Export from ConceptDraw DIAGRAM Document to a Graphic File
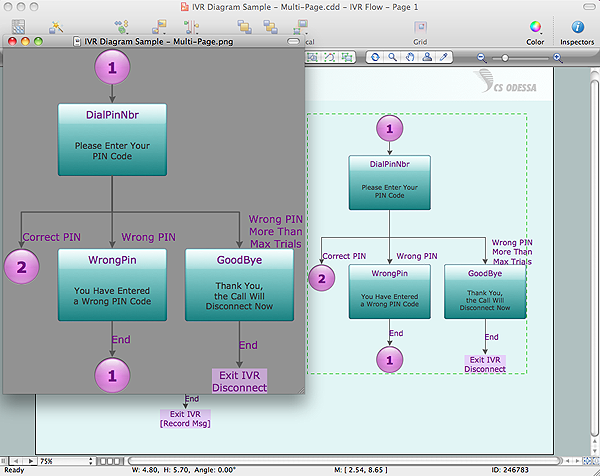
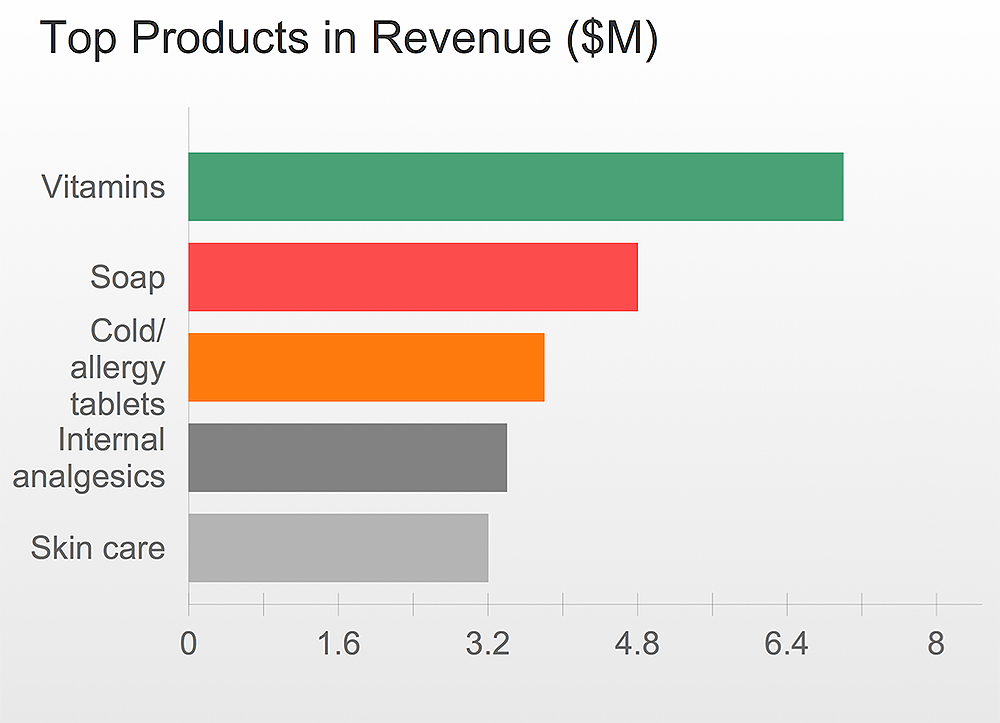
Now it’s easy to share your visual documents with other people in a form most convenient for them. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM can save your drawings and diagrams in a number of highly useful formats, including graphic files. You can save your drawing as a.PNG,.JPG, or other graphic format file.
