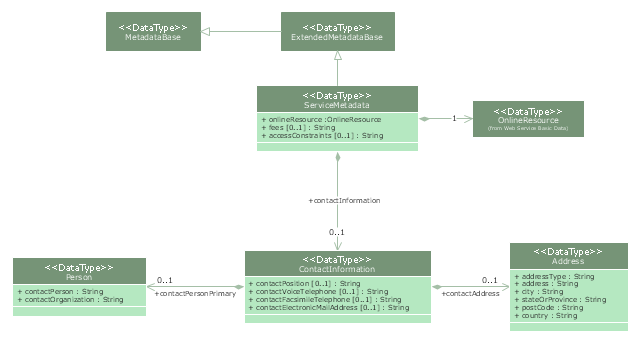
"Metadata is "data about data". The term is ambiguous, as it is used for two fundamentally different concepts (types). Structural metadata is about the design and specification of data structures and is more properly called "data about the containers of data"; descriptive metadata, on the other hand, is about individual instances of application data, the data content.
Metadata are traditionally found in the card catalogs of libraries. As information has become increasingly digital, metadata are also used to describe digital data using metadata standards specific to a particular discipline. By describing the contents and context of data files, the quality of the original data/ files is greatly increased. For example, a webpage may include metadata specifying what language it is written in, what tools were used to create it, and where to go for more on the subject, allowing browsers to automatically improve the experience of users." [Metadata. Wikipedia]
The UML class diagram example "Metadata information model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Metadata are traditionally found in the card catalogs of libraries. As information has become increasingly digital, metadata are also used to describe digital data using metadata standards specific to a particular discipline. By describing the contents and context of data files, the quality of the original data/ files is greatly increased. For example, a webpage may include metadata specifying what language it is written in, what tools were used to create it, and where to go for more on the subject, allowing browsers to automatically improve the experience of users." [Metadata. Wikipedia]
The UML class diagram example "Metadata information model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
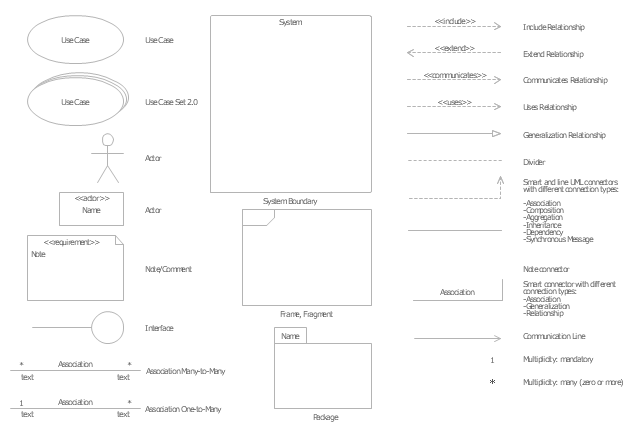
The vector stencils library "UML use case diagrams" contains 25 symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Use case diagrams are usually referred to as behavior diagrams used to describe a set of actions (use cases) that some system or systems (subject) should or can perform in collaboration with one or more external users of the system (actors). Each use case should provide some observable and valuable result to the actors or other stakeholders of the system. ...
Use case diagrams are in fact twofold - they are both behavior diagrams, because they describe behavior of the system, and they are also structure diagrams - as a special case of class diagrams where classifiers are restricted to be either actors or use cases related to each other with associations. ...
Use case is usually shown as an ellipse containing the name of the use case. ...
Name of the use case could also be placed below the ellipse. ...
If a subject (or system boundary) is displayed, the use case ellipse is visually located inside the system boundary rectangle. Note, that this does not necessarily mean that the subject classifier owns the contained use cases, but merely that the use case applies to that classifier. ...
A list of use case properties - operations and attributes - could be shown in a compartment within the use case oval below the use case name. ...
Use case with extension points may be listed in a compartment of the use case with the heading extension points. ...
A use case can also be shown using the standard rectangle notation for classifiers with an ellipse icon in the upper right-hand corner of the rectangle and with optional separate list compartments for its features. ...
Subject (sometimes called a system boundary) is presented by a rectangle with subject's name, associated keywords and stereotypes in the upper left corner. Use cases applicable to the subject are located inside the rectangle and actors - outside of the system boundary. ...
Standard UML notation for actor is "stick man" icon with the name of the actor above or below of the icon. Actor names should follow the capitalization and punctuation guidelines for classes. The names of abstract actors should be shown in italics. ...
Custom icons that convey the kind of actor may also be used to denote an actor, such as using a separate icon(s) for non-human actors. ...
