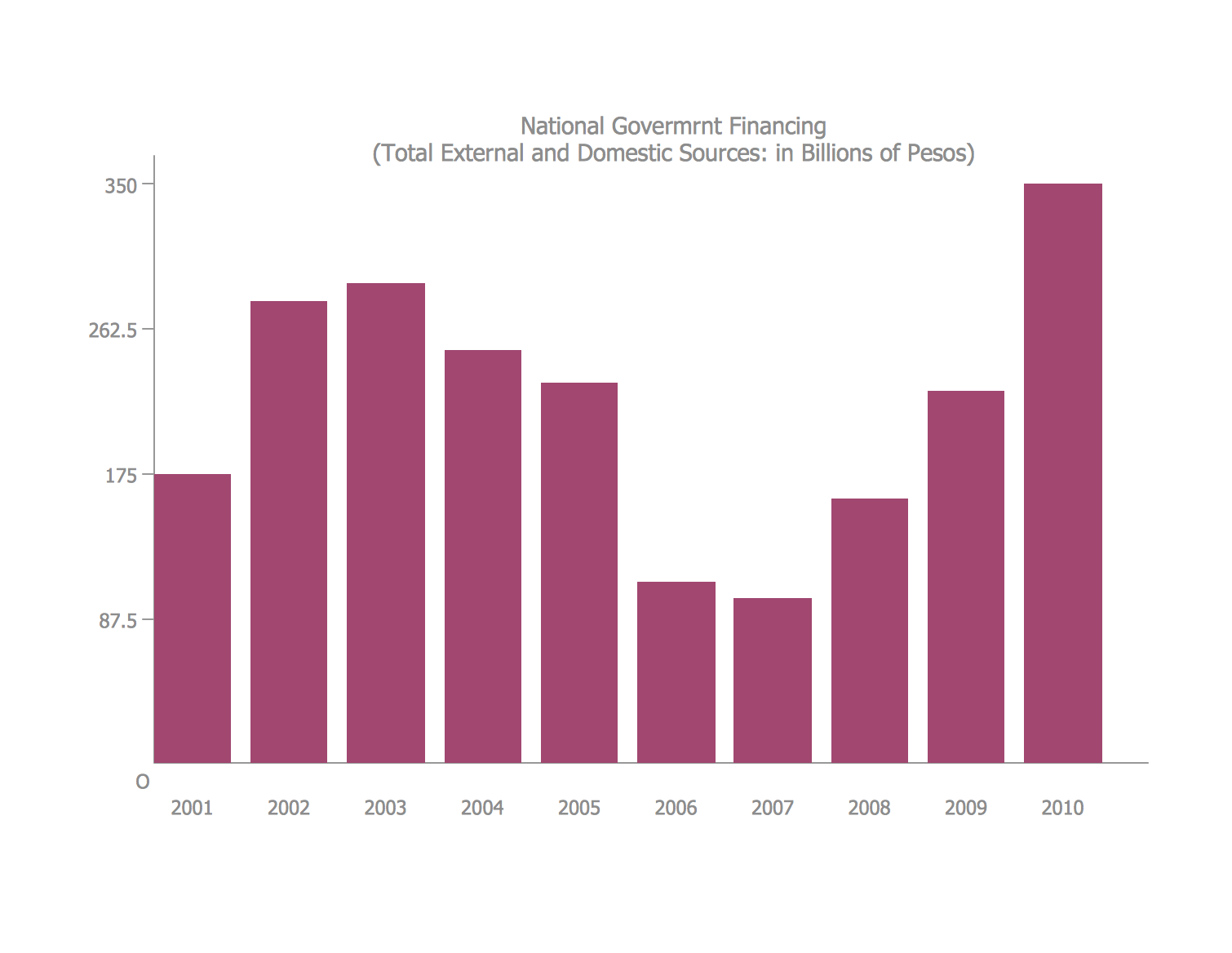
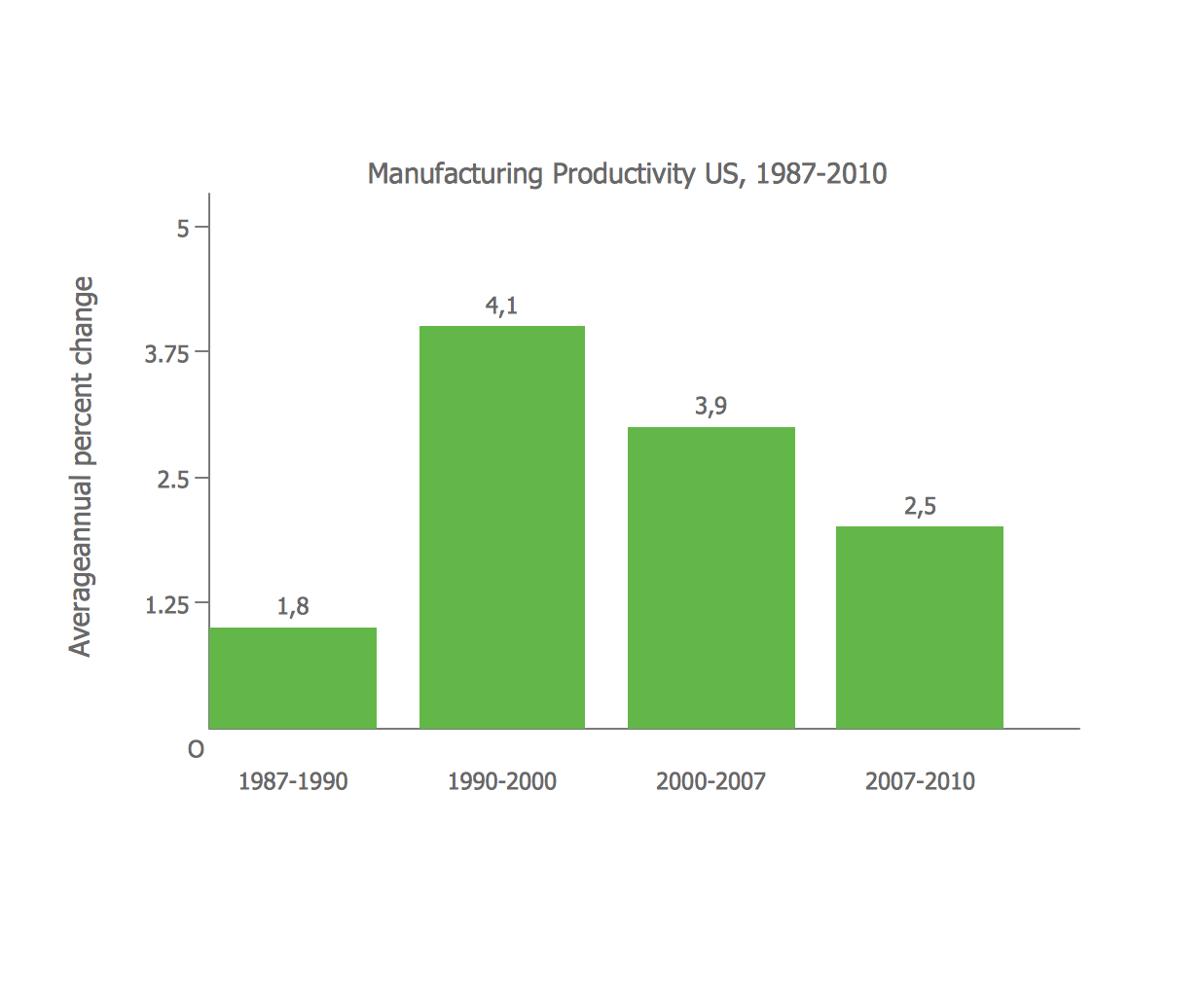
Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving. Create economics and financial bar charts with Bar Graphs Solution
Create bar graphs for visualizing economics problem solving and financial data comparison using the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Bar Graphs Solution from the Graphs and Charts area of ConceptDraw Solition Park.Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving. Create manufacturing and economics bar charts with Bar Graphs Solution
Create bar charts for visualizing problem solving in manufacturing and economics using the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Bar Graphs Solution from the Graphs and Charts area of ConceptDraw Solition Park.Venn Diagram Examples for Problem Solving. Environmental Social Science. Human Sustainability Confluence
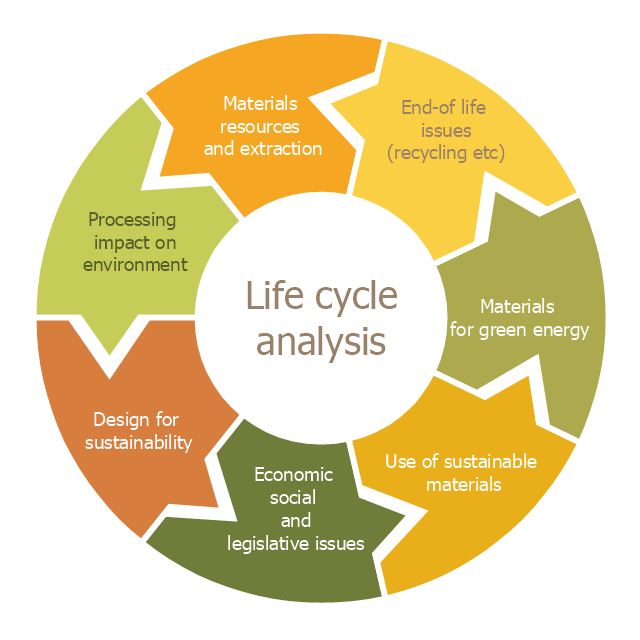
The Venn diagram example below shows sustainable development at the confluence of three constituent parts. Create your Venn diagrams for problem solving in environmental social science using the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Venn Diagrams solution from the area "Diagrams" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.This cycle diagram sample was created on the base of the figure illustrating the article "Environmental Materials" by Cris Arnold from the website of the UK Centre for Materials Education of the Higher Education Academy. "The figure ... schematically shows how the disparate areas under the heading of 'environmental materials' can be linked via a life cycle analysis approach. ...
Life Cycle Analysis.
