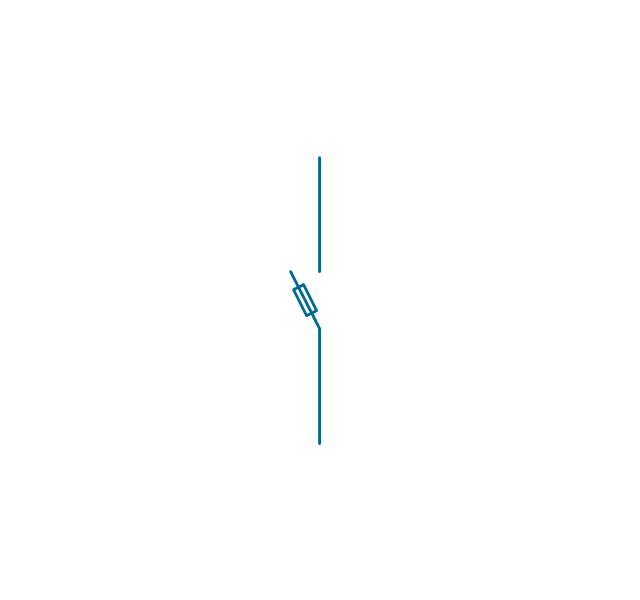
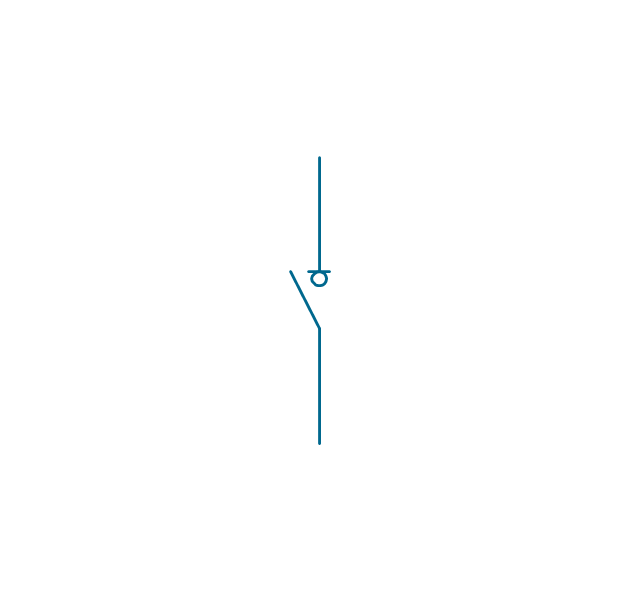
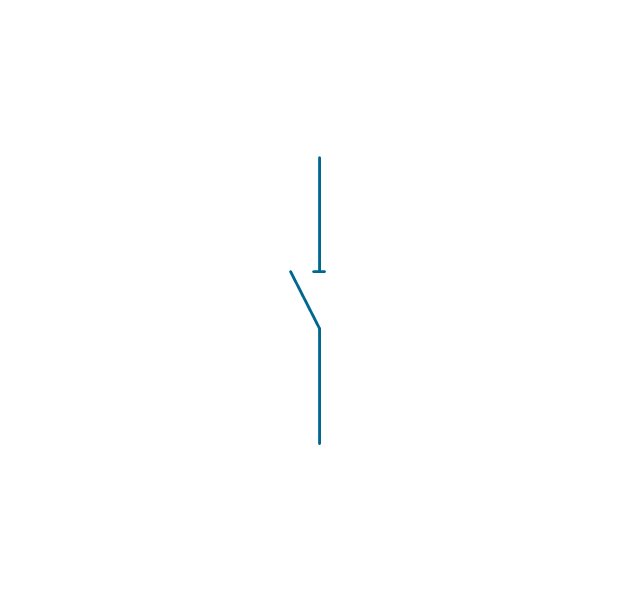
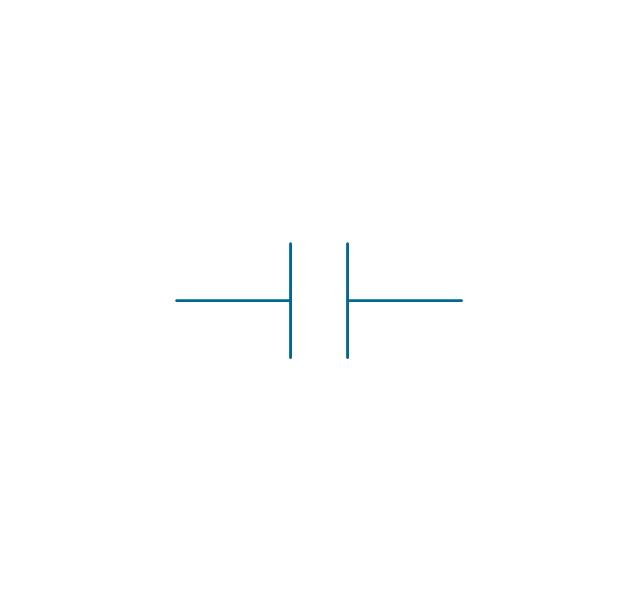
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The mechanism of a switch may be operated directly by a human operator to control a circuit (for example, a light switch or a keyboard button), may be operated by a moving object such as a door-operated switch, or may be operated by some sensing element for pressure, temperature or flow. A relay is a switch that is operated by electricity. Switches are made to handle a wide range of voltages and currents; very large switches may be used to isolate high-voltage circuits in electrical substations. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — Transmission Paths
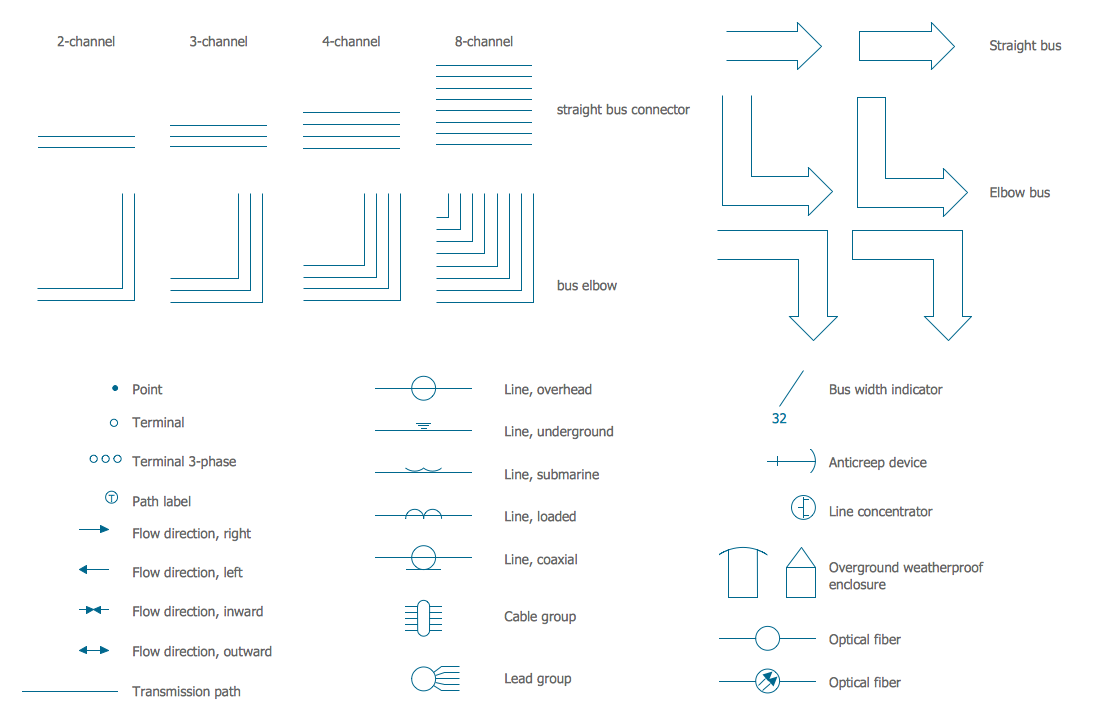
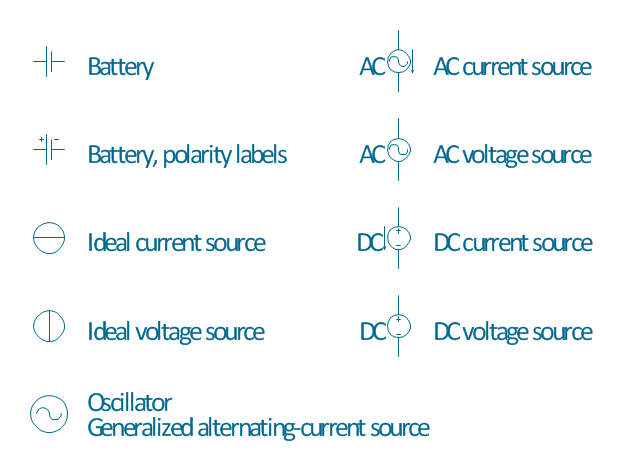
Variable delay elements are often used to manipulate the rising or falling edges of the clock or any other signal in integrated circuits. Delay elements are also used in delay locked loops and in defining a time reference for the movement of data within those systems. