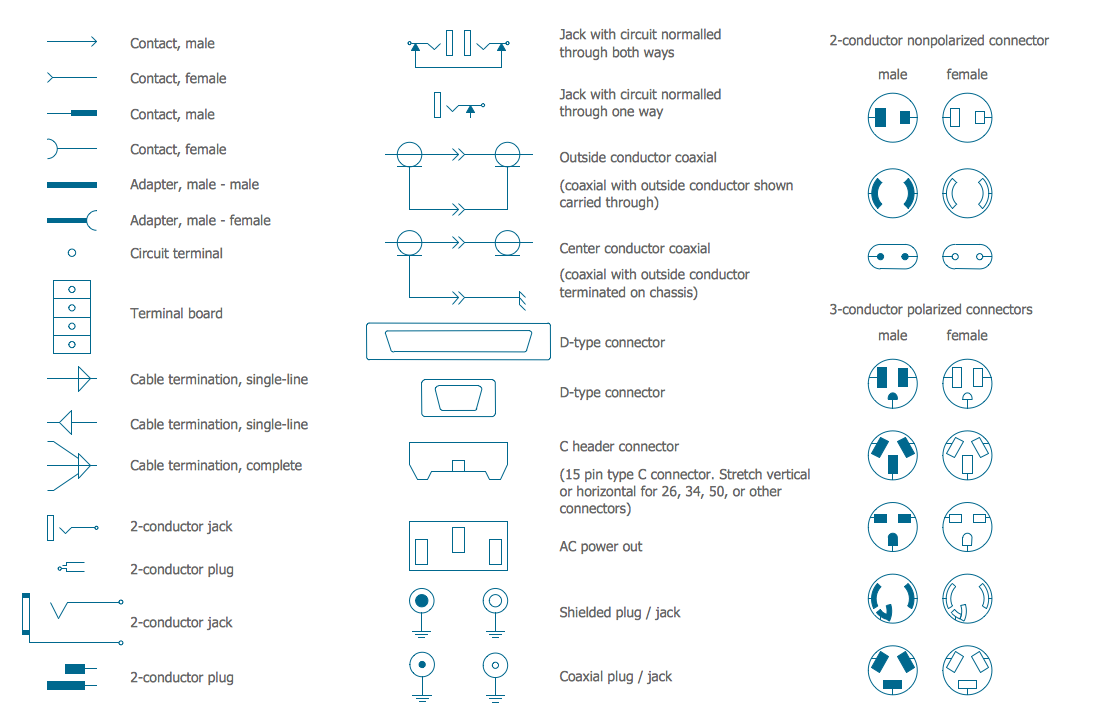
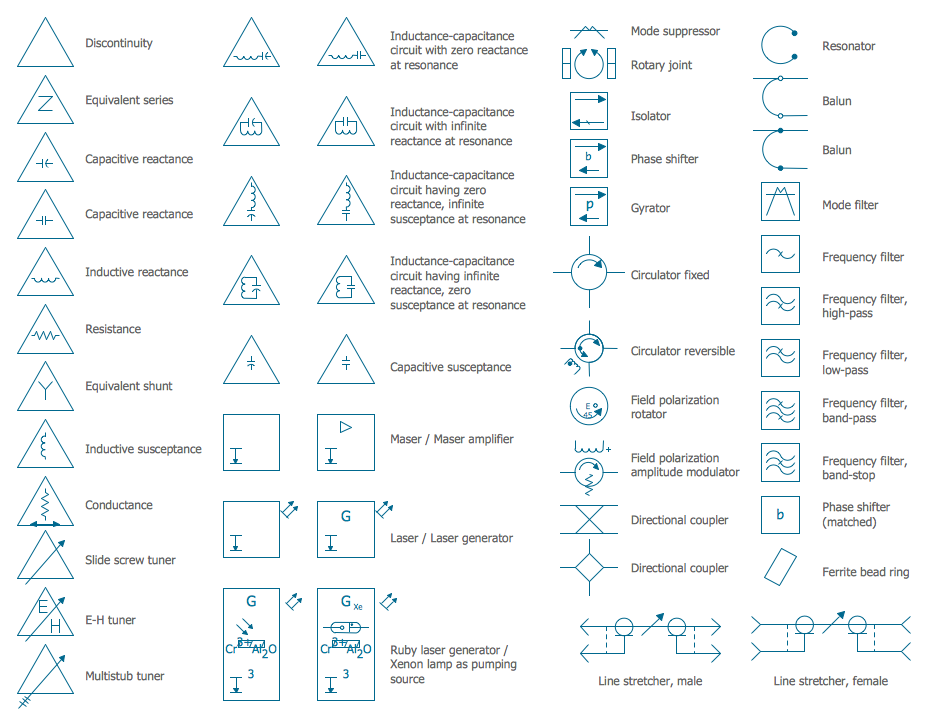
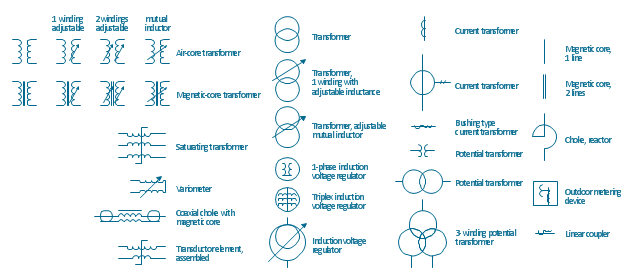
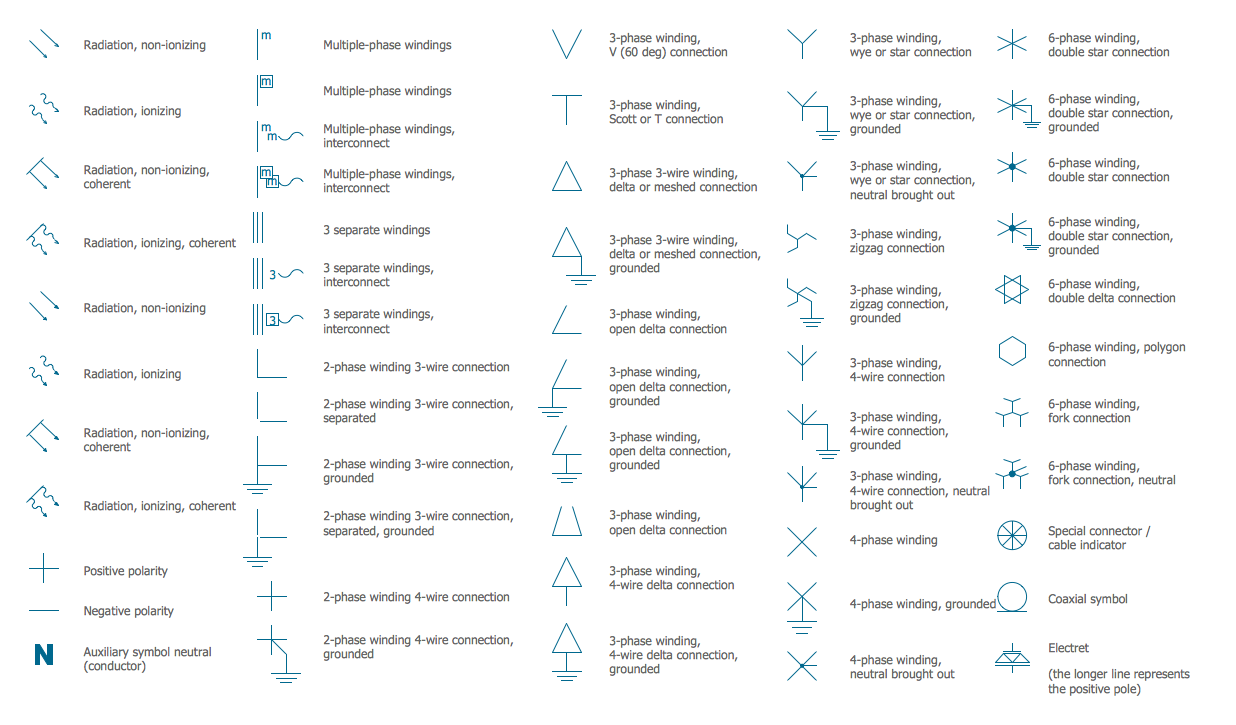
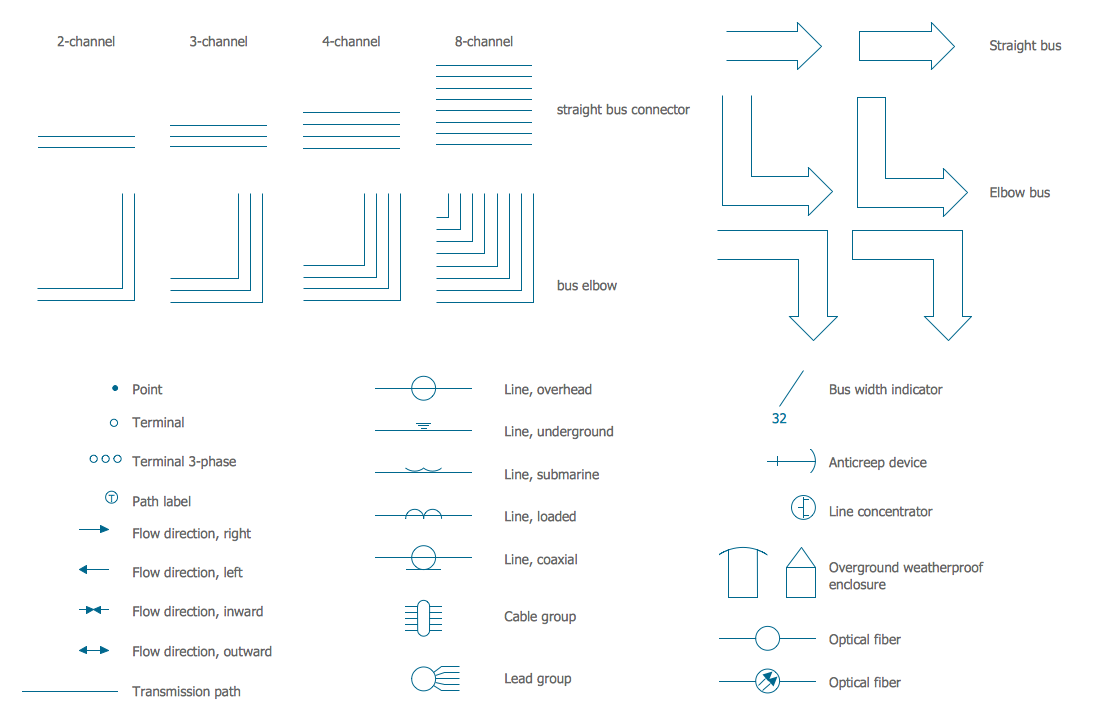
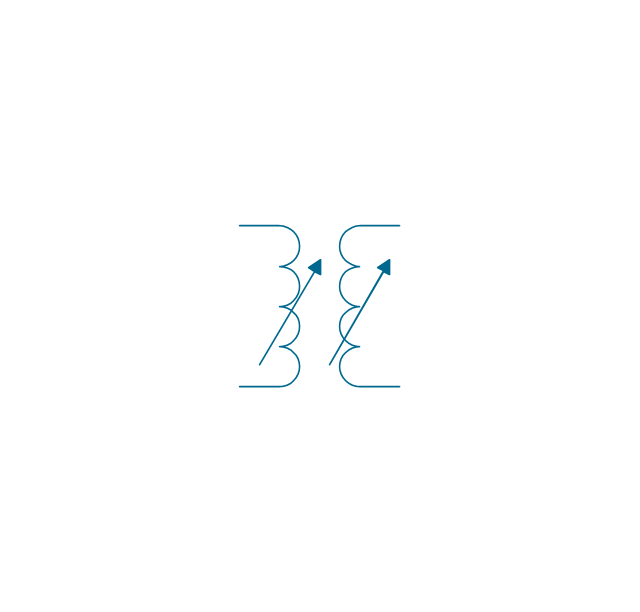Electrical Symbols — Terminals and Connectors
An electrical connector, is an electro-mechanical device used to join electrical terminations and create an electrical circuit. Electrical connectors consist of plugs (male-ended) and jacks (female-ended). The connection may be temporary, as for portable equipment, require a tool for assembly and removal, or serve as a permanent electrical joint between two wires or devices. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — VHF UHF SHF
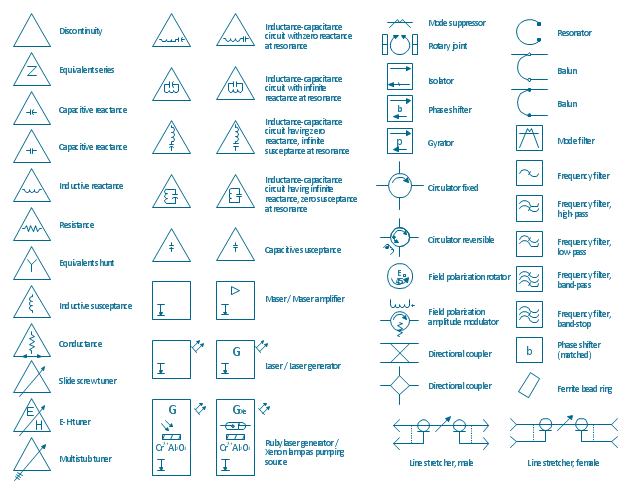