HelpDesk
How to Save a Drawing as a Graphic File
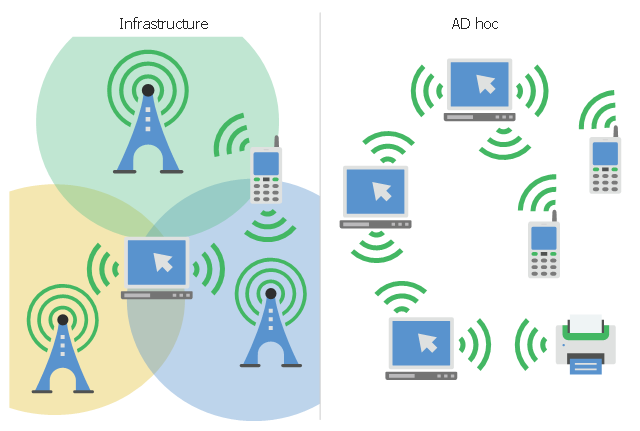
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM can save your drawings and diagrams in a number of highly useful formats, including graphic files. You can save your drawing as a.PNG,.JPG, or other graphic format file.This infographic sample visualizes the Conventional and wireless ad hoc network. It was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Běžná bezdrátová síť a ad hoc síť.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:B%C4%9B%C5%BEn%C3%A1_ bezdr%C3%A1tov%C3%A1_ s%C3%AD%C5%A5_ a_ ad_ hoc_ s%C3%AD%C5%A5.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 4.0/ deed.en]
"A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre existing infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points in managed (infrastructure) wireless networks. Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes, so the determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity. In addition to the classic routing, ad hoc networks can use flooding for forwarding data.
Wireless mobile ad hoc networks are self-configuring, dynamic networks in which nodes are free to move. Wireless networks lack the complexities of infrastructure setup and administration, enabling devices to create and join networks "on the fly" – anywhere, anytime." [Wireless ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The infographic example "Conventional and wireless ad hoc network" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computers and Communications solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:B%C4%9B%C5%BEn%C3%A1_ bezdr%C3%A1tov%C3%A1_ s%C3%AD%C5%A5_ a_ ad_ hoc_ s%C3%AD%C5%A5.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 4.0/ deed.en]
"A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre existing infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points in managed (infrastructure) wireless networks. Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes, so the determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity. In addition to the classic routing, ad hoc networks can use flooding for forwarding data.
Wireless mobile ad hoc networks are self-configuring, dynamic networks in which nodes are free to move. Wireless networks lack the complexities of infrastructure setup and administration, enabling devices to create and join networks "on the fly" – anywhere, anytime." [Wireless ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The infographic example "Conventional and wireless ad hoc network" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computers and Communications solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Pyramid Diagram
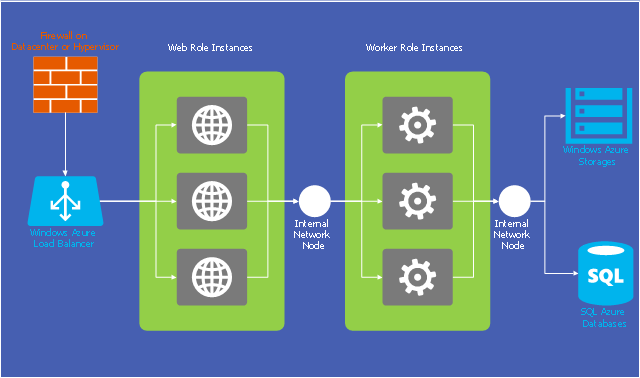
