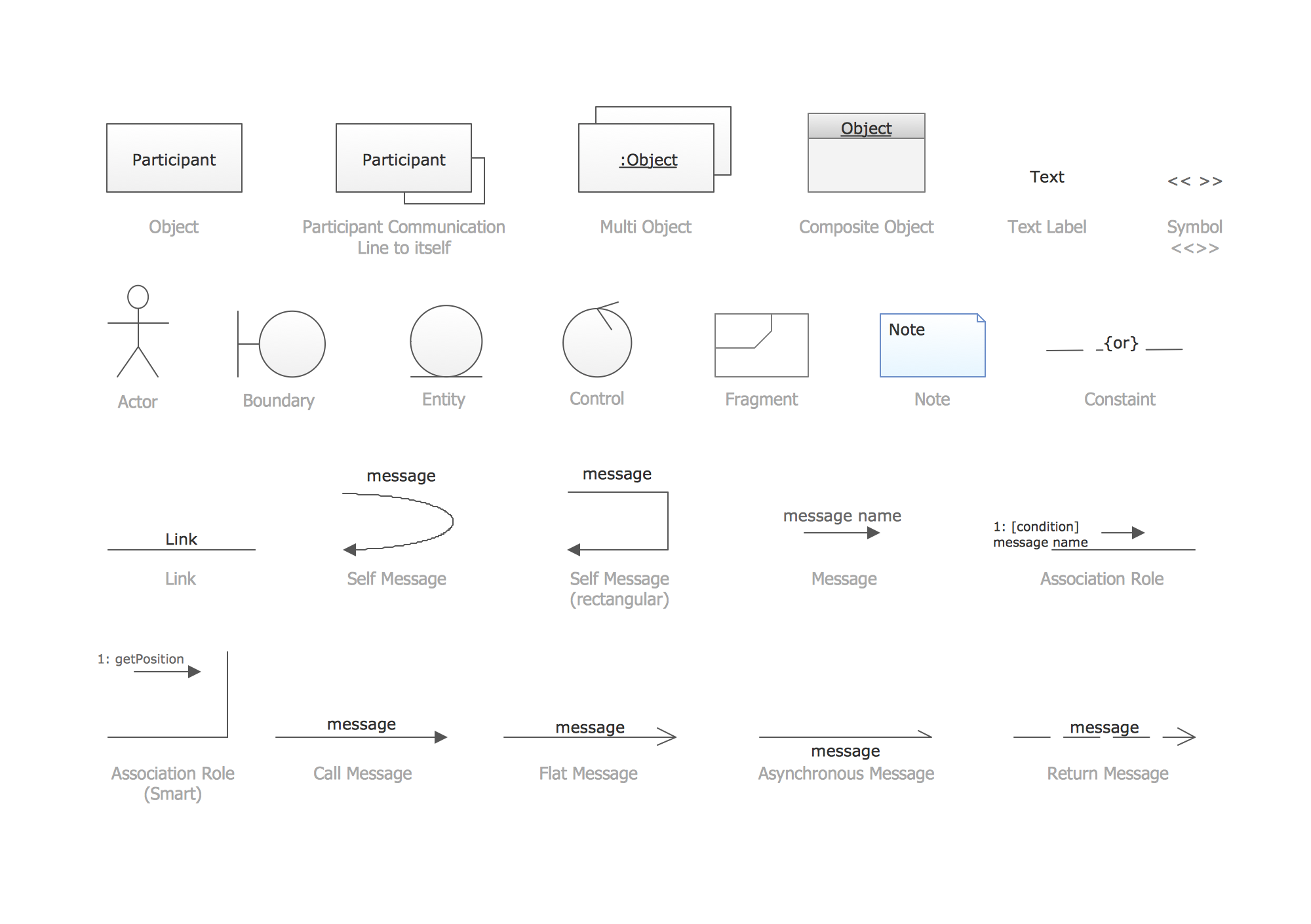
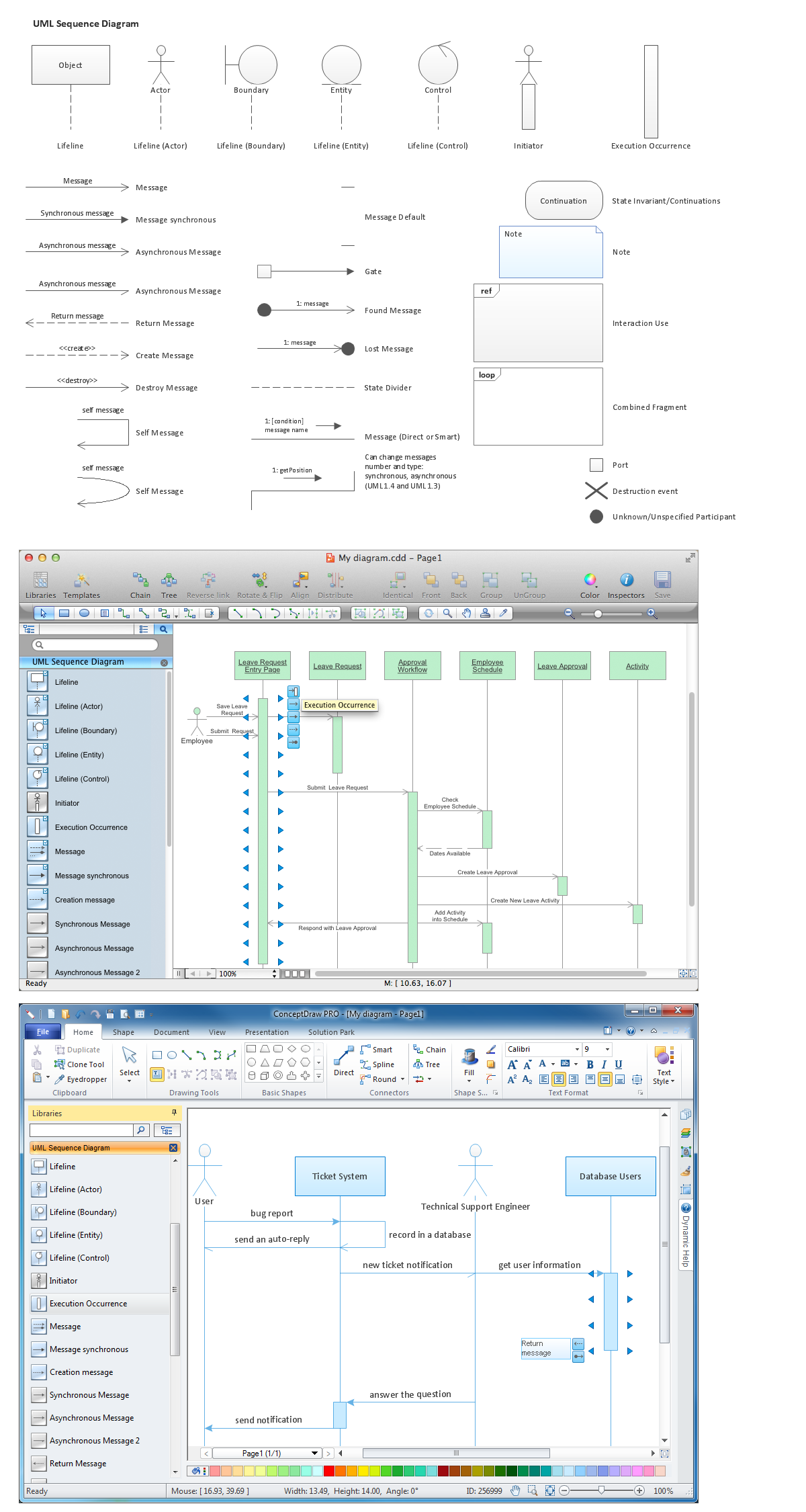
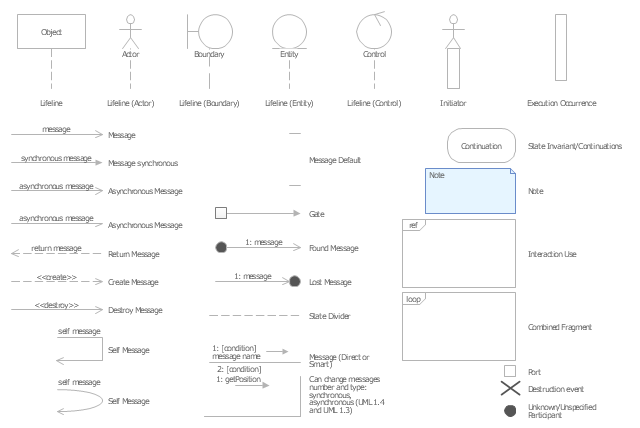
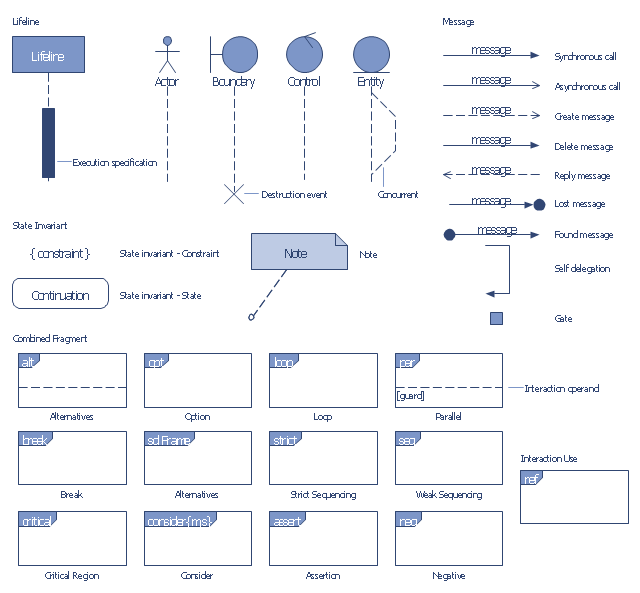
UML Sequence Diagram. Design Elements
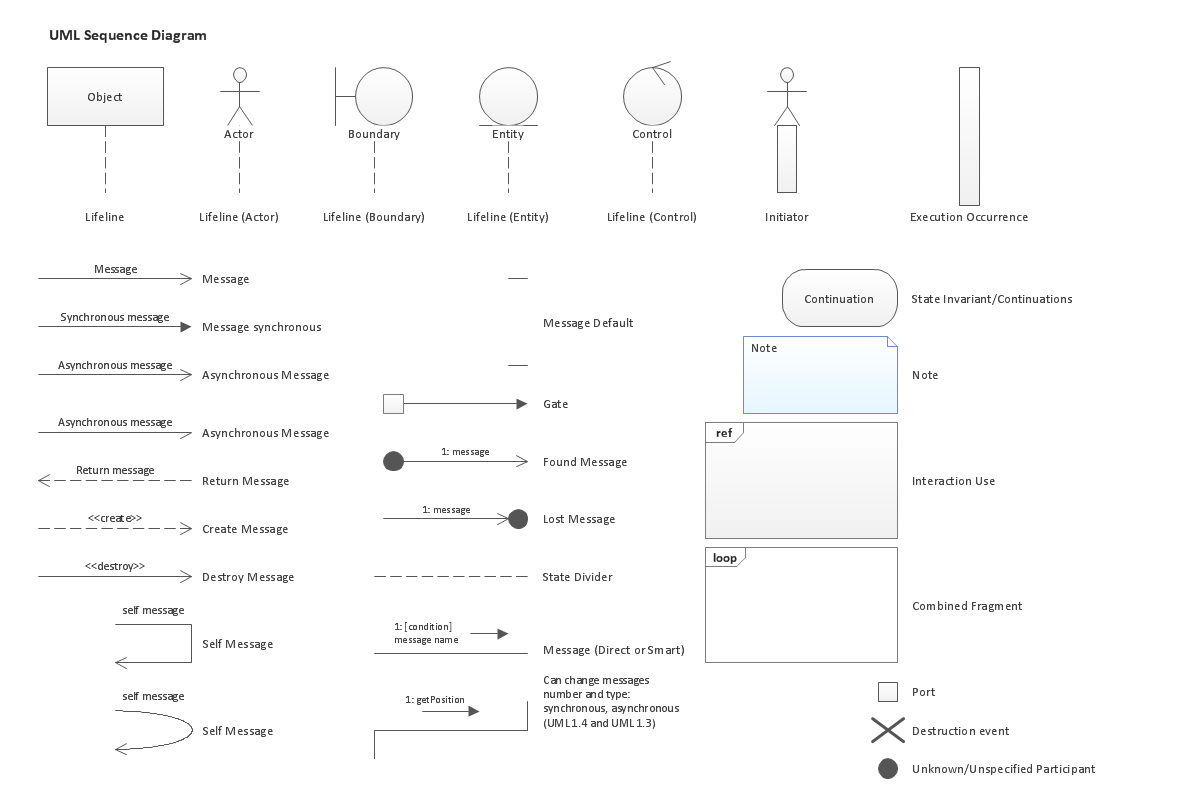
UML Sequence Diagram shows object interactions arranged in time sequence, how processes operate with one another and in what order and illustrate the sequence of messages exchanged between the objects and classes involved in the scenario.
"Sequence diagram is the most common kind of interaction diagram, which focuses on the message interchange between a number of lifelines.
Sequence diagram describes an interaction by focusing on the sequence of messages that are exchanged, along with their corresponding occurrence specifications on the lifelines.
The following nodes and edges are typically drawn in a UML sequence diagram: lifeline, execution specification, message, combined fragment, interaction use, state invariant, continuation, destruction occurrence." [uml-diagrams.org/ sequence-diagrams.html]
The template "UML sequence diagram" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ software-uml
Sequence diagram describes an interaction by focusing on the sequence of messages that are exchanged, along with their corresponding occurrence specifications on the lifelines.
The following nodes and edges are typically drawn in a UML sequence diagram: lifeline, execution specification, message, combined fragment, interaction use, state invariant, continuation, destruction occurrence." [uml-diagrams.org/ sequence-diagrams.html]
The template "UML sequence diagram" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ software-uml
This vector stencils library contains 32 SysML symbols.
