Basic Diagramming
Create flowcharts, organizational charts, bar charts, line graphs, and more with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM.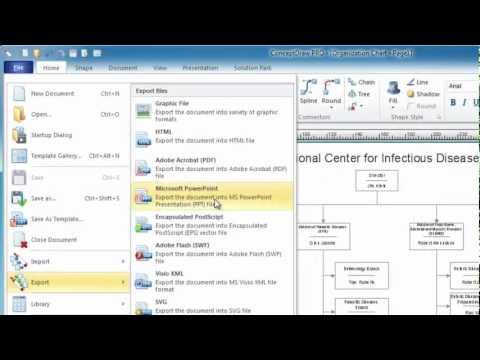
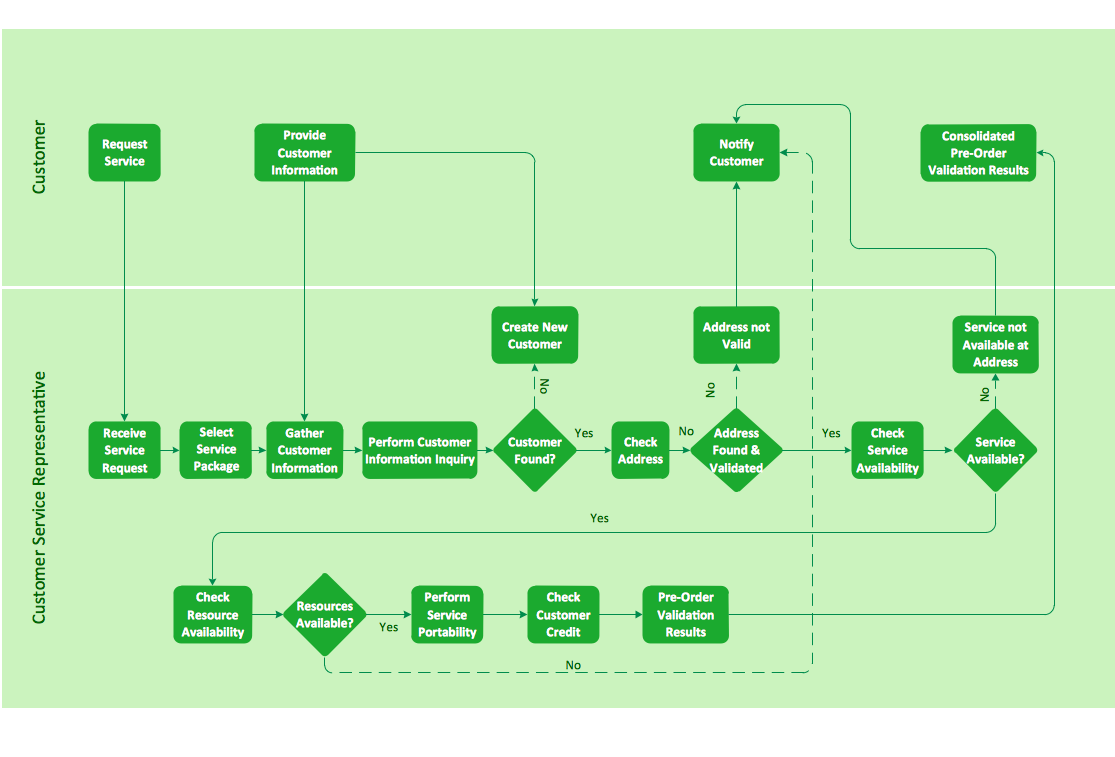
Workflow Diagram Symbols
Workflow Diagram is an acknowledged method of drawing the processes and business processes, which uses the concerted set of symbols for depicting different kinds of steps or relations. Often it is named the Process Flow Diagram, but the real Process Flow Diagram uses different visual notations and different flowchart symbols. The professionally designed Workflow diagram also may be used for the same purpose as a Critical process flow diagram. Nevertheless, there are many cases when you may need to make your Workflow Diagram more bright and graphic. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming software extended with Workflow Diagrams solution from Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park possesses the powerful properties of software for Workflow diagram design. It delivers rich set of business process workflow diagram symbols, which help users to accurately diagram the workflow scenarios and to design great-looking and attractive Workflow Diagrams and Process Flow Diagrams better-suited for presentations, websites, reports, and other documents.Cross-functional flowchart landscape, U.S. units
In Cross-Functional Flowchart first step is to determine how many lanes you want to represent and what the lane titles will be. The choice of vertical or horizontal swim lanes landscape comes down to personal choice or just plain “what fits best”. With ConceptDraw, we make that simple by including different swim lanes templates. Professional looking examples and templates of Swimlane Flowchart which help you create Cross Functional Flowcharts rapidly.This wheel diagram sample was created on the base of figure illustrating the webpage "Chapter 3: Current State of the Ecosystem" of the website of the National Broadband Plan of US Federal Communications Comission (FCC). "The broadband ecosystem includes applications and content: e-mail, search, news, maps, sales and marketing applications used by businesses, user-generated video and hundreds of thousands of more specialized uses. Ultimately, the value of broadband is realized when it delivers useful applications and content to end-users.