The representation of data in a hierarchical or pyramid-like form is one of the most effective and illustrative ways of structuring the data, information, ideas in different fields, among them marketing, management, business, finances, sales, consulting, media, and some others. Pyramid Diagram perfectly suits for this goal, especially if we talk about the representing some marketing strategies, information systems, social strategies. Pyramid Diagram looks like a triangle or reversed triangle that is divided visually on several layers. Each layer can be colored with its own color, this lets visually highlight important moments. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector graphics software extended with Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area provides powerful drawing tools, templates, samples, and built-in vector pyramid objects, thus all required tools for equally easy drawing Three level pyramid diagram, Four level pyramid model, Five level pyramid, etc., at this your Pyramid diagrams can have 2D or 3D view as you like.This example of cloud computing system architecture diagram was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Windows Azure Network and Computes Architecture.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Windows_ Azure_ Network_ and_ Computes_ Architecture.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 2.0/ ]
"Microsoft Azure (formerly Windows Azure before 25 March 2014) is a cloud computing platform and infrastructure, created by Microsoft, for building, deploying and managing applications and services through a global network of Microsoft-managed datacenters. It provides both PaaS and IaaS services and supports many different programming languages, tools and frameworks, including both Microsoft-specific and third-party software and systems." [Microsoft Azure. Wikipedia]
The diagram example "Microsoft Azure network and computes architecture" was created using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Azure Architecture solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 2.0/ ]
"Microsoft Azure (formerly Windows Azure before 25 March 2014) is a cloud computing platform and infrastructure, created by Microsoft, for building, deploying and managing applications and services through a global network of Microsoft-managed datacenters. It provides both PaaS and IaaS services and supports many different programming languages, tools and frameworks, including both Microsoft-specific and third-party software and systems." [Microsoft Azure. Wikipedia]
The diagram example "Microsoft Azure network and computes architecture" was created using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Azure Architecture solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
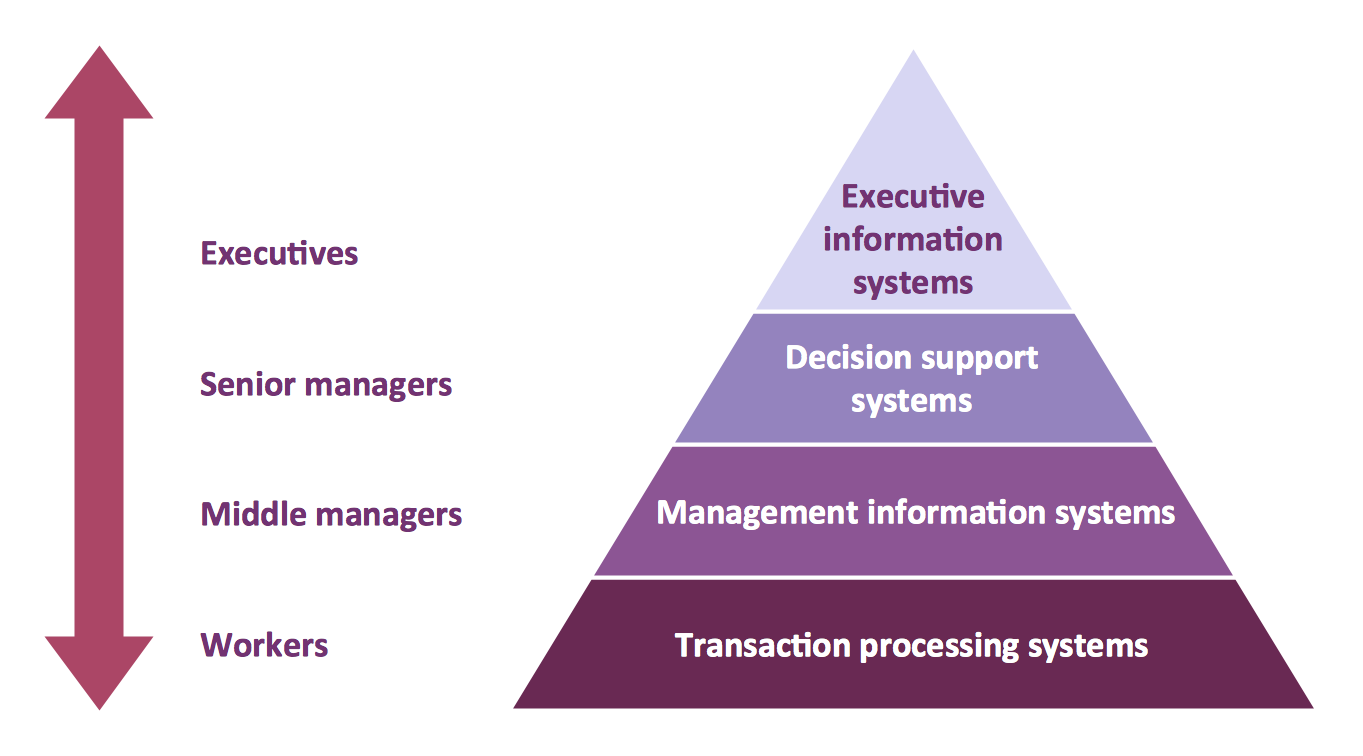
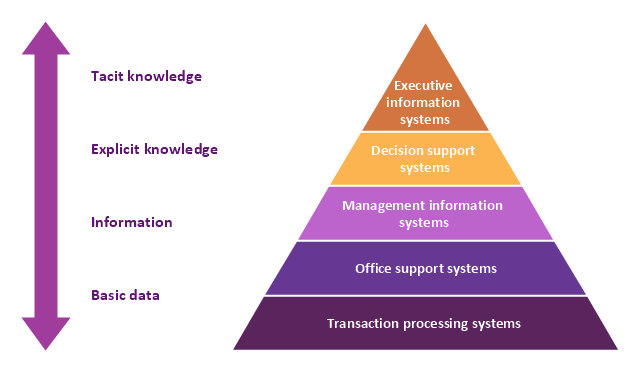