Life Cycle Analysis is essentially a method of considering the entire environmental impact, energy and resource usage of a material or product. It is often known as a 'cradle-to-grave' analysis and can encompass the entire lifetime from extraction to end-of-life disposal. Life cycle analysis can be an extremely effective way of linking many different aspects of the environmental impacts of materials usage. ...
Materials Extraction and Resource Implications.
The environmental impact of raw materials extraction and processing together with global resource issues provides a good place to start consideration of environmental aspects of materials. ...
Environmental Impacts of Processing.
... Topics that would come under this subject area include the specific environmental problems associated with processing of metals, polymers, ceramics, composites etc, and how these problems can be overcome.
Design for Sustainability.
This area ... will ... cover issues such as design for successful recycling, waste minimisation, energy efficiency and increased lifetime.
Economic, Social and Legislative Issues.
... For example, materials selection within the automotive industry is now heavily influenced by 'end-of-life vehicle' and 'hazardous material' regulations.
Use of Sustainable Materials.
... It is probably sensible to define such materials as those that have distinct differences that achieve environmental benefit compared to conventional materials. With this definition, the list would include:
(1) Materials of a significantly plant-based nature, including wood, natural fibre composites, natural polymers.
(2) Materials produced using a large proportion of waste material, including recycled polymers, composites made from waste mineral powders, and arguably also much steel and aluminium.
Materials for Green Energy.