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 MHz and 3 GHz, also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one decimetre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, and numerous other applications. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — Transformers and Windings
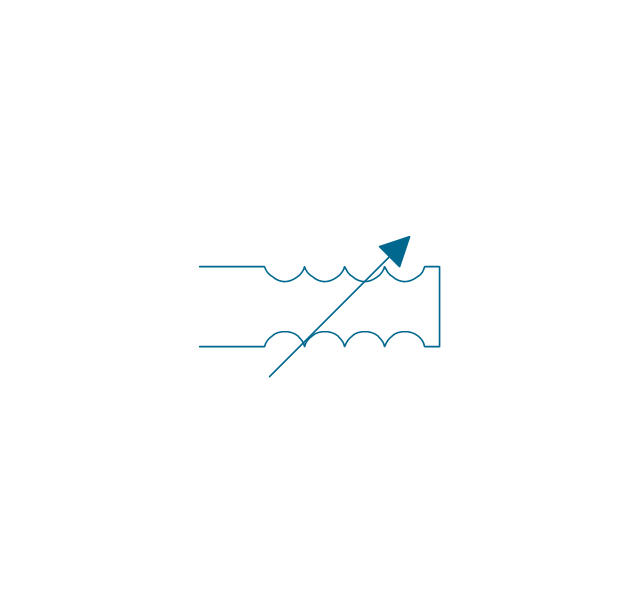
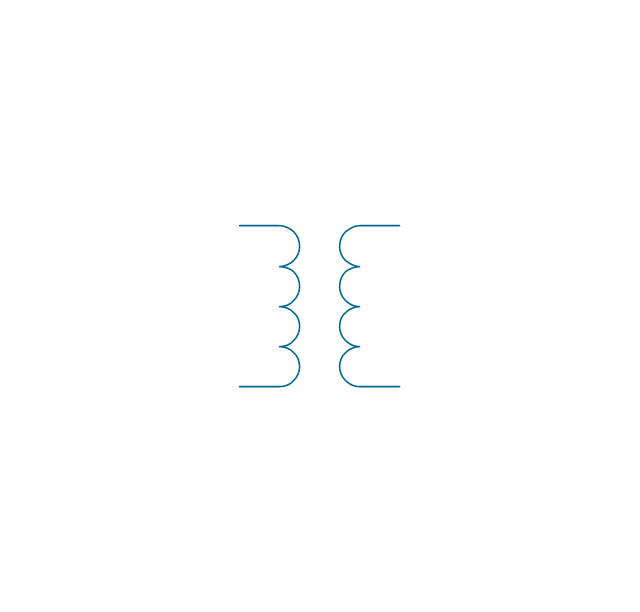
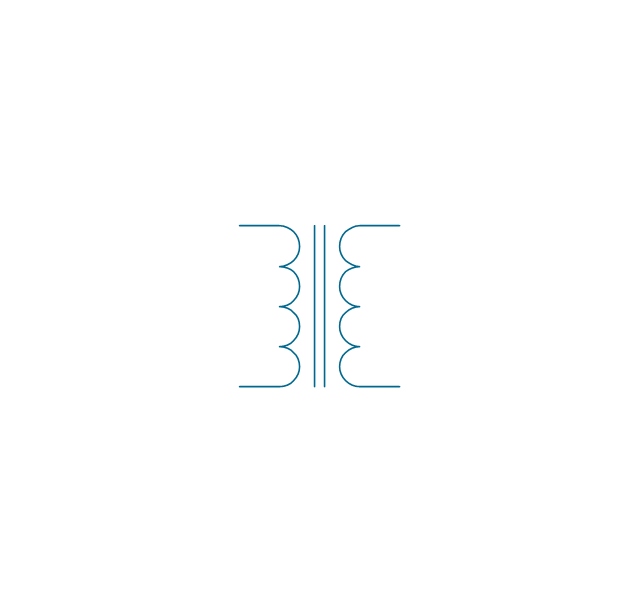
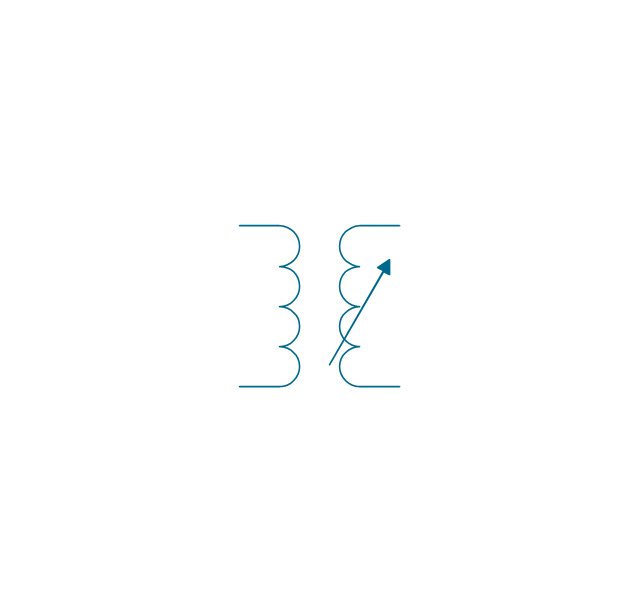
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction produces an electromotive force within a conductor which is exposed to time varying magnetic fields. Transformers are used to increase or decrease the alternating voltages in electric power applications. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols, Electrical Diagram Symbols
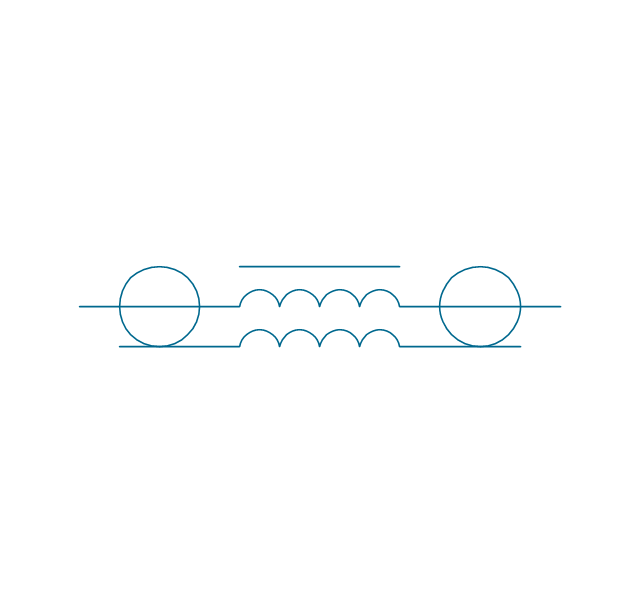
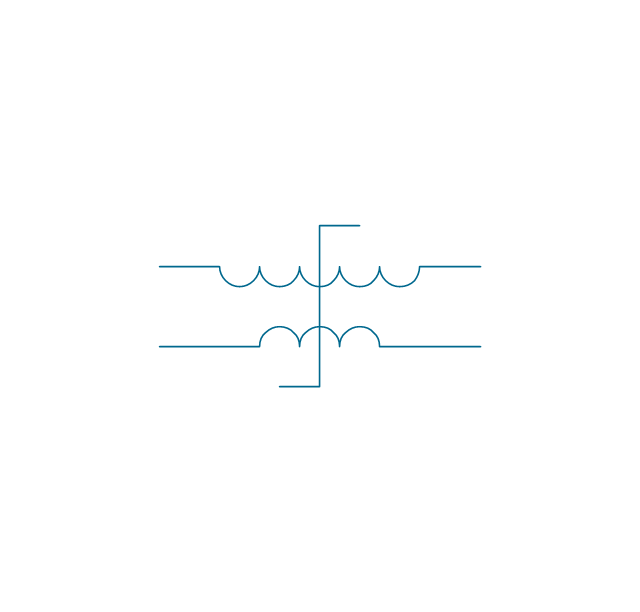