An actor may also be shown as a class rectangle with the standard keyword «actor», having usual notation for class compartments ...
An actor can only have binary associations to use cases, components, and classes. ...
An association between an actor and a use case indicates that the actor and the use case somehow interact or communicate with each other.
Only binary associations are allowed between actors and use cases.
An actor could be associated to one or several use cases. ...
A use case may have one or several associated actors." [uml-diagrams.org/ use-case-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML use case diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Use case diagrams are usually referred to as behavior diagrams used to describe a set of actions (use cases) that some system or systems (subject) should or can perform in collaboration with one or more external users of the system (actors). Each use case should provide some observable and valuable result to the actors or other stakeholders of the system. ...
Use case diagrams are in fact twofold - they are both behavior diagrams, because they describe behavior of the system, and they are also structure diagrams - as a special case of class diagrams where classifiers are restricted to be either actors or use cases related to each other with associations. ...
Use case is usually shown as an ellipse containing the name of the use case. ...
Name of the use case could also be placed below the ellipse. ...
If a subject (or system boundary) is displayed, the use case ellipse is visually located inside the system boundary rectangle. Note, that this does not necessarily mean that the subject classifier owns the contained use cases, but merely that the use case applies to that classifier. ...
A list of use case properties - operations and attributes - could be shown in a compartment within the use case oval below the use case name. ...
Use case with extension points may be listed in a compartment of the use case with the heading extension points. ...
A use case can also be shown using the standard rectangle notation for classifiers with an ellipse icon in the upper right-hand corner of the rectangle and with optional separate list compartments for its features. ...
Subject (sometimes called a system boundary) is presented by a rectangle with subject's name, associated keywords and stereotypes in the upper left corner. Use cases applicable to the subject are located inside the rectangle and actors - outside of the system boundary. ...
Standard UML notation for actor is "stick man" icon with the name of the actor above or below of the icon. Actor names should follow the capitalization and punctuation guidelines for classes. The names of abstract actors should be shown in italics. ...
Custom icons that convey the kind of actor may also be used to denote an actor, such as using a separate icon(s) for non-human actors. ...
An actor may also be shown as a class rectangle with the standard keyword «actor», having usual notation for class compartments ...
An actor can only have binary associations to use cases, components, and classes. ...
An association between an actor and a use case indicates that the actor and the use case somehow interact or communicate with each other.
Only binary associations are allowed between actors and use cases.
An actor could be associated to one or several use cases. ...
A use case may have one or several associated actors." [uml-diagrams.org/ use-case-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML use case diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
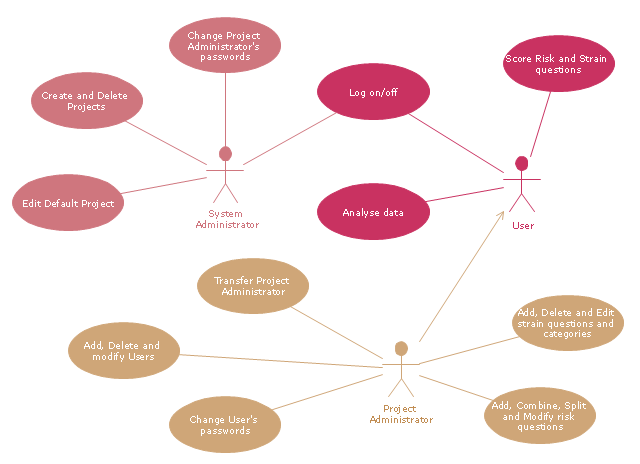
"A project manager is the person responsible for accomplishing the stated project objectives. Key project management responsibilities include creating clear and attainable project objectives, building the project requirements, and managing the constraints of the project management triangle, which are cost, time, scope, and quality.
A project manager is often a client representative and has to determine and implement the exact needs of the client, based on knowledge of the firm they are representing. A project manager is the bridging gap between the production team and client. So he/ she must have a fair knowledge of the industry they are in so that they are capable of understanding and discussing the problems with either party. The ability to adapt to the various internal procedures of the contracting party, and to form close links with the nominated representatives, is essential in ensuring that the key issues of cost, time, quality and above all, client satisfaction, can be realized.