The most exciting developments in Materials Science are in the realm of functional materials, and many of these serve an environmentally-beneficial purpose, particularly in the production of green energy.
These include:
(1) Solar-cell materials.
(2) Fuel-cell technology.
(3) Catalytic pollution control.
End-of-Life Issues.
The treatment of materials at the end of their lifetime is a significant subject area and encompasses aspects such as recycling techniques and materials limitations, biodegradabilty and composting, chemical recovery and energy recovery." [materials.ac.uk/ guides/ environmental.asp]
The ring chart example "Life cycle analysis" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
Life Cycle Analysis.
Life Cycle Analysis is essentially a method of considering the entire environmental impact, energy and resource usage of a material or product. It is often known as a 'cradle-to-grave' analysis and can encompass the entire lifetime from extraction to end-of-life disposal. Life cycle analysis can be an extremely effective way of linking many different aspects of the environmental impacts of materials usage. ...
Materials Extraction and Resource Implications.
The environmental impact of raw materials extraction and processing together with global resource issues provides a good place to start consideration of environmental aspects of materials. ...
Environmental Impacts of Processing.
... Topics that would come under this subject area include the specific environmental problems associated with processing of metals, polymers, ceramics, composites etc, and how these problems can be overcome.
Design for Sustainability.
This area ... will ... cover issues such as design for successful recycling, waste minimisation, energy efficiency and increased lifetime.
