ConceptDraw Solution Park
ConceptDraw Solution Park
ConceptDraw Solution Park collects graphic extensions, examples and learning materials
 Physics
Physics
Physics solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils for drawing the physical illustrations, diagrams and charts.
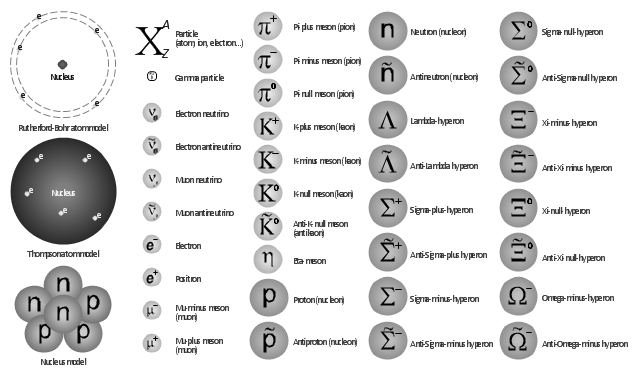
The vector shapes library "Nuclear physics" contains 39 symbol icons of elementary particles for drawing diagrams of nuclear reactions and experiments in nuclear physics.
"Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies the constituents and interactions of atomic nuclei. The most commonly known applications of nuclear physics are nuclear power generation and nuclear weapons technology, but the research has provided application in many fields, including those in nuclear medicine and magnetic resonance imaging, ion implantation in materials engineering, and radiocarbon dating in geology and archaeology.
The field of particle physics evolved out of nuclear physics and is typically taught in close association with nuclear physics." [Nuclear physics. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Nuclear physics" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-physics
"Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies the constituents and interactions of atomic nuclei. The most commonly known applications of nuclear physics are nuclear power generation and nuclear weapons technology, but the research has provided application in many fields, including those in nuclear medicine and magnetic resonance imaging, ion implantation in materials engineering, and radiocarbon dating in geology and archaeology.
The field of particle physics evolved out of nuclear physics and is typically taught in close association with nuclear physics." [Nuclear physics. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Nuclear physics" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-physics
"In physics, ray tracing is a method for calculating the path of waves or particles through a system with regions of varying propagation velocity, absorption characteristics, and reflecting surfaces. Under these circumstances, wavefronts may bend, change direction, or reflect off surfaces, complicating analysis. Ray tracing solves the problem by repeatedly advancing idealized narrow beams called rays through the medium by discrete amounts. Simple problems can be analyzed by propagating a few rays using simple mathematics. More detailed analyses can be performed by using a computer to propagate many rays.
When applied to problems of electromagnetic radiation, ray tracing often relies on approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray theory does not describe phenomena such as interference and diffraction, which require wave theory (involving the phase of the wave)." [Ray tracing (physics). Wikipedia]
The example "Ray tracing diagram for concave lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-physics
When applied to problems of electromagnetic radiation, ray tracing often relies on approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray theory does not describe phenomena such as interference and diffraction, which require wave theory (involving the phase of the wave)." [Ray tracing (physics). Wikipedia]
The example "Ray tracing diagram for concave lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-physics
- Business Diagram Software | Physics | Simple & Fast Diagram ...
- Business Diagram Software | Physics | ConceptDraw Arrows10 ...
- Physics | Education | Mathematical pendulum diagram |
- Ray tracing diagram for convex lens | Universal Diagramming Area ...
- Physics | Universal Diagramming Area | Mathematical pendulum ...
- Physics | Education | Scientific Symbols Chart | - Conceptdraw.com
- Physics | Mathematical pendulum diagram | - Conceptdraw.com
- Physics | Ray tracing diagram for convex lens |
- Physics | Ray tracing diagram for concave lens | Free-body diagram |
- Universal Diagramming Area | Mathematical pendulum diagram ...
- Physics | Biology | Language Learning |
- Physics | Scientific Symbols Chart |
- Physics | Design elements - Nuclear physics | Education |
- Physics | Language Learning | Astronomy |
- Chemistry | Mathematics | Physics |
- Biology | Chemistry | Business Diagram Software |
- Basic Circles Venn Diagram . Venn Diagram Example | ORM ...
- Using Fishbone Diagrams for Problem Solving | Education ...
- Sentence diagram sample | Sentence diagram - Compound ...
- Simple & Fast Diagram Software | Venn Diagram Examples for ...