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.The vector stencils library "Power sources" contains 9 element symbols of power sources and batteries for drawing the electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A power supply is a device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The term is most commonly applied to electric power converters that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy (mechanical, chemical, solar) to electrical energy. A regulated power supply is one that controls the output voltage or current to a specific value; the controlled value is held nearly constant despite variations in either load current or the voltage supplied by the power supply's energy source.
Every power supply must obtain the energy it supplies to its load, as well as any energy it consumes while performing that task, from an energy source. Depending on its design, a power supply may obtain energy from:
(1) Electrical energy transmission systems. Common examples of this include power supplies that convert AC line voltage to DC voltage.
(2) Energy storage devices such as batteries and fuel cells.
(3) Electromechanical systems such as generators and alternators.
(4) Solar power." [Power supply. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Power sources" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A power supply is a device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The term is most commonly applied to electric power converters that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy (mechanical, chemical, solar) to electrical energy. A regulated power supply is one that controls the output voltage or current to a specific value; the controlled value is held nearly constant despite variations in either load current or the voltage supplied by the power supply's energy source.
Every power supply must obtain the energy it supplies to its load, as well as any energy it consumes while performing that task, from an energy source. Depending on its design, a power supply may obtain energy from:
(1) Electrical energy transmission systems. Common examples of this include power supplies that convert AC line voltage to DC voltage.
(2) Energy storage devices such as batteries and fuel cells.
(3) Electromechanical systems such as generators and alternators.