A five level pyramid model of different types of Information Systems based on the information processing requirement of different levels in the organization. The first level represents transaction processing systems to process basic data. The second level represents office support systems to process information in office. The third level represents management information systems to process information by managers. The fourth level represents decision support systems to process explicit knowledge. The fifth level represents executive information systems to process tacit knowledge.
"A Computer(-Based) Information System is essentially an IS using computer technology to carry out some or all of its planned tasks. The basic components of computer based information system are:
(1) Hardware - these are the devices like the monitor, processor, printer and keyboard, all of which work together to accept, process, show data and information.
(2) Software - are the programs that allow the hardware to process the data.
(3) Databases - are the gathering of associated files or tables containing related data.
(4) Networks - are a connecting system that allows diverse computers to distribute resources.
(5) Procedures - are the commands for combining the components above to process information and produce the preferred output.
The first four components (hardware, software, database and network) make up what is known as the information technology platform. Information technology workers could then use these components to create information systems that watch over safety measures, risk and the management of data. These actions are known as information technology services." [Information systems. Wikipedia]
This pyramid diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Five-Level-Pyramid-model.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Five-Level-Pyramid-model.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The triangle chart example "Information systems types" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A Computer(-Based) Information System is essentially an IS using computer technology to carry out some or all of its planned tasks. The basic components of computer based information system are:
(1) Hardware - these are the devices like the monitor, processor, printer and keyboard, all of which work together to accept, process, show data and information.
(2) Software - are the programs that allow the hardware to process the data.
(3) Databases - are the gathering of associated files or tables containing related data.
(4) Networks - are a connecting system that allows diverse computers to distribute resources.
(5) Procedures - are the commands for combining the components above to process information and produce the preferred output.