Applications run on devices that attach to the network and allow users to communicate: computers, smartphones, set-top boxes, e-book readers, sensors, private branch exchanges (PBX), local area network routers, modems and an ever-growing list of other devices. New devices mean new opportunities for applications and content.
Finally, broadband networks can take multiple forms: wired or wireless, fixed or mobile, terrestrial or satellite. Different types of networks have different capabilities, benefits and costs.
The value of being connected to the network increases as more people and businesses choose to adopt broadband and use applications and devices that the network supports. Several factors contribute to their decisions. These include whether they can afford a connection, whether they are comfortable with digital technology and whether they believe broadband is useful.
Networks, devices and applications drive each other in a virtuous cycle. If networks are fast, reliable and widely available, companies produce more powerful, more capable devices to connect to those networks. These devices, in turn, encourage innovators and entrepreneurs to develop exciting applications and content. These new applications draw interest among end-users, bring new users online and increase use among those who already subscribe to broadband services. This growth in the broadband ecosystem reinforces the cycle, encouraging service providers to boost the speed, functionality and reach of their networks."
[broadband.gov/ plan/ 3-current-state-of-the-ecosystem/ ]
The circle pie chart example "Forces shaping the broadband ecosystem in the US" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
Applications run on devices that attach to the network and allow users to communicate: computers, smartphones, set-top boxes, e-book readers, sensors, private branch exchanges (PBX), local area network routers, modems and an ever-growing list of other devices. New devices mean new opportunities for applications and content.
Finally, broadband networks can take multiple forms: wired or wireless, fixed or mobile, terrestrial or satellite. Different types of networks have different capabilities, benefits and costs.
The value of being connected to the network increases as more people and businesses choose to adopt broadband and use applications and devices that the network supports. Several factors contribute to their decisions. These include whether they can afford a connection, whether they are comfortable with digital technology and whether they believe broadband is useful.
Networks, devices and applications drive each other in a virtuous cycle. If networks are fast, reliable and widely available, companies produce more powerful, more capable devices to connect to those networks. These devices, in turn, encourage innovators and entrepreneurs to develop exciting applications and content. These new applications draw interest among end-users, bring new users online and increase use among those who already subscribe to broadband services. This growth in the broadband ecosystem reinforces the cycle, encouraging service providers to boost the speed, functionality and reach of their networks."
