The vector stencils library "Cisco products additional" contains 141 symbols of computer network devices and equipment for drawing Cisco network diagrams.
The symbols example "Cisco products additional - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-networks-cisco
The symbols example "Cisco products additional - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-networks-cisco
This computer security diagram example was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Firewall.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Firewall.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"In computing, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted, secure internal network and another outside network, such as the Internet, that is assumed to not be secure or trusted. Firewalls are often categorized as either network firewalls or host-based firewalls. Network firewalls are a software appliance running on general purpose hardware or hardware-based firewall computer appliances that filter traffic between two or more networks. Host-based firewalls provide a layer of software on one host that controls network traffic in and out of that single machine. Firewall appliances may also offer other functionality to the internal network they protect such as acting as a DHCP or VPN server for that network." [Firewall (computing). Wikipedia]
The cybersecurity diagram example "Firewall between LAN and WAN" was created using the ConceprDraw PRO software extended with the Network Security Diagrams solution from the Computer and Neworks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Firewall.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"In computing, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted, secure internal network and another outside network, such as the Internet, that is assumed to not be secure or trusted. Firewalls are often categorized as either network firewalls or host-based firewalls. Network firewalls are a software appliance running on general purpose hardware or hardware-based firewall computer appliances that filter traffic between two or more networks. Host-based firewalls provide a layer of software on one host that controls network traffic in and out of that single machine. Firewall appliances may also offer other functionality to the internal network they protect such as acting as a DHCP or VPN server for that network." [Firewall (computing). Wikipedia]
The cybersecurity diagram example "Firewall between LAN and WAN" was created using the ConceprDraw PRO software extended with the Network Security Diagrams solution from the Computer and Neworks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Computer peripheral devices" contains 18 clipart images of computer peripheral devices and equipment for drawing network diagrams.
"A peripheral is a device that is connected to a host computer, but not an integral part of it. It expands the host's capabilities but does not form part of the core computer architecture. It is often, but not always, partially or completely dependent on the host.
There are three different types of peripherals:
(1) Input, used to interact with, or send data to the computer (mouse, keyboards, etc.).
(2) Output, which provides output to the user from the computer (monitors, printers, etc.).
(3) Storage, which stores data processed by the computer (hard drives, flash drives, etc.)" [Peripheral. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Computer peripheral devices - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A peripheral is a device that is connected to a host computer, but not an integral part of it. It expands the host's capabilities but does not form part of the core computer architecture. It is often, but not always, partially or completely dependent on the host.
There are three different types of peripherals:
(1) Input, used to interact with, or send data to the computer (mouse, keyboards, etc.).
(2) Output, which provides output to the user from the computer (monitors, printers, etc.).
(3) Storage, which stores data processed by the computer (hard drives, flash drives, etc.)" [Peripheral. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Computer peripheral devices - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Logical symbols" contains 49 logical symbols for drawing logical network topology diagrams.
"Logical topology, or signal topology, is the arrangement of devices on a computer network and how they communicate with one another. How devices are connected to the network through the actual cables that transmit data, or the physical structure of the network, is called the physical topology. Physical topology defines how the systems are physically connected. It represents the physical layout of the devices on the network. The logical topology defines how the systems communicate across the physical topologies.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and describe how data is moved across the network. ... EXAMPLE : twisted pair Ethernet is a logical bus topology in a physical star topology layout. While IBM's token ring is a logical ring topology, it is physically set up in star topology." [Logical topology. Wikipedia]
The icons example "Logical symbols - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-and-networks
"Logical topology, or signal topology, is the arrangement of devices on a computer network and how they communicate with one another. How devices are connected to the network through the actual cables that transmit data, or the physical structure of the network, is called the physical topology. Physical topology defines how the systems are physically connected. It represents the physical layout of the devices on the network. The logical topology defines how the systems communicate across the physical topologies.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and describe how data is moved across the network. ... EXAMPLE : twisted pair Ethernet is a logical bus topology in a physical star topology layout. While IBM's token ring is a logical ring topology, it is physically set up in star topology." [Logical topology. Wikipedia]
The icons example "Logical symbols - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-and-networks
"A subnetwork, or subnet, is a logically visible subdivision of an IP network. The practice of dividing a network into two or more networks is called subnetting.
All computers that belong to a subnet are addressed with a common, identical, most-significant bit-group in their IP address. This results in the logical division of an IP address into two fields, a network or routing prefix and the rest field or host identifier. The rest field is an identifier for a specific host or network interface.
The routing prefix is expressed in CIDR notation. It is written as the first address of a network, followed by a slash character (/ ), and ending with the bit-length of the prefix. ...
