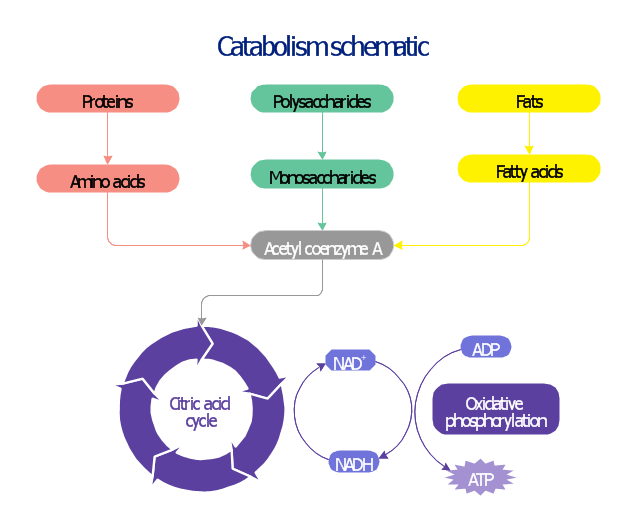
This biochemical chart display how proteins, polysaccharides and fats from food are digested into gastrointestinal tract into aminoacids, monosaccharides and fatty acids, and then broken down and oxidized to carbon dioxide and water in cellular processes of energy generation.
This metabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikipedia file: Catabolism schematic.svg. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Catabolism_ schematic.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Catabolism schematic" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
This metabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikipedia file: Catabolism schematic.svg. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Catabolism_ schematic.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Catabolism schematic" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
The vector stencils library " Biochemistry of metabolism" contains 46 metabolite symbols for drawing metabolic pathways maps, biochemical diagrams and metabolism process flow charts using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. ...
The metabolome forms a large network of metabolic reactions, where outputs from one enzymatic chemical reaction are inputs to other chemical reactions." [Metabolite. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Biochemistry of metabolism" is included in the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
"Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. ...
The metabolome forms a large network of metabolic reactions, where outputs from one enzymatic chemical reaction are inputs to other chemical reactions." [Metabolite. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Biochemistry of metabolism" is included in the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
- Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ) | Biochemical metabolic pathway map ...
- LLNL Flow Charts | Manufacturing and Maintenance | Citric acid ...
- Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ) | Biochemical metabolic pathway map ...
- Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ) | Biochemical metabolic pathway map ...
- Circular arrows diagram - Quality cycle | Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ...
- Biology | Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ) | - Conceptdraw.com
- Biology | ConceptDraw Solution Park | Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ) |
- Glycolysis overview diagram | Catabolism schematic | Glucose ...
- Drawing a Nature Scene | Nature | Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ) |
- Biology | ConceptDraw Solution Park | Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ) |
- Business Diagram Software | Physics | ConceptDraw Arrows10 ...
- Conventional energy resources | Resources and energy vector ...
- Drawing a Nature Scene | Drawing Illustration | Water Cycle |
- Drawing Illustration | Drawing a Nature Scene | Water Cycle |
- Physics | Language Learning | Astronomy |
- Water cycle diagram | Drawing a Nature Scene | Drawing Illustration |
- Physics | Biology | Language Learning |
- Metabolic pathway map - Biochemical diagram | Catabolism ...
- Business Diagram Software | Org chart - University | Business ...
- Biology | Glycolysis overview diagram | Biochemical metabolic ...