(4) Solar power." [Power supply. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Power sources" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
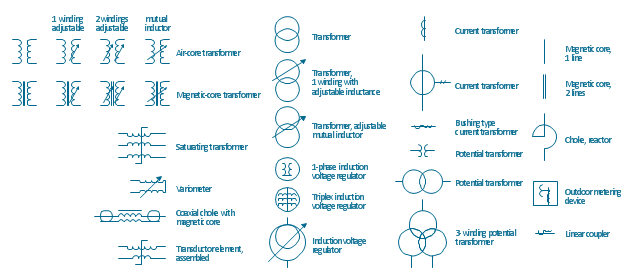
The vector stencils library "Transformers and windings" contains 29 element symbols of transformers, windings, couplers, metering devices, transductors, magnetic cores, chokes, and a variometer.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
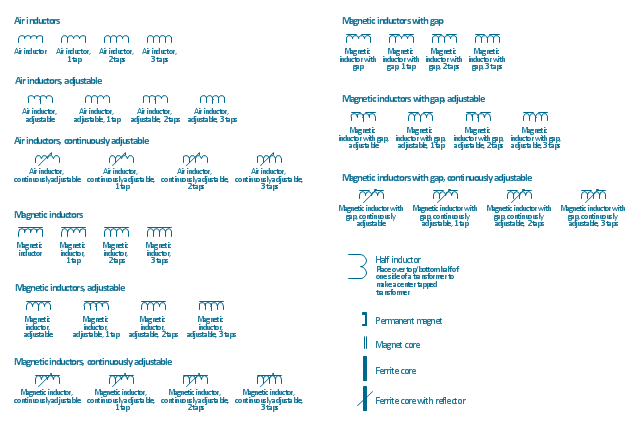
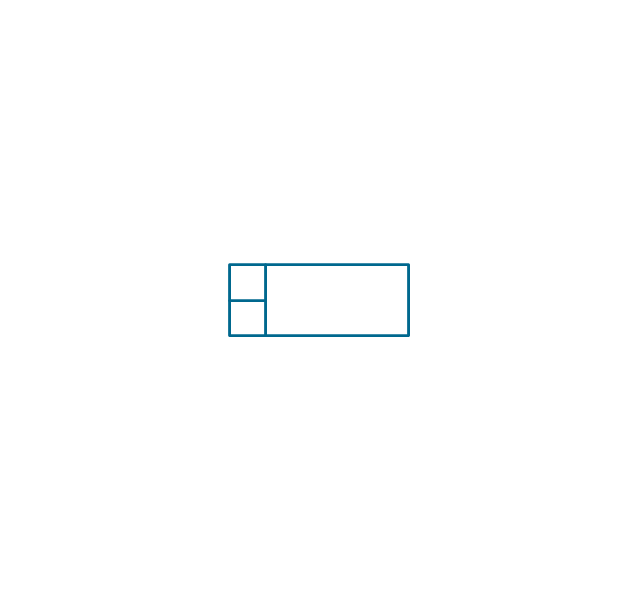
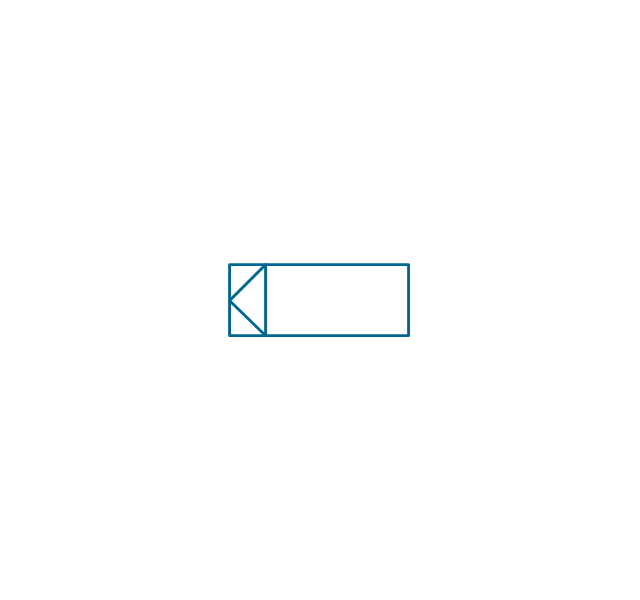
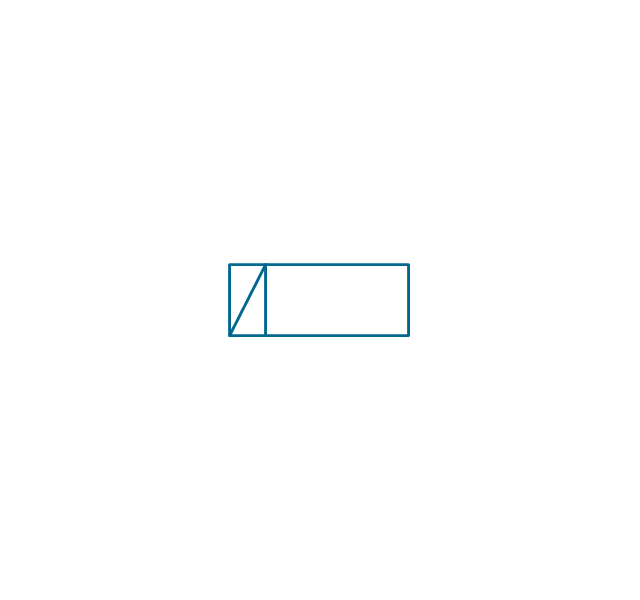
The vector stencils library "Inductors" contains 41 symbols of inductor elements for drawing electronic circuit diagrams.