Economic, Social and Legislative Issues.
... For example, materials selection within the automotive industry is now heavily influenced by 'end-of-life vehicle' and 'hazardous material' regulations.
Use of Sustainable Materials.
... It is probably sensible to define such materials as those that have distinct differences that achieve environmental benefit compared to conventional materials. With this definition, the list would include:
(1) Materials of a significantly plant-based nature, including wood, natural fibre composites, natural polymers.
(2) Materials produced using a large proportion of waste material, including recycled polymers, composites made from waste mineral powders, and arguably also much steel and aluminium.
Materials for Green Energy.
The most exciting developments in Materials Science are in the realm of functional materials, and many of these serve an environmentally-beneficial purpose, particularly in the production of green energy.
These include:
(1) Solar-cell materials.
(2) Fuel-cell technology.
(3) Catalytic pollution control.
End-of-Life Issues.
The treatment of materials at the end of their lifetime is a significant subject area and encompasses aspects such as recycling techniques and materials limitations, biodegradabilty and composting, chemical recovery and energy recovery." [materials.ac.uk/ guides/ environmental.asp]
The ring chart example "Life cycle analysis" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
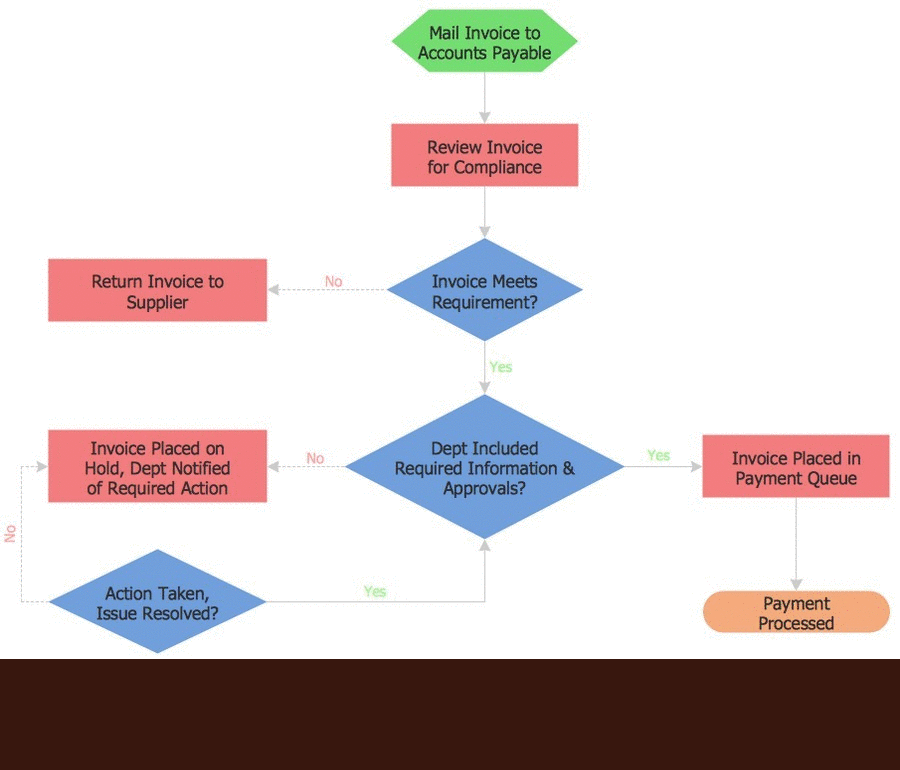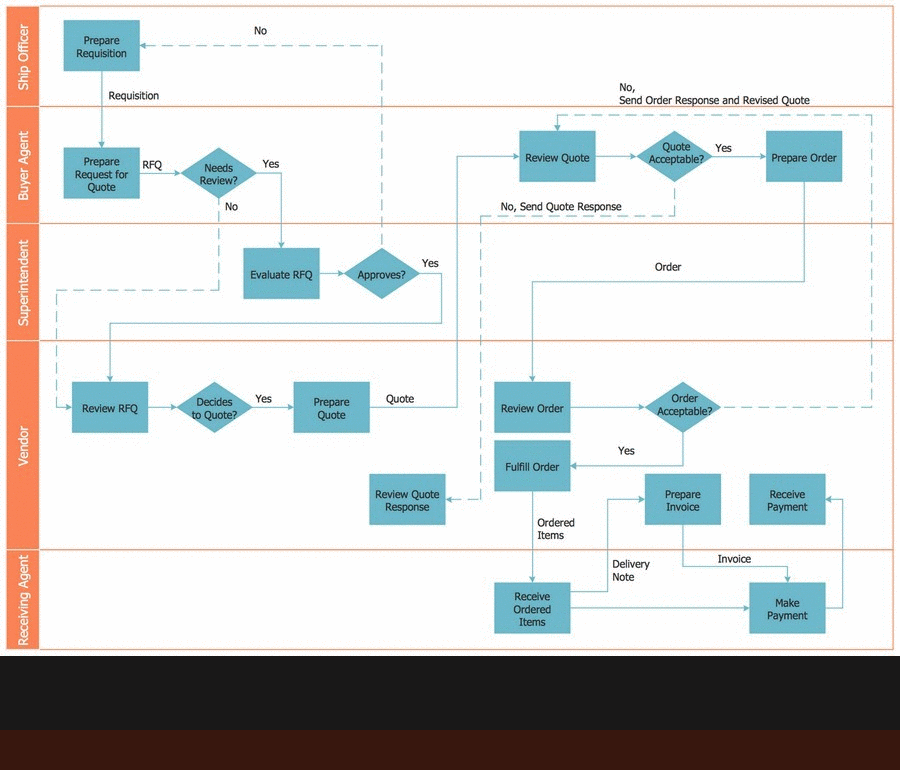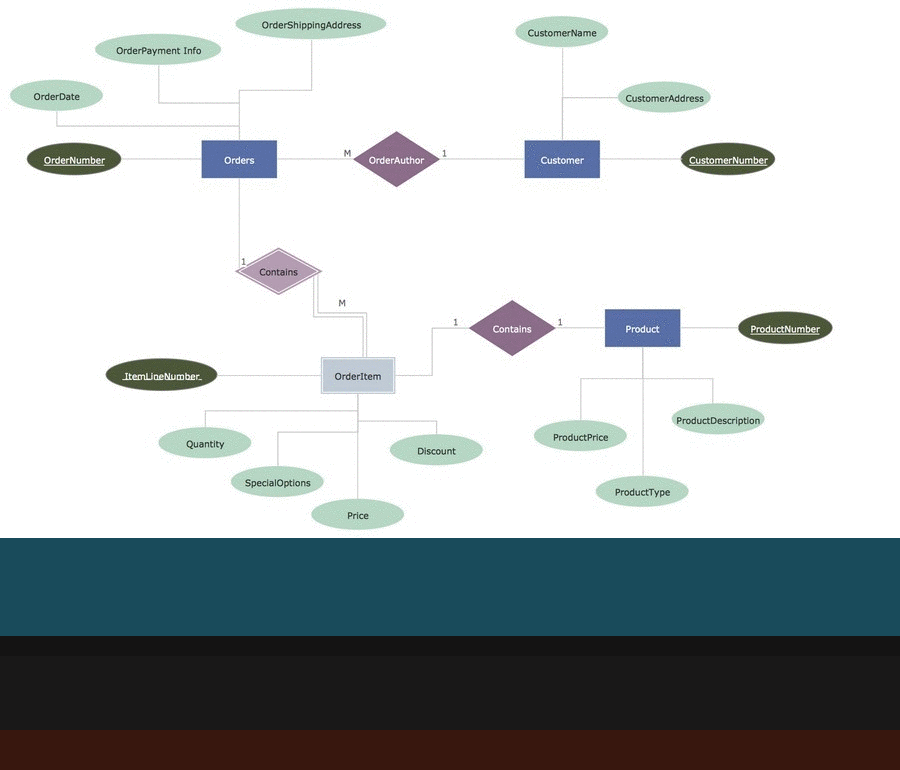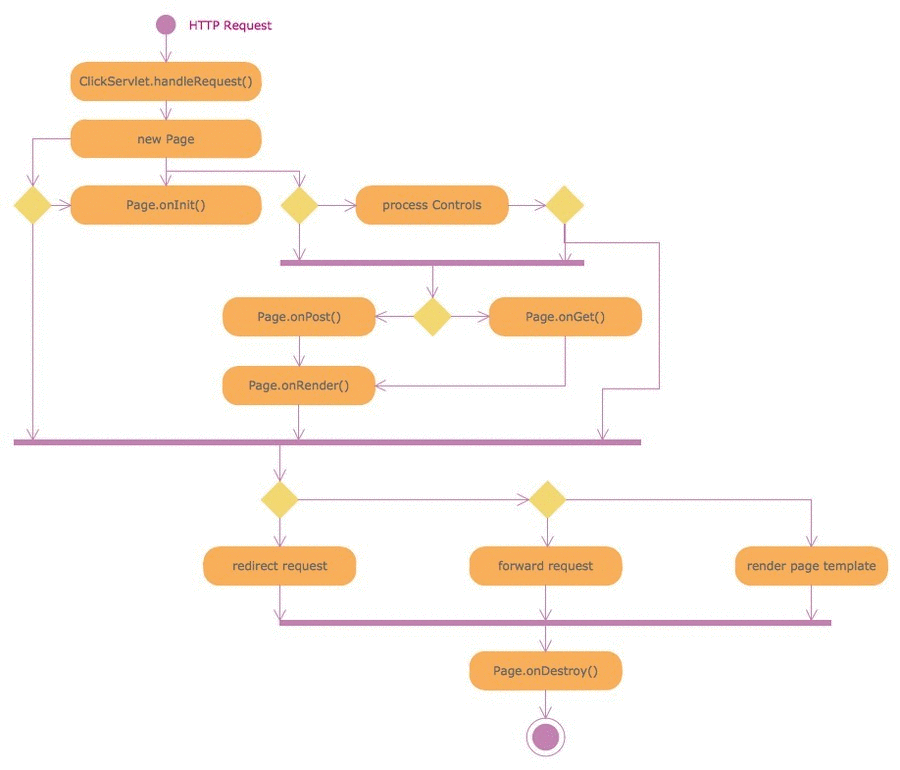
Flowchart Software
Flowchart is a simple diagram, map or graphical schematic representation the sequence of actions within a process. It is ideal for displaying how a process currently flows or can function ideally. The Flowcharts let define the steps and boundaries of a process, uncover problems or miscommunications. The Flowcharts are widely used in education, software development, business, economics, thanks to their visuality they are ideal for presentations, reports, for using on conferences to help the audience comprehend the content better, or easy find flaws in a process flow diagrams. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is professional flowcharts software and feature-rich flowchart maker, which supports Mac OS X and Windows. It contains at ConceptDraw Solution Park a rich