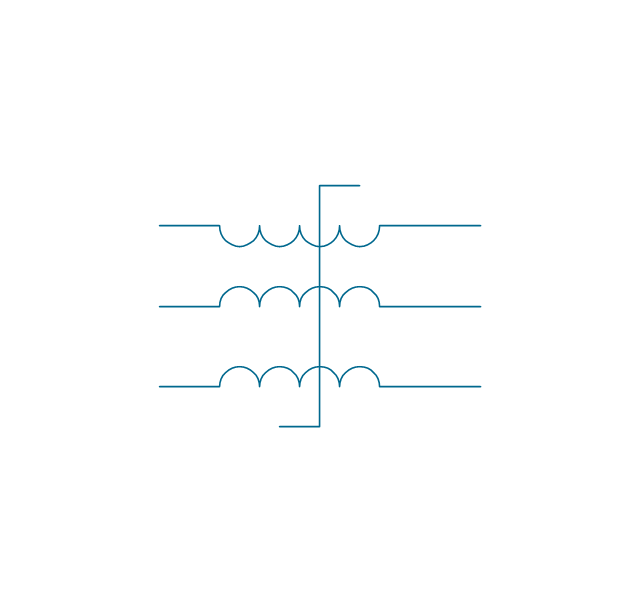
When drawing Electrical Schematics, Electrical Circuit Diagrams, Power Systems Diagrams, Circuit and Wiring Diagrams, Digital and Analog Logic Schemes, you will obligatory need the electrical symbols and pictograms to represent various electrical and electronic devices, such as resistors, wires, transistors, inductors, batteries, switches, lamps, readouts, amplifiers, repeaters, relays, transmission paths, semiconductors, generators, and many more. Today these symbols are internationally standardized, so the diagrams designed using them are recognizable and comprehensible by specialists from different countries. Electrical Engineering Solution included to ConceptDraw Solution Park provides 26 libraries with 926 commonly used electrical schematic and electrical engineering symbols making the reality the easy drawing