Use it to design your sequence diagrams using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
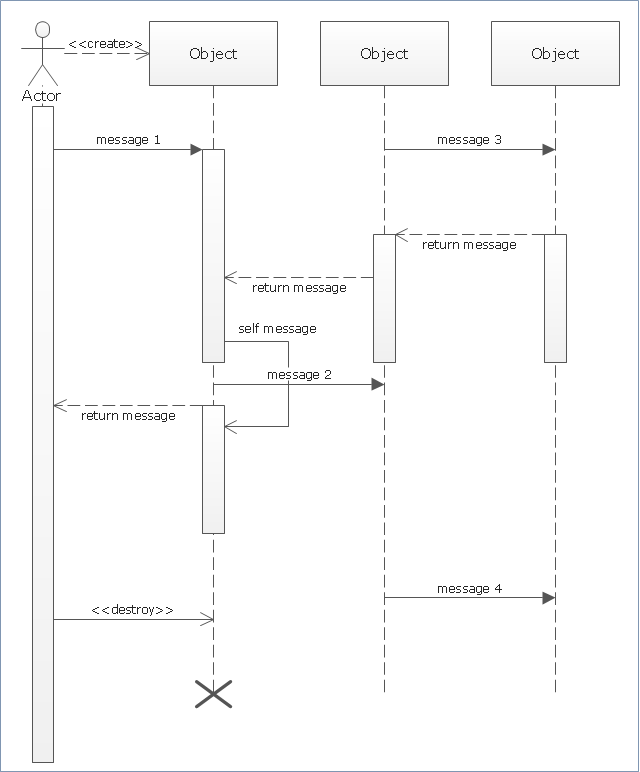
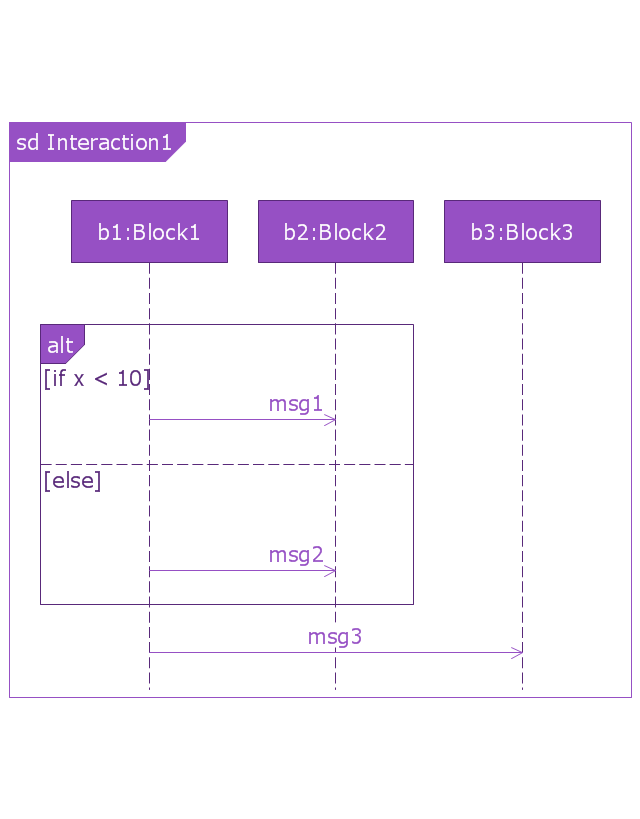
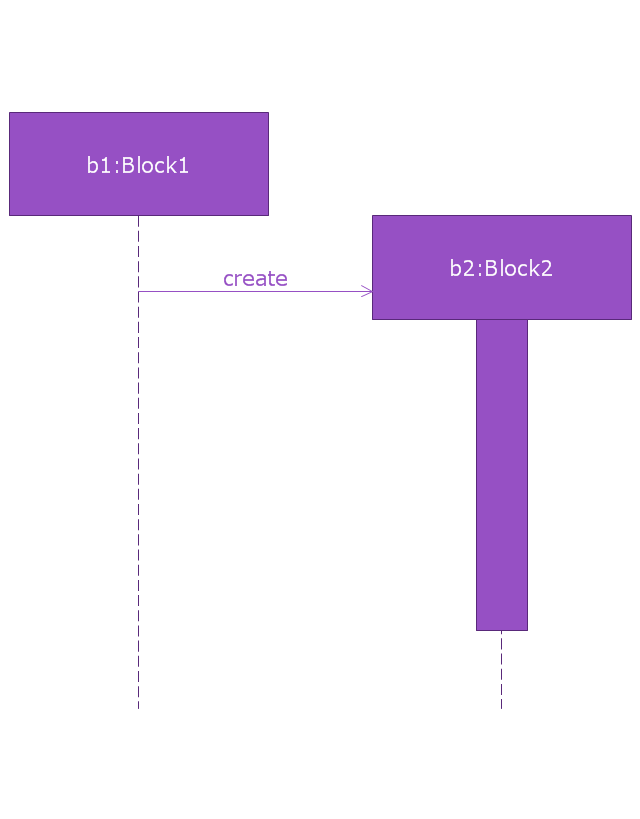
"A sequence diagram shows, as parallel vertical lines (lifelines), different processes or objects that live simultaneously, and, as horizontal arrows, the messages exchanged between them, in the order in which they occur. This allows the specification of simple runtime scenarios in a graphical manner. ...