The IPv6 address specification 2001:db8::/ 32 is a large address block with 296 addresses, having a 32-bit routing prefix. In IPv4 the routing prefix is also specified in the form of the subnet mask, which is expressed in quad-dotted decimal representation like an address. ...
Traffic between subnetworks is exchanged or routed with special gateways called routers which constitute the logical or physical boundaries between the subnets.
The benefits of subnetting vary with each deployment scenario. In the address allocation architecture of the Internet using Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and in large organizations, it is necessary to allocate address space efficiently. It may also enhance routing efficiency, or have advantages in network management when subnetworks are administratively controlled by different entities in a larger organization. Subnets may be arranged logically in a hierarchical architecture, partitioning an organization's network address space into a tree-like routing structure." [Subnetwork. Wikipedia]
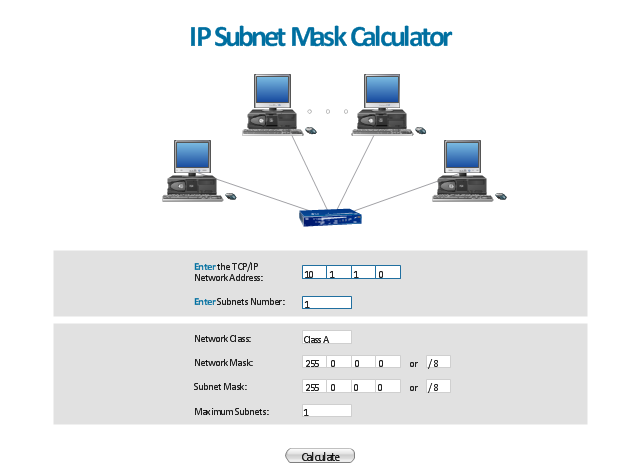
The template "IP Subnet mask calculator" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
All computers that belong to a subnet are addressed with a common, identical, most-significant bit-group in their IP address. This results in the logical division of an IP address into two fields, a network or routing prefix and the rest field or host identifier. The rest field is an identifier for a specific host or network interface.
The routing prefix is expressed in CIDR notation. It is written as the first address of a network, followed by a slash character (/ ), and ending with the bit-length of the prefix. ...
The IPv6 address specification 2001:db8::/ 32 is a large address block with 296 addresses, having a 32-bit routing prefix. In IPv4 the routing prefix is also specified in the form of the subnet mask, which is expressed in quad-dotted decimal representation like an address. ...
Traffic between subnetworks is exchanged or routed with special gateways called routers which constitute the logical or physical boundaries between the subnets.
The benefits of subnetting vary with each deployment scenario. In the address allocation architecture of the Internet using Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and in large organizations, it is necessary to allocate address space efficiently. It may also enhance routing efficiency, or have advantages in network management when subnetworks are administratively controlled by different entities in a larger organization. Subnets may be arranged logically in a hierarchical architecture, partitioning an organization's network address space into a tree-like routing structure." [Subnetwork. Wikipedia]
The template "IP Subnet mask calculator" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The ski jumping competition of the Vancouver 2010 Olympics was held at Whistler Olympic Park between 12 and 22 February 2010. ...
For the three events, there are a maximum 70 athletes allowed to compete. No nation can have more than five skiers. For each event, a nation can enter four skiers in individual event or one team in the team event.
Host nation Canada is expected to enter skiers in all events. If no skier meets the qualification standards, they can enter one skier per event.
Quota allocation per nation is based on the World Ranking List (WRL) consisting of Ski Jumping World Cup and Grand Prix points, followed by Continental Cup Standings from the 2008-09 and 2009-10 Ski Jumping World Cup. This will be made by assigning one quota slot per skier from the top of the standings downwards until the maximum five slots have been reached, including host nation Canada." [Ski jumping at the 2010 Winter Olympics. Wikipedia]
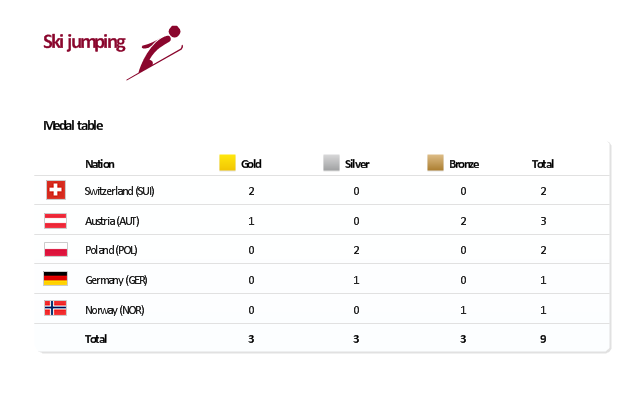
This medal table example "Ski jumping at the 2010 Winter Olympics" is created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Winter Sports solution.
The Winter Sports solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park contains the vector stencils library "Winter sports pictograms" and examples of diagrams and infographics.
For the three events, there are a maximum 70 athletes allowed to compete. No nation can have more than five skiers. For each event, a nation can enter four skiers in individual event or one team in the team event.
Host nation Canada is expected to enter skiers in all events. If no skier meets the qualification standards, they can enter one skier per event.
Quota allocation per nation is based on the World Ranking List (WRL) consisting of Ski Jumping World Cup and Grand Prix points, followed by Continental Cup Standings from the 2008-09 and 2009-10 Ski Jumping World Cup. This will be made by assigning one quota slot per skier from the top of the standings downwards until the maximum five slots have been reached, including host nation Canada." [Ski jumping at the 2010 Winter Olympics. Wikipedia]
This medal table example "Ski jumping at the 2010 Winter Olympics" is created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Winter Sports solution.
The Winter Sports solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park contains the vector stencils library "Winter sports pictograms" and examples of diagrams and infographics.
- Server Host Workstations Diagram
- Host Computer And Workstation Diagram
- Communication network diagram | Host Router And Hub In Diagram
- Host In Computer Network
- Workstation And Host Computers On A Network
- Bus Topology Host Computer
- VS C3000 or SC2200 host
- Describe Nodes Host And Workstation In One Diagram
- Host Computer Connect Switch Connect Router Connect Network
- Host Computer And Workstations Differences In With Diagram
- Azure Architecture | Redis Cluster On Remote Host Architecture
- How To Represent Host System In Uml Diagram
- Write About Host Computer And The Work Station Illustrate With
- Computer peripheral devices - Vector stencils library | Computer ...
- Illustrate Host Computer And Work Station With Full Diagram
- Host Icon
- Design elements - Bank UML deployment diagram | AWS ...
- Host Computer With Diagram
- Diagrame Of Workstation Computers




-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)






-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)

-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
















-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)


-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)



-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)















-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)


-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)















-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)



-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)


-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)




-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-cisco-products-additional---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
























-logical-symbols---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)