The first four components (hardware, software, database and network) make up what is known as the information technology platform. Information technology workers could then use these components to create information systems that watch over safety measures, risk and the management of data. These actions are known as information technology services." [Information systems. Wikipedia]
This pyramid diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Five-Level-Pyramid-model.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Five-Level-Pyramid-model.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The triangle chart example "Information systems types" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
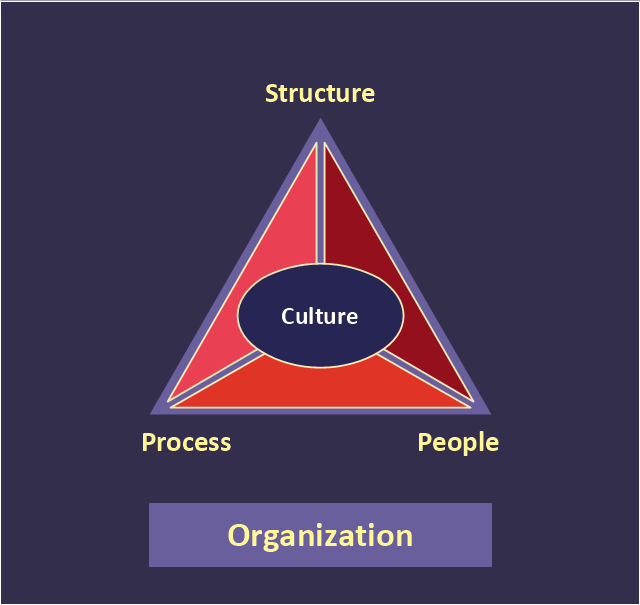
"At the base of the identity of an organisational is its organizational culture. A culture is comprised of the shared values, customs, traditions, rituals, behaviours and beliefs shared by a social group (national, ethnic, organizational, etc.). Cultures also share languages, or ways of speaking. From a communication perspective, cultures are made and remade through the words we use to describe our world. Culture represents a common set of values (“shared meanings”), shared by members of a population, a organization, a project/ programme purpose unit or a profession (e.g., engineers versus scientists). Culture change with the times but the speed at which the culture of different institutions change varies widely." [Development Cooperation Handbook/ The development aid organization/ Organizational Culture. Wikibooks]
This organizational culture triangle diagram example derived from Parker and Benson's model. It's for explaination of the Regatta: Adoption Method.
The pyramid diagram example "Organizational culture" was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Organization_ Triangle.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Organization_ Triangle.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.5 Generic license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 2.5/ deed.en]
The triangular chart sample "Organizational culture" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This organizational culture triangle diagram example derived from Parker and Benson's model. It's for explaination of the Regatta: Adoption Method.
The pyramid diagram example "Organizational culture" was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Organization_ Triangle.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Organization_ Triangle.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.5 Generic license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 2.5/ deed.en]
The triangular chart sample "Organizational culture" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
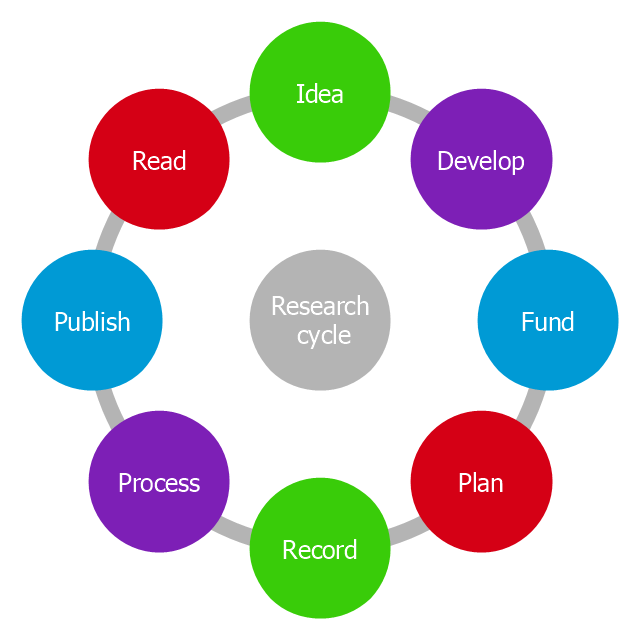
This circle diagram sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Research cycle.png. "Some of the basic elements of the scientific method, arranged in a cycle to emphasize that it is an iterative process." [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Research_ cycle.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 2.0/ deed.en]
"The scientific method is a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of reasoning. ...
Four essential elements of the scientific method are iterations, recursions, interleavings, or orderings of the following:
(1) Characterizations (observations, definitions, and measurements of the subject of inquiry).
(2) Hypotheses (theoretical, hypothetical explanations of observations and measurements of the subject).