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
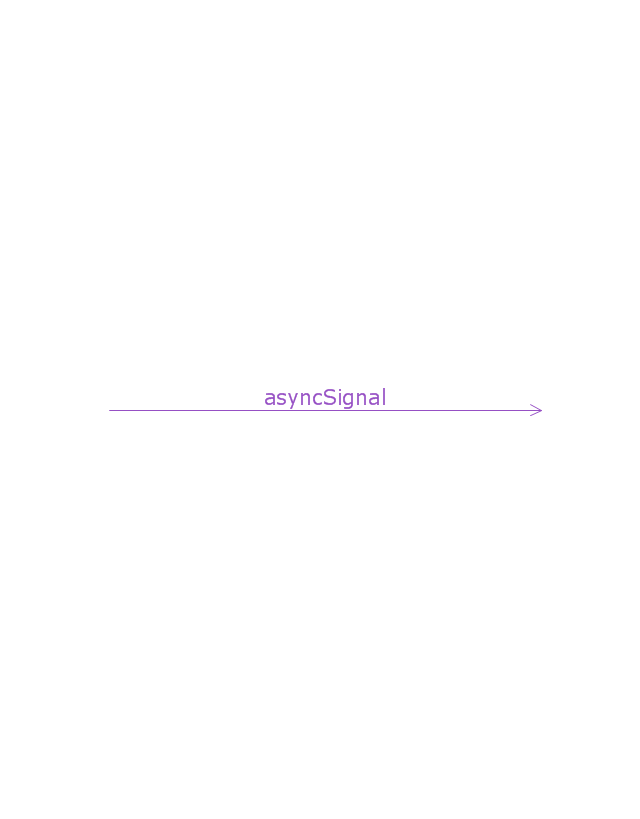
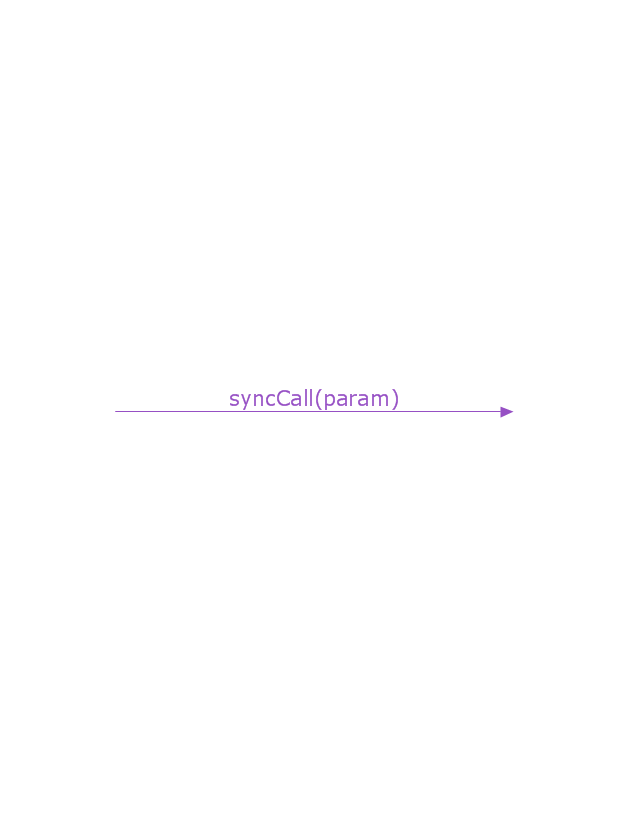
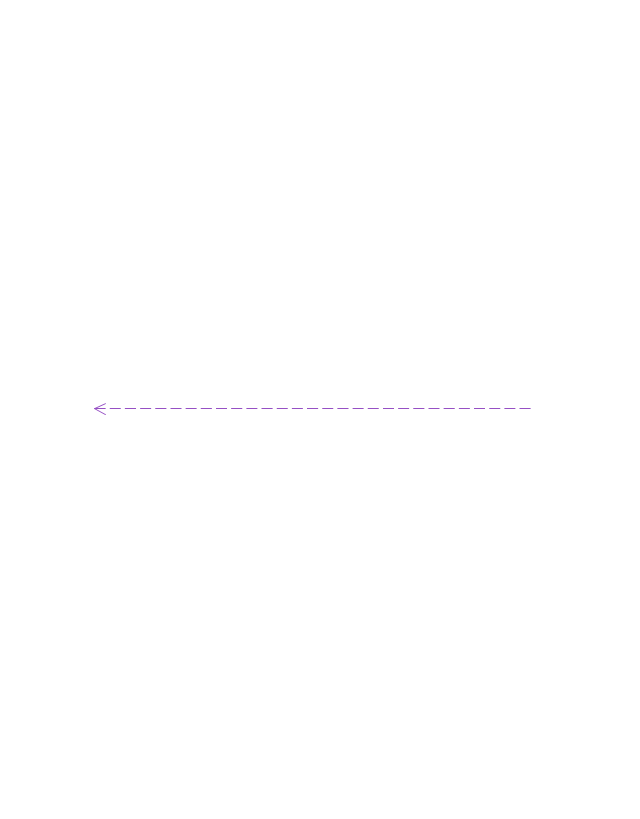
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. If a caller sends a synchronous message, it must wait until the message is done, such as invoking a subroutine. If a caller sends an asynchronous message, it can continue processing and doesn’t have to wait for a response. Asynchronous calls are present in multithreaded applications and in message-oriented middleware. Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
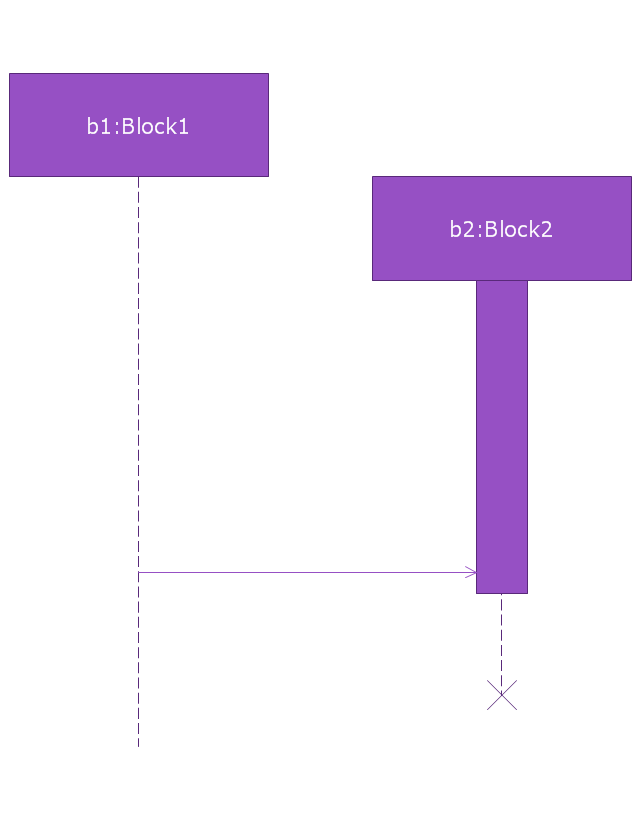
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it (this is not the case in the first example though). It should be the result of a message, either from the object itself, or another.