set of stencils and professional flowchart symbols for design. It lets create simply professional-looking Flowcharts based on thousand free flowchart templates, colored symbols and examples. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a 3 times cheaper alternative to MS Visio available for both Mac and PC. It’s is another full featured business and technical diagramming application that can easily take care of Visio files within OS X. Another bonus with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM – it's cross-platform. You can work on a document in both OS X and Windows, skipping Visio entirely.
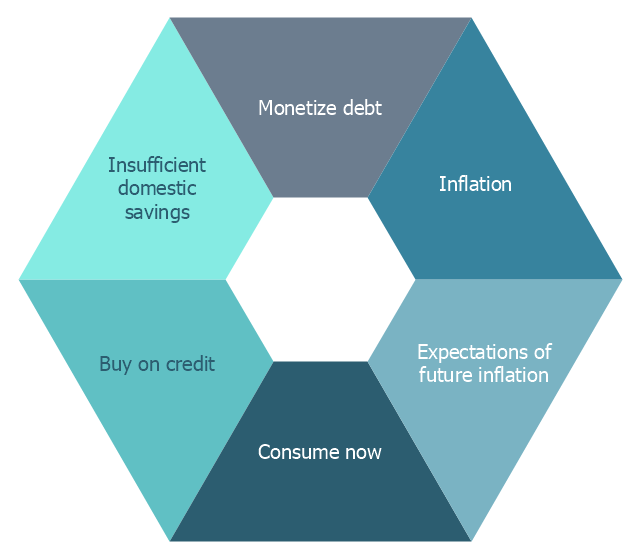
This hexagon diagram sample was redesigned from the Wikipedia file: Vicious circle in macroeconomics.svg. "An example of the use of a vicious circle in macroeconomics." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Vicious_ circle_ in_ macroeconomics.svg]
"A virtuous circle and a vicious circle (also referred to as virtuous cycle and vicious cycle) are economic terms. They refer to a complex chain of events that reinforces itself through a feedback loop. A virtuous circle has favorable results, while a vicious circle has detrimental results.