(3) Predictions (reasoning including logical deduction from the hypothesis or theory).
(4) Experiments (tests of all of the above)...
A linearized, pragmatic scheme of the four points above is sometimes offered as a guideline for proceeding:
(1) Define a question.
(2) Gather information and resources (observe).
(3) Form an explanatory hypothesis.
(4) Test the hypothesis by performing an experiment and collecting data in a reproducible manner.
(5) Analyze the data.
(6) Interpret the data and draw conclusions that serve as a starting point for new hypothesis.
(7) Publish results.
(8) Retest (frequently done by other scientists).
The iterative cycle inherent in this step-by-step method goes from point 3 to 6 back to 3 again." [Scientific method. Wikipedia]
The circle diagram example "Research cycle" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 2.0/ deed.en]
"The scientific method is a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of reasoning. ...
Four essential elements of the scientific method are iterations, recursions, interleavings, or orderings of the following:
(1) Characterizations (observations, definitions, and measurements of the subject of inquiry).
(2) Hypotheses (theoretical, hypothetical explanations of observations and measurements of the subject).
(3) Predictions (reasoning including logical deduction from the hypothesis or theory).
(4) Experiments (tests of all of the above)...
A linearized, pragmatic scheme of the four points above is sometimes offered as a guideline for proceeding:
(1) Define a question.
(2) Gather information and resources (observe).
(3) Form an explanatory hypothesis.
(4) Test the hypothesis by performing an experiment and collecting data in a reproducible manner.
(5) Analyze the data.
(6) Interpret the data and draw conclusions that serve as a starting point for new hypothesis.
(7) Publish results.
(8) Retest (frequently done by other scientists).
The iterative cycle inherent in this step-by-step method goes from point 3 to 6 back to 3 again." [Scientific method. Wikipedia]
The circle diagram example "Research cycle" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
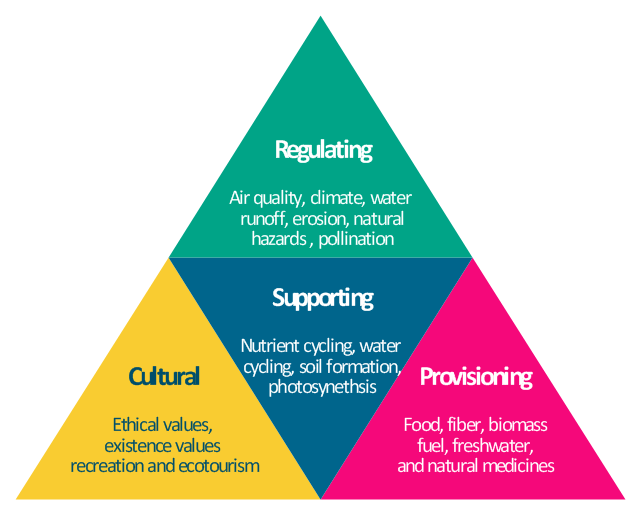
"Ecosystems represent sources of natural capital and provide goods and services to society, also called ecosystem services. The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment identified over 24 ecosystem services that can be divided up into 4 general groups including: 1) provisioning, 2) supporting, 3) regulating and 4) cultural." [User:Sawtoothgirl/ Sustainable Real Estate Development. Wikipedia]
"Humankind benefits in a multitude of ways from ecosystems. Collectively, these benefits are known as ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are regularly involved in the provisioning of clean drinking water and the decomposition of wastes. While scientists and environmentalists have discussed ecosystem services implicitly for decades, these the ecosystem services concept itself was popularized by the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) in the early 2000s. This grouped ecosystem services into four broad categories: provisioning, such as the production of food and water; regulating, such as the control of climate and disease; supporting, such as nutrient cycles and crop pollination; and cultural, such as spiritual and recreational benefits. To help inform decision-makers, many ecosystem services are being assigned economic values." [Ecosystem services. Wikipedia]
The segmented pyramid diagram example "Ecosystem goods and services" was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file ES_ triangle.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:ES_ triangle.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