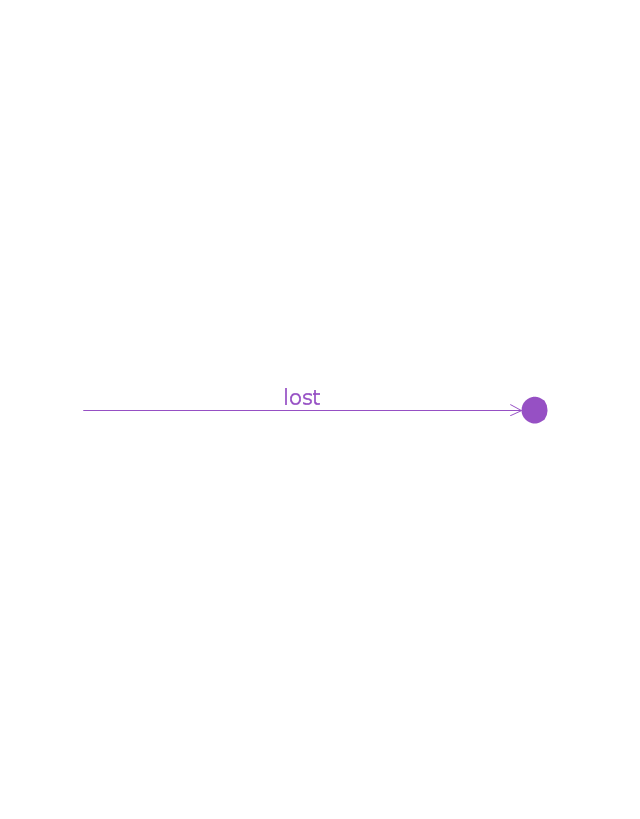
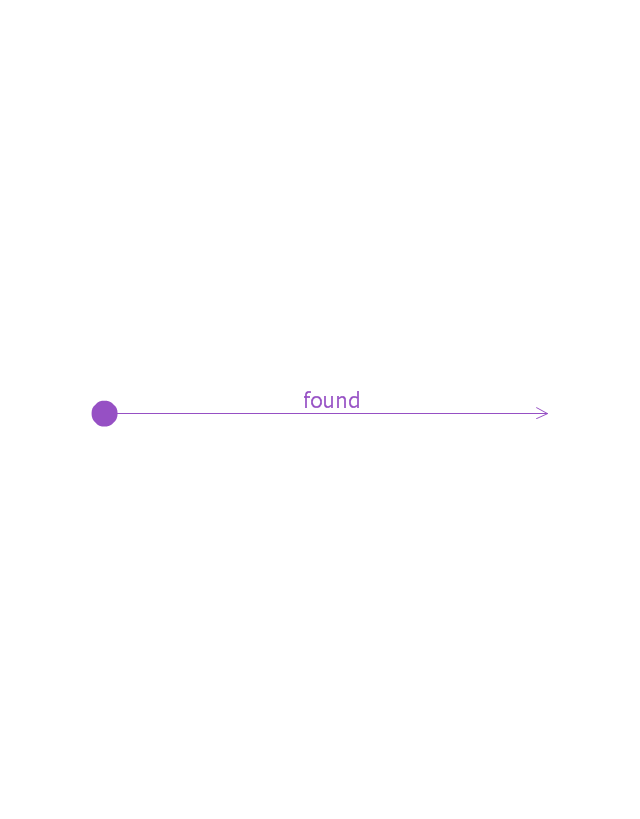
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
The vector stencils library "Sequence diagram" is included in the SysML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to design your sequence diagrams using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"A sequence diagram shows, as parallel vertical lines (lifelines), different processes or objects that live simultaneously, and, as horizontal arrows, the messages exchanged between them, in the order in which they occur. This allows the specification of simple runtime scenarios in a graphical manner. ...