[broadband.gov/ plan/ 3-current-state-of-the-ecosystem/ ]
The circle pie chart example "Forces shaping the broadband ecosystem in the US" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
HelpDesk
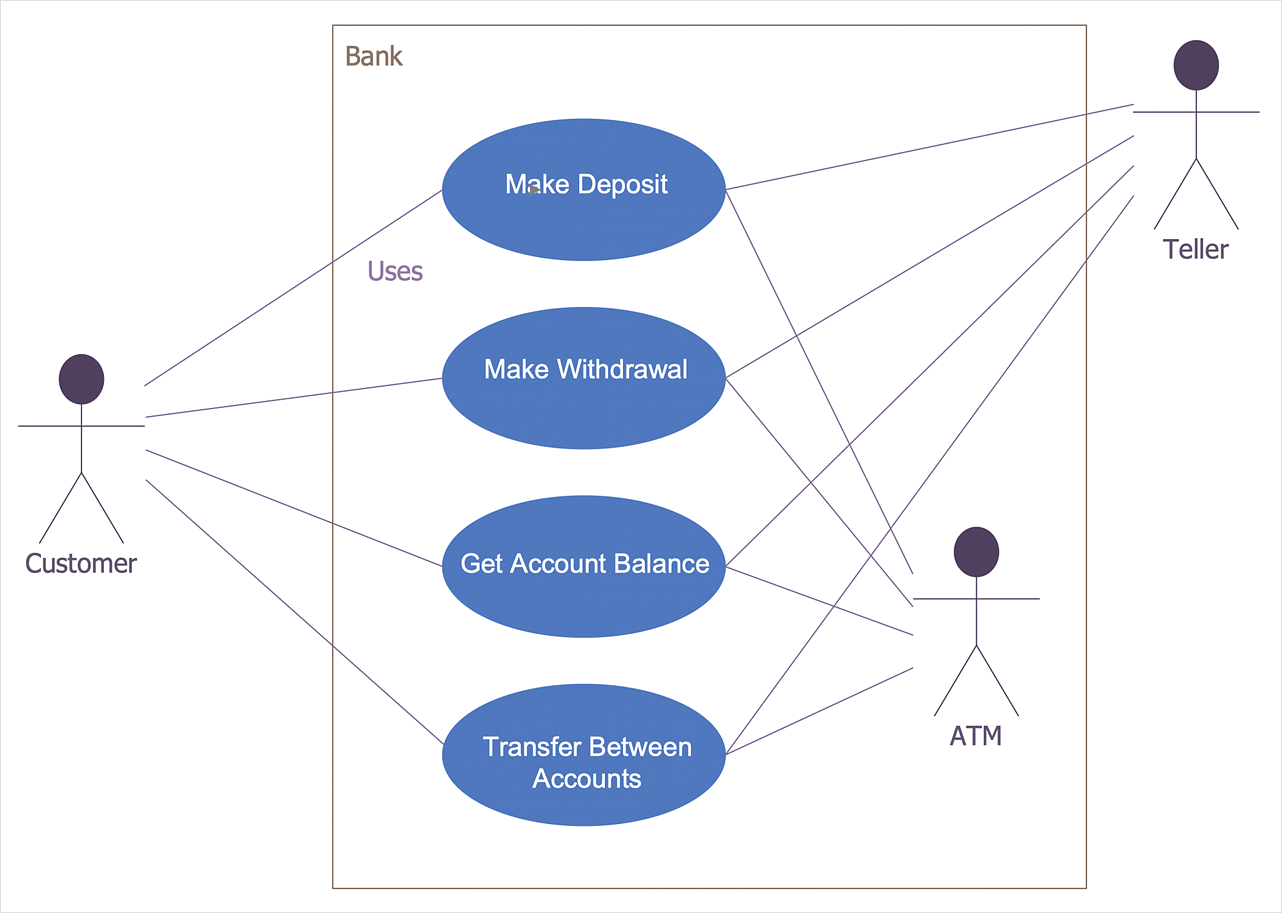
How to Create a Bank ATM Use Case Diagram
UML diagrams are often used in banking management for documenting a banking system. In particular, the interaction of bank customers with an automated teller machine (ATM) can be represented in a Use Case diagram. Before the software code for an ATM, or any other system design, is written, it is necessary to create a visual representation of any object-oriented processes. This is done most effectively by creating a Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram, using object-oriented modeling. UML works as a general purpose modeling language for software engineers or system analysts, offering a number of different diagram styles with which to visually depict all aspects of a software system. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming software, enhanced and expanded with the ATM UML Diagrams solution, offers the full range of icons, templates and design elements needed to faithfully represent ATM and banking information system architecture using UML standards. The ATM UML Diagrams solution is useful for beginner and advanced users alike. More experienced users will appreciate a full range of vector stencil libraries and ConceptDraw DIAGRAM 's powerful software, that allows you to create your ATM UML diagram in a matter of moments.
 IDEF Business Process Diagrams
IDEF Business Process Diagrams
Use the IDEF Business Process Diagrams solution to create effective database designs and object-oriented designs, following the integration definition methodology.
This wheel diagram sample was created on the base of figure illustrating the webpage "Chapter 3: Current State of the Ecosystem" of the website of the National Broadband Plan of US Federal Communications Comission (FCC). "The broadband ecosystem includes applications and content: e-mail, search, news, maps, sales and marketing applications used by businesses, user-generated video and hundreds of thousands of more specialized uses. Ultimately, the value of broadband is realized when it delivers useful applications and content to end-users.
Applications run on devices that attach to the network and allow users to communicate: computers, smartphones, set-top boxes, e-book readers, sensors, private branch exchanges (PBX), local area network routers, modems and an ever-growing list of other devices. New devices mean new opportunities for applications and content.
