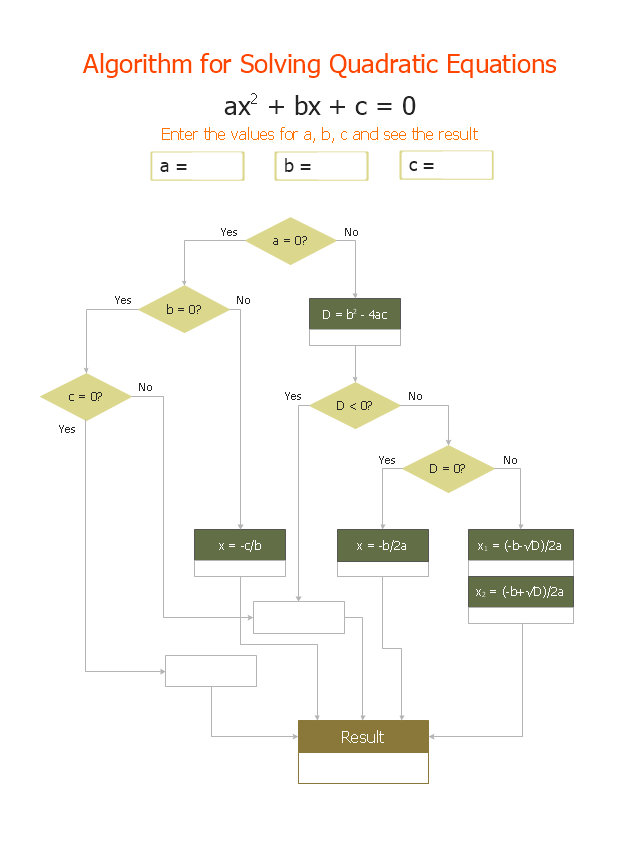
"In elementary algebra, a quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for "square") is any equation having the form
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In mathematics, the Euclidean algorithm, or Euclid's algorithm, is a method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two (usually positive) integers, also known as the greatest common factor (GCF) or highest common factor (HCF). ...
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
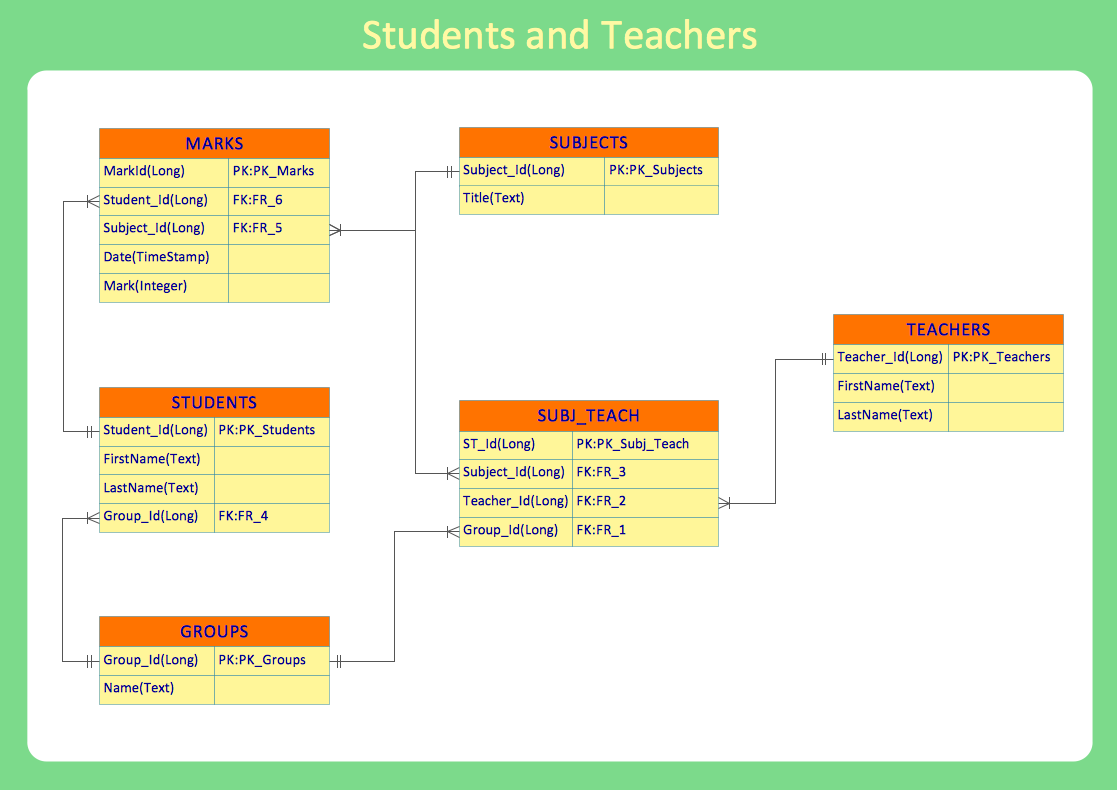
Software development with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM
Modern software development requires creation of large amount of graphic documentation, these are the diagrams describing the work of applications in various notations and cuts, also GUI design and documentation on project management. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM technical and business graphics application possesses powerful tools for software development and designing technical documentation for object-oriented projects. Solutions included to the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park provide the specialists with possibility easily and quickly create graphic documentation. They deliver effective help in drawing thanks to the included package of templates, samples, examples, and libraries with numerous ready-to-use vector objects that allow easily design class hierarchies, object hierarchies, visual object-oriented designs, flowcharts, GUI designs, database designs, visualize the data with use of the most popular notations, including the UML and Booch notations, easy manage the development projects, automate projection and development.HelpDesk