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. If a caller sends a synchronous message, it must wait until the message is done, such as invoking a subroutine. If a caller sends an asynchronous message, it can continue processing and doesn’t have to wait for a response. Asynchronous calls are present in multithreaded applications and in message-oriented middleware. Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it (this is not the case in the first example though). It should be the result of a message, either from the object itself, or another.
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
The vector stencils library "Sequence diagram" is included in the SysML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
UML Collaboration Diagram. Design Elements
UML Collaboration Diagram illustrates how components are wired together to larger components and software systems that shows the structure of arbitrarily complex systems.ConceptDraw has 393 vector stencils in the 13 libraries that helps you to start using software for designing your own UML Diagrams. You can use the appropriate stencils of UML notation from UML Collaboration library with 36 objects
Diagramming Software for designing UML Sequence Diagrams
Sequence Diagrams shows how objects communicate with each other in terms of a sequence of messages. Also indicates the lifespans of objects relative to those messages.
The vector stencils library "UML sequence diagrams" contains 50 symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Sequence diagram ... building blocks.
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Note that leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. If a caller sends a synchronous message, it must wait until the message is done, such as invoking a subroutine. If a caller sends an asynchronous message, it can continue processing and doesn’t have to wait for a response. Asynchronous calls are present in multithreaded applications and in message-oriented middleware. Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it (this is not the case in the first example though). It should be the result of a message, either from the object itself, or another.
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - UML sequence diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Sequence diagram ... building blocks.
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Note that leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. If a caller sends a synchronous message, it must wait until the message is done, such as invoking a subroutine. If a caller sends an asynchronous message, it can continue processing and doesn’t have to wait for a response. Asynchronous calls are present in multithreaded applications and in message-oriented middleware. Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it (this is not the case in the first example though). It should be the result of a message, either from the object itself, or another.
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - UML sequence diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Bank UML sequence diagram" contains 34 shapes for drawing UML sequence diagrams.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
"A sequence diagram shows, as parallel vertical lines (lifelines), different processes or objects that live simultaneously, and, as horizontal arrows, the messages exchanged between them, in the order in which they occur. This allows the specification of simple runtime scenarios in a graphical manner.
Diagram building blocks.
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. ...
Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it ...
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML sequence diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
"A sequence diagram shows, as parallel vertical lines (lifelines), different processes or objects that live simultaneously, and, as horizontal arrows, the messages exchanged between them, in the order in which they occur. This allows the specification of simple runtime scenarios in a graphical manner.
Diagram building blocks.
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. ...
Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it ...