of Electrical diagrams, schematics and blueprints. Now you need only a few minutes to create great-looking Electrical diagram, simply choose required electrical design elements from the libraries, drag them on the needed places at the document and connect in a suitable way.The vector stencils library "Transformers and windings" contains 29 element symbols of transformers, windings, couplers, metering devices, transductors, magnetic cores, chokes, and a variometer.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Electrical Symbols — Qualifying
A qualifying symbol is graphics or text added to the basic outline of a device’s logic symbol to describe the physical or logical characteristics of the device. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.The vector stencils library "Transformers and windings" contains 29 element symbols of transformers, windings, couplers, metering devices, transductors, magnetic cores, chokes, and a variometer.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
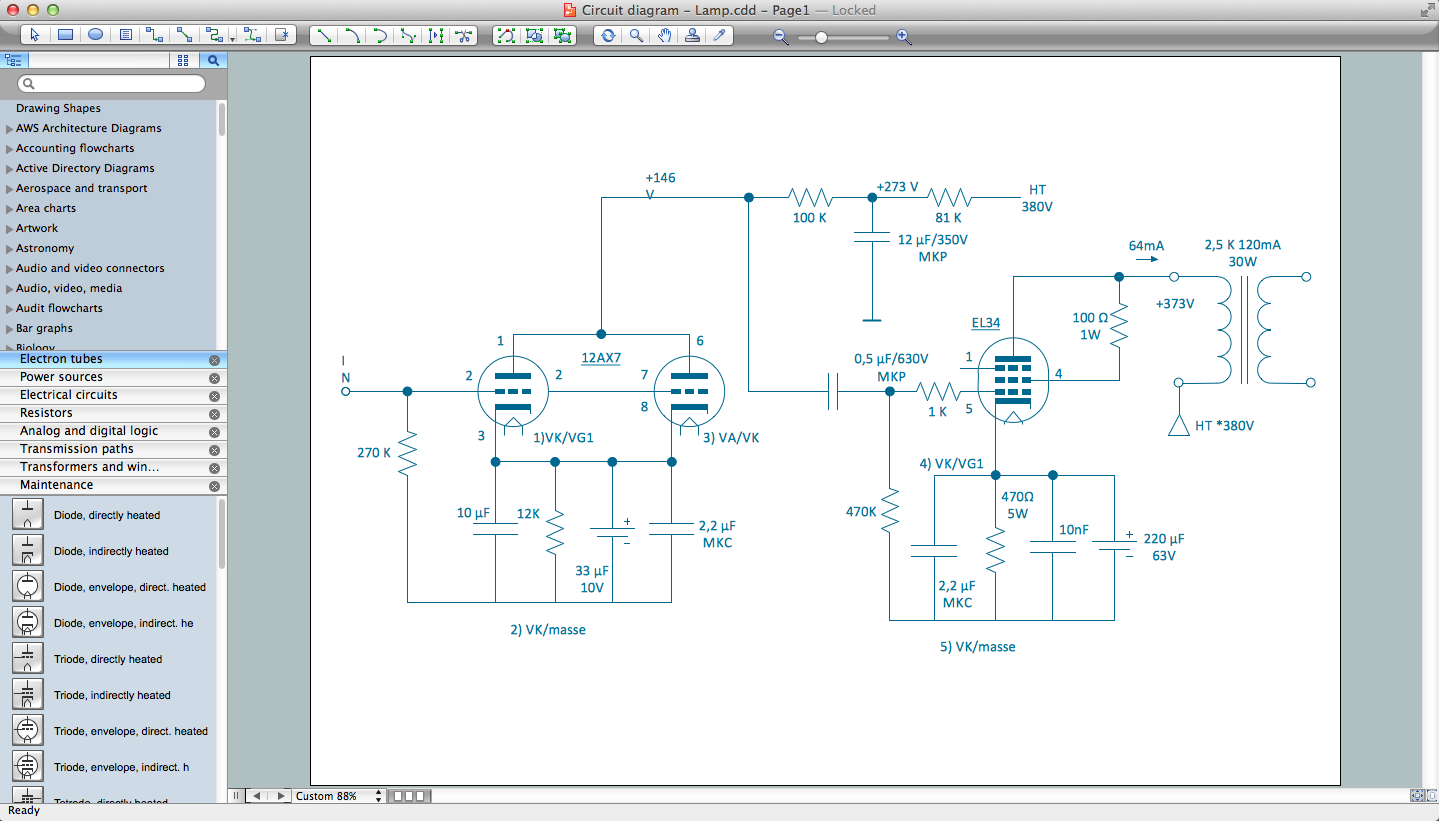
Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols
Any electrical device could not be created without electrical diagram, wiring also cannot be laid without pre-designed and approved scheme or plan. Electrical drawing is a type of technical drawing that depicts scheme of some electrical device and includes the information about power, lighting, etc. Electrical plan designed for architectural or engineering project visually displays location of electrical devices and connections. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is ideal electrical software for construction professional-looking Electrical Circuits, Electrical Schematics, Electrical Layouts, Electrical Wiring, Automotive Wiring, Cabling Layout Diagrams, Circuits and Logic Schematics, Logic Gate Diagrams, Digital Circuits, Parallel Circuits, Blue Prints with help of 926 standard electrical symbols offered by 26 libraries of Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area for ConceptDraw DIAGRAM. It makes drawing Electrical diagrams very easy even for beginners, and also extends your work with various export methods.Electrical Symbols — Transmission Paths
Variable delay elements are often used to manipulate the rising or falling edges of the clock or any other signal in integrated circuits. Delay elements are also used in delay locked loops and in defining a time reference for the movement of data within those systems. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.The vector stencils library "VHF UHF SHF" contains 52 symbols for VHF, UHF, and SHF circuit design, including capacitance measurers, nonreciprocal devices, modulators, phase shifters, field polarization devices, and filters.
"Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU-designated range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, with corresponding wavelengths of one to ten meters. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).
Common uses for VHF are FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, land mobile stations (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometres with radio modems, amateur radio, and marine communications. Air traffic control communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR, DME & ILS) work at distances of 100 kilometres or more to aircraft at cruising altitude.