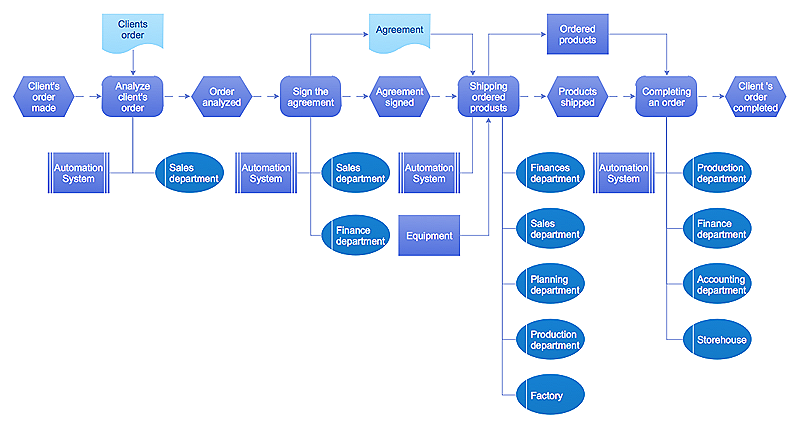
Event-driven Process Chain (EPC) Diagram Software
An EPC diagram is a type of flowchart used in business process analysis. It shows different business processes through various work flows. The workflows are shown as processes and events that are related to different executes and tasks that allow business workflow to be completed. An EPC diagram shows different business processes through various workflows. The workflows are seen as functions and events that are connected by different teams or people, as well as tasks that allow business processes to be executed. The best thing about this type of enterprise modelling is that creating an EPC diagram is quick and simple as long as you have the proper tool. One of the main usages of the EPC diagrams is in the modelling, analyzing and re-engineering of business processes. With the use of the flowchart, businesses are able to see inefficiencies in the processes and modify to make them more productive. Event-driven process chain diagrams are also used to configure an enterprise resource pla"Value Stream Map (VSM)
1. A tool used to improve a process by identifying added value and eliminating waste.
2. A process map that follows the value creation process.
A. “strap yourself to the product (or service) and see where you go”
3. A process map with data added.
A. Times: processing, wait, cycle.
B. Quality: number of rejects.
C. Inventory.
D. Resources.
1) Number of people.