This segmented pyramid diagram example "Ecosystem goods and services" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Humankind benefits in a multitude of ways from ecosystems. Collectively, these benefits are known as ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are regularly involved in the provisioning of clean drinking water and the decomposition of wastes. While scientists and environmentalists have discussed ecosystem services implicitly for decades, these the ecosystem services concept itself was popularized by the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) in the early 2000s. This grouped ecosystem services into four broad categories: provisioning, such as the production of food and water; regulating, such as the control of climate and disease; supporting, such as nutrient cycles and crop pollination; and cultural, such as spiritual and recreational benefits. To help inform decision-makers, many ecosystem services are being assigned economic values." [Ecosystem services. Wikipedia]
The segmented pyramid diagram example "Ecosystem goods and services" was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file ES_ triangle.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:ES_ triangle.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
This segmented pyramid diagram example "Ecosystem goods and services" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
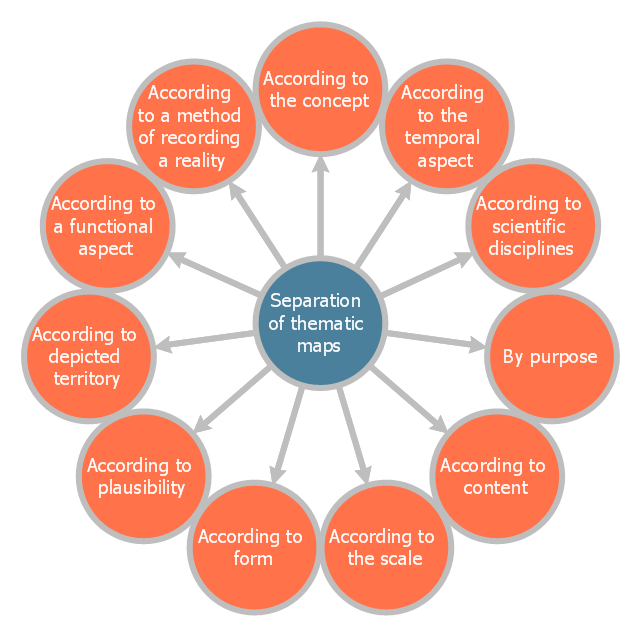
This circle-spoke diagram sample shows the basic division of thematic maps. It was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Dělení tematických map.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:D%C4%9Blen%C3%AD_ tematick%C3%BDch_ map.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 4.0/ deed.en]
"A thematic map is a map that focuses on a specific theme or subject area. This is in contrast to general reference maps, which regularly show the variety of phenomena — geological, geographical, political — together. The contrast between them lies in the fact that thematic maps use the base data, such as coastlines, boundaries and places, only as points of reference for the phenomenon being mapped. General maps portray the base data, such as landforms, lines of transportation, settlements, and political boundaries, for their own sake.
Thematic maps emphasize spatial variation of one or a small number of geographic distributions. These distributions may be physical phenomena such as climate or human characteristics such as population density and health issues." [Thematic map. Wikipedia]
The hub-and-spoke diagram example "Division of thematic maps" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Circle-Spoke Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:D%C4%9Blen%C3%AD_ tematick%C3%BDch_ map.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 4.0/ deed.en]
"A thematic map is a map that focuses on a specific theme or subject area. This is in contrast to general reference maps, which regularly show the variety of phenomena — geological, geographical, political — together. The contrast between them lies in the fact that thematic maps use the base data, such as coastlines, boundaries and places, only as points of reference for the phenomenon being mapped. General maps portray the base data, such as landforms, lines of transportation, settlements, and political boundaries, for their own sake.
Thematic maps emphasize spatial variation of one or a small number of geographic distributions. These distributions may be physical phenomena such as climate or human characteristics such as population density and health issues." [Thematic map. Wikipedia]
The hub-and-spoke diagram example "Division of thematic maps" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Circle-Spoke Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.