Finally, broadband networks can take multiple forms: wired or wireless, fixed or mobile, terrestrial or satellite. Different types of networks have different capabilities, benefits and costs.
The value of being connected to the network increases as more people and businesses choose to adopt broadband and use applications and devices that the network supports. Several factors contribute to their decisions. These include whether they can afford a connection, whether they are comfortable with digital technology and whether they believe broadband is useful.
Networks, devices and applications drive each other in a virtuous cycle. If networks are fast, reliable and widely available, companies produce more powerful, more capable devices to connect to those networks. These devices, in turn, encourage innovators and entrepreneurs to develop exciting applications and content. These new applications draw interest among end-users, bring new users online and increase use among those who already subscribe to broadband services. This growth in the broadband ecosystem reinforces the cycle, encouraging service providers to boost the speed, functionality and reach of their networks."
[broadband.gov/ plan/ 3-current-state-of-the-ecosystem/ ]
The circle pie chart example "Forces shaping the broadband ecosystem in the US" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
Applications run on devices that attach to the network and allow users to communicate: computers, smartphones, set-top boxes, e-book readers, sensors, private branch exchanges (PBX), local area network routers, modems and an ever-growing list of other devices. New devices mean new opportunities for applications and content.
Finally, broadband networks can take multiple forms: wired or wireless, fixed or mobile, terrestrial or satellite. Different types of networks have different capabilities, benefits and costs.
The value of being connected to the network increases as more people and businesses choose to adopt broadband and use applications and devices that the network supports. Several factors contribute to their decisions. These include whether they can afford a connection, whether they are comfortable with digital technology and whether they believe broadband is useful.
Networks, devices and applications drive each other in a virtuous cycle. If networks are fast, reliable and widely available, companies produce more powerful, more capable devices to connect to those networks. These devices, in turn, encourage innovators and entrepreneurs to develop exciting applications and content. These new applications draw interest among end-users, bring new users online and increase use among those who already subscribe to broadband services. This growth in the broadband ecosystem reinforces the cycle, encouraging service providers to boost the speed, functionality and reach of their networks."