2) Space.
3) Distance traveled.
E. Whatever else is useful for analyzing the process." [ocw.mit.edu/ courses/ aeronautics-and-astronautics/ 16-660j-introduction-to-lean-six-sigma-methods-january-iap-2012/ lecture-notes/ MIT16_ 660JIAP12_ 1-6.pdf]
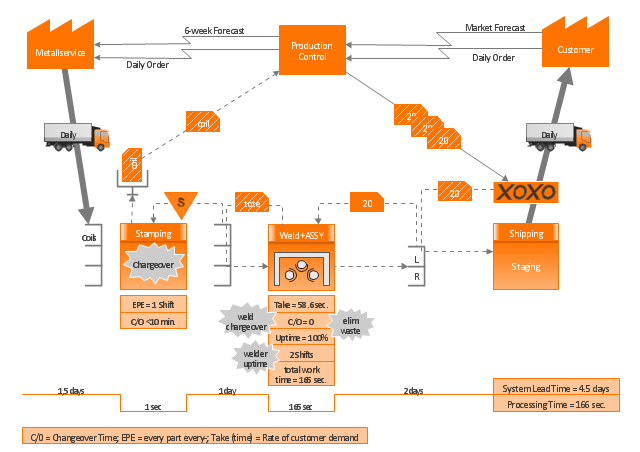
This sample VSM flowchart shows the value stream in a manufacturing, production control and shipping processes.
This value stream mapping diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Value Stream Mapping solution from the Quality area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
1. A tool used to improve a process by identifying added value and eliminating waste.
2. A process map that follows the value creation process.
A. “strap yourself to the product (or service) and see where you go”
3. A process map with data added.
A. Times: processing, wait, cycle.
B. Quality: number of rejects.
C. Inventory.
D. Resources.
1) Number of people.
2) Space.
3) Distance traveled.
E. Whatever else is useful for analyzing the process." [ocw.mit.edu/ courses/ aeronautics-and-astronautics/ 16-660j-introduction-to-lean-six-sigma-methods-january-iap-2012/ lecture-notes/ MIT16_ 660JIAP12_ 1-6.pdf]
This sample VSM flowchart shows the value stream in a manufacturing, production control and shipping processes.
This value stream mapping diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Value Stream Mapping solution from the Quality area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 PM Response
PM Response
The PM Response solution extends the functional abilities in project management for all three ConceptDraw products by helping to improve the response time to project changes, to plan on how to effectively respond on issues and events impacting the project. It supplies the project managers, team leaders, and all other project participants with wide abilities of iteration planning, creative collaboration, effective decision-making, discussions of the project layout approaches and solving the project challenges, lets them use mind mapping technique for iteration planning and applying the project changes, to represent the projects data as Mind Maps and use them to construct the clear plans, to convert project maps to project implementations, to use different kinds of Visual diagrams to solve the current project problems and to make correct decisions, to plan resources usage and to respond to changes in the project environment.
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Euclidean algorithm ...
- Flowchart C
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Solving quadratic equation ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Simple Flow Chart ...
- Algorithm Flowchart And C Programming For Selection Sort
- Algorithm flowchart - Selection sorting method | Flow Chart for ...
- Contact Management System In C Using Data Flow Diagram
- Types of Flowcharts | Types of Flowchart - Overview | Basic ...
- Flowchart C Question And Answer For Structure With Its Explanation
- A Diagram Of A Flow C
- Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart | Basic Flowchart ...
- C Programming Algorithms Flowcharts
- Euclidean Algorithm To Find Gcd In C With Flowchart
- Example Of Selection In C In Flowchart
- Algorithm Flow Chart Example
- Flowchart Calculation Method
- Invoice payment process - Flowchart | Accounting Flowchart ...
- Flowchart In C Programming
- Method Of Calculating Of Flow Chart
- Algorithm And Flowchart Examples In C