The term and title 'project manager' has come to be used generically to describe anyone given responsibility to complete a project. However, it is more properly used to describe a person with full responsibility and the same level of authority required to complete a project. If a person does not have high levels of both responsibility and authority then they are better described as a project administrator, coordinator, facilitator or expeditor." [Project manager. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "Project administrator" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
A project manager is often a client representative and has to determine and implement the exact needs of the client, based on knowledge of the firm they are representing. A project manager is the bridging gap between the production team and client. So he/ she must have a fair knowledge of the industry they are in so that they are capable of understanding and discussing the problems with either party. The ability to adapt to the various internal procedures of the contracting party, and to form close links with the nominated representatives, is essential in ensuring that the key issues of cost, time, quality and above all, client satisfaction, can be realized.
The term and title 'project manager' has come to be used generically to describe anyone given responsibility to complete a project. However, it is more properly used to describe a person with full responsibility and the same level of authority required to complete a project. If a person does not have high levels of both responsibility and authority then they are better described as a project administrator, coordinator, facilitator or expeditor." [Project manager. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "Project administrator" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
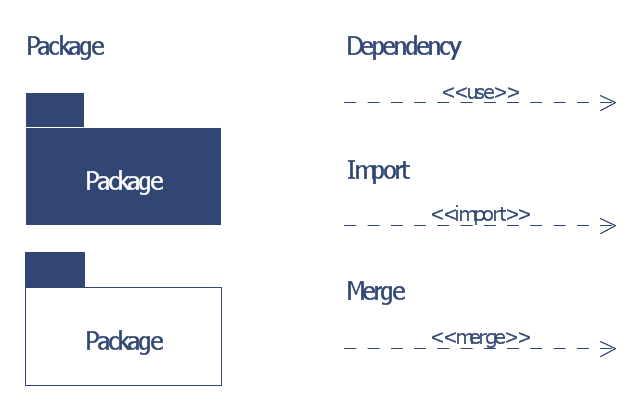
The vector stencils library "Bank UML package diagram" contains 5 shapes for drawing UML package diagrams.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
"A package diagram in the Unified Modeling Language depicts the dependencies between the packages that make up a model.
In addition to the standard UML Dependency relationship, there are two special types of dependencies defined between packages:
* package import,
* package merge.
Elements.
1. Package: a general purpose mechanism for organizing model elements & diagrams into groups. It provides an encapsulated namespace within which all the names must be unique. It is used to group semantically related elements. It is a namespace as well as an element that can be contained in other packages' namespaces.
2. Class: a representation of an object that reflects its structure and behavior within the system. It is a template from which running instances are created. Classes usually describe the logical structure of the system.
3. Interface: a specification of behavior. An implementation class must be written to support the behavior of an interface class.
4. Object: an instance of a class. It is often used in analysis to represent an artifact or other item.
5. Table: a stereotyped class." [Package diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML package diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
"A package diagram in the Unified Modeling Language depicts the dependencies between the packages that make up a model.
In addition to the standard UML Dependency relationship, there are two special types of dependencies defined between packages:
* package import,
* package merge.
Elements.
1. Package: a general purpose mechanism for organizing model elements & diagrams into groups. It provides an encapsulated namespace within which all the names must be unique. It is used to group semantically related elements. It is a namespace as well as an element that can be contained in other packages' namespaces.
2. Class: a representation of an object that reflects its structure and behavior within the system. It is a template from which running instances are created. Classes usually describe the logical structure of the system.
3. Interface: a specification of behavior. An implementation class must be written to support the behavior of an interface class.
4. Object: an instance of a class. It is often used in analysis to represent an artifact or other item.
5. Table: a stereotyped class." [Package diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML package diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- UML Deployment Diagram
- UML Diagram | Design elements - Bank UML package diagram ...
- UML Use Case Diagram Example Social Networking Sites Project ...
- 5 level pyramid model diagram of information systems types ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Activity Diagrams | Software ...
- UML Diagram Types List | UML Diagrams with ConceptDraw PRO ...
- UML Diagrams with ConceptDraw PRO | Use Case Diagrams ...
- UML Tool & UML Diagram Examples | Credit Card Processing ...
- UML Component Diagram | Diagramming Software for Design UML ...
- UML Use Case Diagram Example. Services UML Diagram. ATM ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Package Diagrams | UML ...
- UML Deployment Diagram Example - ATM System | UML ...
- UML Deployment Diagram Example - ATM System | UML ...
- Design elements - UML use case diagrams | UML Diagram Types ...
- Design elements - UML use case diagrams
- Timing diagram | UML timing diagram - Template | Diagramming ...
- UML Diagram Editor | UML Diagrams with ConceptDraw PRO ...
- UML Class Diagram Generalization Example | UML Sample Project ...
- UML activity diagram - Cash withdrawal from ATM | UML Activity ...
- UML Use Case Diagram Example Social Networking Sites Project ...