[broadband.gov/ plan/ 3-current-state-of-the-ecosystem/ ]
The circle pie chart example "Forces shaping the broadband ecosystem in the US" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
Chart Software for Better Presentations
Easy charting software comes with beautiful chart templates and examples. This makes it easy to create professional charts without prior experience. Graphs and Charts Area provide a wide collection of professional looking predesigned templates, samples and ready-to-use vector stencils that will help you to draw the charts and diagrams of various types: Pie Charts, Donut Charts, Line Charts, Column Charts, Bar Charts, Pyramids, Scatter Charts, Venn Diagrams, Spider Charts, Area Charts, Divided Bar Graphs.ERD Symbols and Meanings
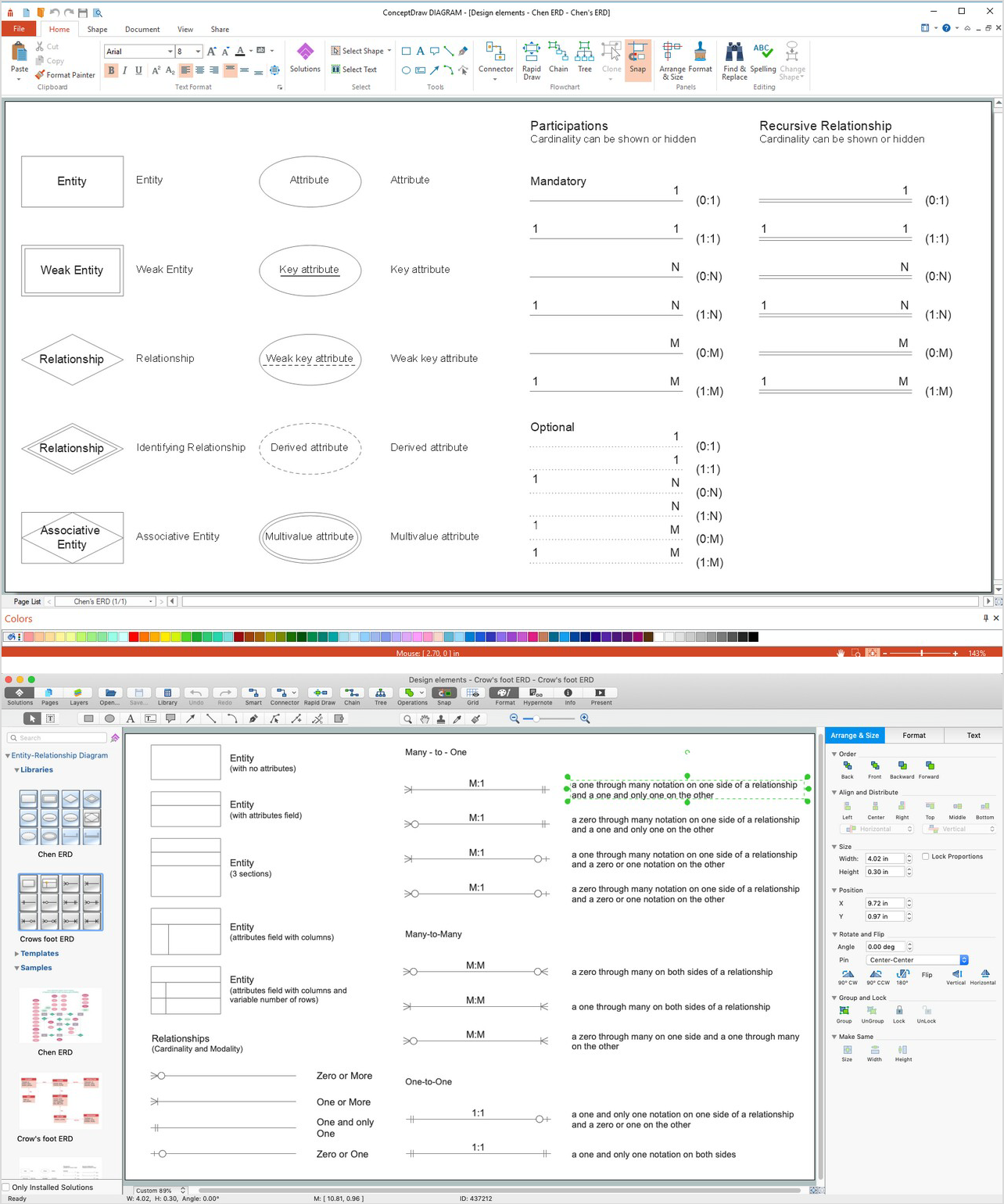
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) is a popular software engineering tool for database modeling and illustration the logical structure of databases, which uses one of two notations - Chen's or Crow’s Foot. Crow's foot notation is effective when used in software engineering, information engineering, structured systems analysis and design. Each of these notations applies its own set of ERD symbols. Crow's foot diagrams use boxes to represent entities and lines between these boxes to show relationships. Varied shapes at the ends of lines depict the cardinality of a given relationship. Chen's ERD notation is more detailed way to represent entities and relationships. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM application enhanced with all-inclusive Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) solution allows design professional ER diagrams with Chen's or Crow’s Foot notation on your choice. It contains the full set of ready-to-use standardized ERD symbols and meanings helpful for quickly drawing, collection of predesigned ERD samples, examples and templates. ConceptDraw Pro is a great alternative to Visio for Mac users as it offers more features and can easily handle the most demanding professional needs.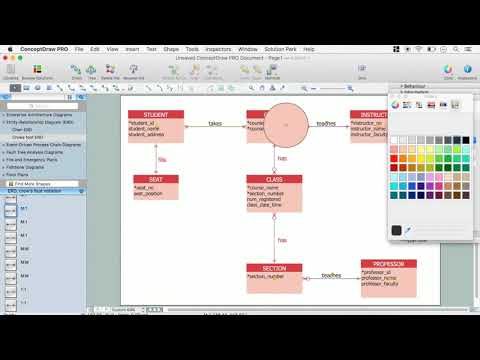
- Diagram Of The United States
- Energy Pyramid Diagram | Chart Examples | U.S. energy ...
- Cross-functional flowchart landscape, U.S. units | Service Industry ...
- Energy resources diagram | Pie Charts | U.S. energy consumption ...
- Show Us A Flow Diagram Of Biomass Energy
- Cross-functional flowchart landscape, U.S. units | ConceptDraw ...
- How Process Flow Diagram Help Us Design Interface
- Energy Pyramid Diagram | Energy resources diagram | U.S. energy ...
- Usa Diagram