"An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. When a current flows through it, energy is stored temporarily in a magnetic field in the coil. When the current flowing through an inductor changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which opposes the change in current that created it.
An inductor is characterized by its inductance, the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current, which has units of henries (H). Inductors have values that typically range from 1 µH (10-6H) to 1 H. Many inductors have a magnetic core made of iron or ferrite inside the coil, which serves to increase the magnetic field and thus the inductance. Along with capacitors and resistors, inductors are one of the three passive linear circuit elements that make up electric circuits. Inductors are widely used in alternating current (AC) electronic equipment, particularly in radio equipment. They are used to block the flow of AC current while allowing DC to pass; inductors designed for this purpose are called chokes. They are also used in electronic filters to separate signals of different frequencies, and in combination with capacitors to make tuned circuits, used to tune radio and TV receivers." [Inductor. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - Inductors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. When a current flows through it, energy is stored temporarily in a magnetic field in the coil. When the current flowing through an inductor changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which opposes the change in current that created it.
An inductor is characterized by its inductance, the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current, which has units of henries (H). Inductors have values that typically range from 1 µH (10-6H) to 1 H. Many inductors have a magnetic core made of iron or ferrite inside the coil, which serves to increase the magnetic field and thus the inductance. Along with capacitors and resistors, inductors are one of the three passive linear circuit elements that make up electric circuits. Inductors are widely used in alternating current (AC) electronic equipment, particularly in radio equipment. They are used to block the flow of AC current while allowing DC to pass; inductors designed for this purpose are called chokes. They are also used in electronic filters to separate signals of different frequencies, and in combination with capacitors to make tuned circuits, used to tune radio and TV receivers." [Inductor. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - Inductors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Switches and relays" contains 58 symbols of electrical contacts, switches, relays, circuit breakers, selectors, connectors, disconnect devices, switching circuits, current regulators, and thermostats for electrical devices.
Use these shapes for drawing electrical diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use these shapes for drawing electrical diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
- Design elements - Power sources | Electrical Drawing Software and ...
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Design ...
- Mechanical Engineering Drawing Symbol Of Power Plug
- Voltage Converter Symbol
- Electrical Engineering Drawing Symbol
- Electrical Symbols — Power Sources | Chemical Engineering ...
- Mechanical Engineering | Design elements - Power sources ...
- Design elements - Power sources | Power sources - Vector stencils ...
- Mechanical Drawing Symbols | Mechanical Engineering | How to ...
- Mechanical Drawing Symbols | Mechanical Engineering | Electrical ...
- Symbol Of Electric Current
- Electrical Symbols , Electrical Diagram Symbols | How To use House ...
- Electrical Drawing Software | Electrical Engineering | Design ...
- Mechanical Drawing Symbols | Electrical Symbols — Transformers ...
- Symbols Engineering Drawing Turning
- Design elements - Power sources | Electrical Symbols , Electrical ...
- Motor Winding Symbol
- How To use Appliances Symbols for Building Plan | Electrical and ...
- Design elements - Transformers and windings | Electrical Drawing ...
- Design elements - Power sources | Power sources - Vector stencils ...