Both circles are complexes of events with no tendency towards equilibrium (at least in the short run). Both systems of events have feedback loops in which each iteration of the cycle reinforces the previous one (positive feedback). These cycles will continue in the direction of their momentum until an external factor intervenes and breaks the cycle. The prefix "hyper-" is sometimes used to describe these cycles if they are extreme. The best-known example of a vicious circle is hyperinflation. ...
Example in macroeconomics.
Vicious circle.
Hyperinflation is a spiral of inflation which causes even higher inflation. The initial exogenous event might be a sudden large increase in international interest rates or a massive increase in government debt due to excessive spendings. Whatever the cause, the government could pay down some of its debt by printing more money (called monetizing the debt). This increase in the money supply could increase the level of inflation. In an inflationary environment, people tend to spend their money quickly because they expect its value to decrease further in the future. They convert their financial assets into physical assets while their money still has some purchasing power. Often they will purchase on credit. Eventually, the currency loses all of its value. Because of this, the level of savings in the country is very low and the government could have problems refinancing its debt. Its solution could be to print still more money starting another iteration of the vicious cycle." [Virtuous circle and vicious circle. Wikipedia]
The crystal diagram example "Vicious circle" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
"A virtuous circle and a vicious circle (also referred to as virtuous cycle and vicious cycle) are economic terms. They refer to a complex chain of events that reinforces itself through a feedback loop. A virtuous circle has favorable results, while a vicious circle has detrimental results.
Both circles are complexes of events with no tendency towards equilibrium (at least in the short run). Both systems of events have feedback loops in which each iteration of the cycle reinforces the previous one (positive feedback). These cycles will continue in the direction of their momentum until an external factor intervenes and breaks the cycle. The prefix "hyper-" is sometimes used to describe these cycles if they are extreme. The best-known example of a vicious circle is hyperinflation. ...
Example in macroeconomics.
Vicious circle.
Hyperinflation is a spiral of inflation which causes even higher inflation. The initial exogenous event might be a sudden large increase in international interest rates or a massive increase in government debt due to excessive spendings. Whatever the cause, the government could pay down some of its debt by printing more money (called monetizing the debt). This increase in the money supply could increase the level of inflation. In an inflationary environment, people tend to spend their money quickly because they expect its value to decrease further in the future. They convert their financial assets into physical assets while their money still has some purchasing power. Often they will purchase on credit. Eventually, the currency loses all of its value. Because of this, the level of savings in the country is very low and the government could have problems refinancing its debt. Its solution could be to print still more money starting another iteration of the vicious cycle." [Virtuous circle and vicious circle. Wikipedia]
The crystal diagram example "Vicious circle" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
 ConceptDraw Solution Park
ConceptDraw Solution Park
ConceptDraw Solution Park collects graphic extensions, examples and learning materials
- Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving. Create manufacturing and ...
- Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving. Create economics and financial ...
- Fishbone Problem Solving | Venn Diagram Examples for Problem ...
- Financial Comparison Chart | Audit Flowcharts | Bar Diagrams for ...
- Financial Comparison Chart | Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving ...
- Geo Map - Asia - Philippines | Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving ...
- Bar Chart Software | Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving. Create ...
- Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving. Create event management bar ...
- Process Flowchart | Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving. Create ...
- Pyramid Diagram | Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving. Create ...
- Bar Chart Examples | Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving. Create ...
- Economics Application Of Graph And Line
- Manufacturing and Maintenance | Bar Diagrams for Problem Solving ...
- Using Fishbone Diagrams for Problem Solving | Bar Diagrams for ...
- Using Fishbone Diagrams for Problem Solving | Cause and Effect ...
- Sector weightings - Exploded pie chart | Bar Diagrams for Problem ...
- Sales Growth. Bar Graphs Example | Bar Diagrams for Problem ...
- Fishbone Diagram | Lean Manufacturing Diagrams | Bar Diagrams ...
- Venn Diagram | Pyramid Diagram and Pyramid Chart | Market Chart ...
- Bar Graphs | Sales Growth. Bar Graphs Example | Bar Diagrams for ...