VHF was previously used for analog television stations in the US." [Very high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Ultra-high frequency (UHF) designates the ITU radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz (3,000 MHz), also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres; that is 1 decimetre to 1 metre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is high enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting (digital and analogue), cordless phones, walkie-talkies, satellite communication, and numerous other applications.
The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IEEE radar band overlap the ITU UHF band: the L band between 1 and 2 GHz and the S band between 2 and 4 GHz." [Ultra high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Super high frequency (or SHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3 GHz and 30 GHz. This band of frequencies is also known as the centimetre band or centimetre wave as the wavelengths range from ten to one centimetres. These frequencies fall within the microwave band, so radio waves with these frequencies are called microwaves. The small wavelength of microwaves allows them to be directed in narrow beams by aperture antennas such as parabolic dishes, so they are used for point-to-point communication and data links, and for radar. This frequency range is used for most radar transmitters, microwave ovens, wireless LANs, cell phones, satellite communication, microwave radio relay links, and numerous short range terrestrial data links. The commencing wireless USB technology will be using approximately 1/ 3 of this spectrum.
Frequencies in the SHF range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations." [Super high frequency. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - VHF UHF SHF" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU-designated range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, with corresponding wavelengths of one to ten meters. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).
Common uses for VHF are FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, land mobile stations (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometres with radio modems, amateur radio, and marine communications. Air traffic control communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR, DME & ILS) work at distances of 100 kilometres or more to aircraft at cruising altitude.
VHF was previously used for analog television stations in the US." [Very high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Ultra-high frequency (UHF) designates the ITU radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz (3,000 MHz), also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres; that is 1 decimetre to 1 metre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is high enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting (digital and analogue), cordless phones, walkie-talkies, satellite communication, and numerous other applications.
The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IEEE radar band overlap the ITU UHF band: the L band between 1 and 2 GHz and the S band between 2 and 4 GHz." [Ultra high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Super high frequency (or SHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3 GHz and 30 GHz. This band of frequencies is also known as the centimetre band or centimetre wave as the wavelengths range from ten to one centimetres. These frequencies fall within the microwave band, so radio waves with these frequencies are called microwaves. The small wavelength of microwaves allows them to be directed in narrow beams by aperture antennas such as parabolic dishes, so they are used for point-to-point communication and data links, and for radar. This frequency range is used for most radar transmitters, microwave ovens, wireless LANs, cell phones, satellite communication, microwave radio relay links, and numerous short range terrestrial data links. The commencing wireless USB technology will be using approximately 1/ 3 of this spectrum.
Frequencies in the SHF range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations." [Super high frequency. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - VHF UHF SHF" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Total Quality Management Definition
The Total Quality Management Diagram solution helps you and your organization visualize business and industrial processes. Create Total Quality Management diagrams for business process with ConceptDraw software.- Symbol Of Bus Coupler
- Electrical Symbols , Electrical Diagram Symbols | Electrical Drawing ...
- Electrical Symbols , Electrical Diagram Symbols | 4 Port Coupler ...
- Design elements - VHF UHF SHF | Rf Directional Coupler Symbol
- Electrical Symbols — Transformers and Windings | Transformers ...
- Electrical Symbols , Electrical Diagram Symbols | Transformers and ...
- VHF UHF SHF - Vector stencils library | Electrical Symbols — VHF ...
- Electrical Symbols — Transformers and Windings | Electrical ...
- VHF UHF SHF - Vector stencils library | Waveguide Isolator Symbol
- Mechanical Drawing Symbols | Technical Drawing Software ...
- Symbols For Current And Voltage Transformer
- Electrical Symbols — Inductors | Process Flow Diagram Symbols ...
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Electrical ...
- Electrical Symbols , Electrical Diagram Symbols | Electrical Symbols ...
- Design elements - Transformers and windings | Electrical Symbols ...
- Cisco Optical. Cisco icons, shapes, stencils and symbols | Cisco ...
- Electrical Symbols — Inductors | Design elements - Transformers ...
- Electrical Symbols — Terminals and Connectors | Electrical Drawing ...
- Electrical Symbols — Power Sources | Design elements - Power ...
- Electrical Symbols — Power Sources | Functional Block Diagram ...