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML sequence diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Sequence Diagram Tool
ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software as a sequence diagram tool provides the Rapid UML Solution from the Software Development Area that contains the UML Sequence library.Sequence Diagram for Cloud Computing
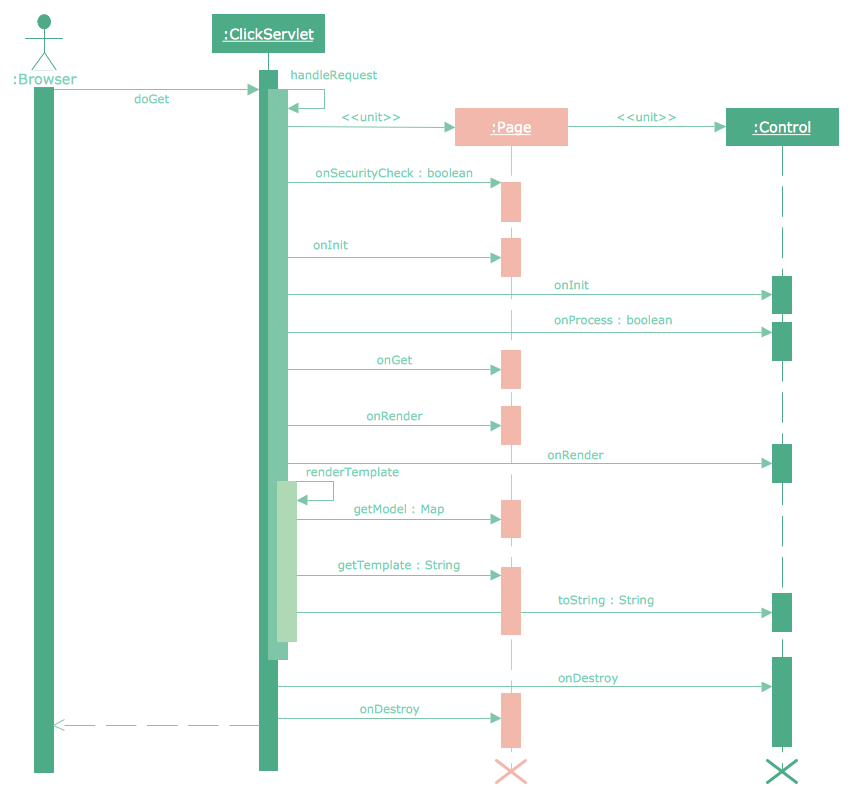
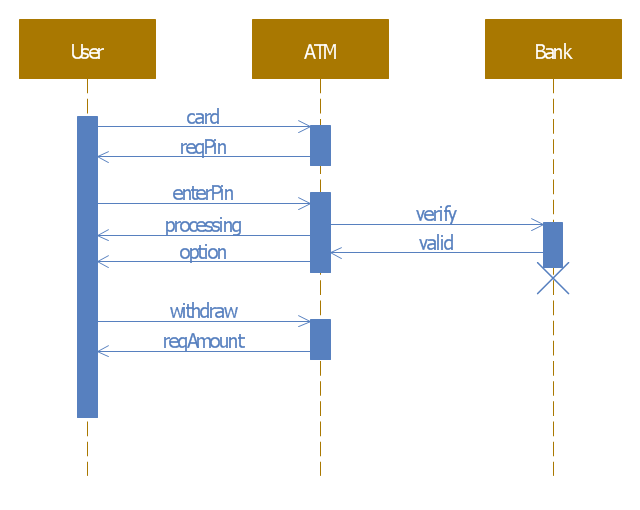
One of the ways effectively visualize what is a Cloud computing or Cloud computing architecture, is to create the Sequence diagram for Cloud computing. The ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software enhanced with Cloud Computing Diagrams solution from the Computers and Network area of ConceptDraw Solution Park will help you design all desired types of diagrams related with cloud computing.This example of automated teller machine (ATM) UML sequence diagram was created on the base of figure 5 "Sequence diagram" on the webpage "Message Sequence Charts and their Ilk" from the website of the University of California Irvine (UCI) Donald Bren School of Information and Computer Sciences.
"A UML sequence diagram or SD is similar to an MSC but written with a different notation. Presumably the same semantic issues arise, but possibly not since UML semantics are not well-defined. An example is shown in Figure 5.
The timelines are dotted rather than solid, and the name of the component is inside a box at the head of each timeline. The narrow rectangles apparently show when a component is active (unsure precisely what "active" means). An X on a timeline indicates that the component ceases to exist in some sense (unsure precisely how this is meant also). In the example, the Bank timeline has an X simply as an example (presumably the Bank does continue to exist)."
[www.ics.uci.edu/ ~alspaugh/ cls/ shr/ msc.html]
This example of bank ATM sequence diagram was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A UML sequence diagram or SD is similar to an MSC but written with a different notation. Presumably the same semantic issues arise, but possibly not since UML semantics are not well-defined. An example is shown in Figure 5.
The timelines are dotted rather than solid, and the name of the component is inside a box at the head of each timeline. The narrow rectangles apparently show when a component is active (unsure precisely what "active" means). An X on a timeline indicates that the component ceases to exist in some sense (unsure precisely how this is meant also). In the example, the Bank timeline has an X simply as an example (presumably the Bank does continue to exist)."
[www.ics.uci.edu/ ~alspaugh/ cls/ shr/ msc.html]
This example of bank ATM sequence diagram was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Message Between Lifelines In Sequential Diagrams
- Difference Between Lifeline Entity And Lifeline In Sequence Diagram
- Difference Between Actor And Lifeline In Sequence Diagram
- Vector stencils library - Sequence diagram | UML sequence diagram ...
- Order processing center - UML sequence diagram | UML sequence ...
- Design elements - UML sequence diagrams | Design elements ...
- Symbols Of Sequence Diagram
- Design elements - Bank UML sequence diagram | Design elements ...
- Vector stencils library - Sequence diagram | UML sequence diagram ...
- Design elements - UML sequence diagrams | ATM Sequence ...
- ERD | Entity Relationship Diagrams, ERD Software for Mac and Win
- Flowchart | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning
- Flowchart | Flowchart Design - Symbols, Shapes, Stencils and Icons
- Flowchart | Flow Chart Symbols
- Electrical | Electrical Drawing - Wiring and Circuits Schematics
- Flowchart | Common Flowchart Symbols
- Flowchart | Common Flowchart Symbols