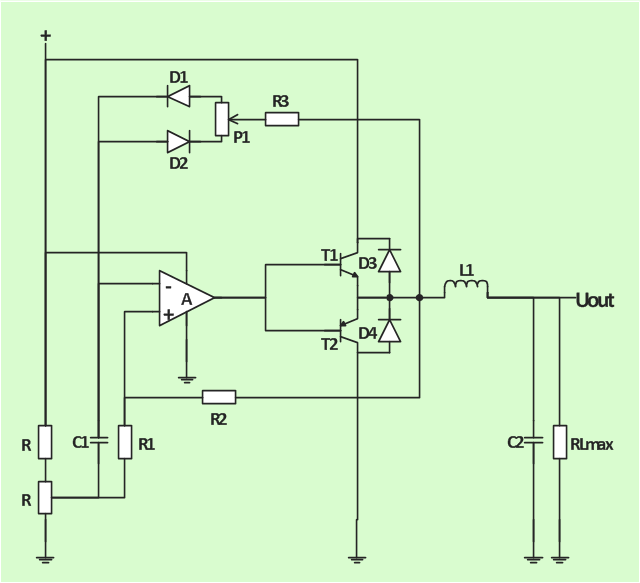
The analogue electronics diagram "Simple switched supply" was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Switchat.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Switchat.png]
"Analogue electronics (or analog in American English) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal." [Analogue electronics. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Simple switched supply" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Switchat.png]
"Analogue electronics (or analog in American English) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal." [Analogue electronics. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Simple switched supply" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube (in North America), tube, or thermionic valve or valve (in British English) is a device controlling electric current through a vacuum in a sealed container. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode, contains only two elements; current can only flow in one direction through the device between the two electrodes, as electrons emitted by the hot cathode travel through the tube and are collected by the anode. Addition of a third and additional electrodes allows the current flowing between cathode and anode to be controlled in various ways. The device can be used as an electronic amplifier, a rectifier, an electronically controlled switch, an oscillator, and for other purposes.
Vacuum tubes mostly rely on thermionic emission of electrons from a hot filament or a cathode heated by the filament. Some electron tube devices rely on the properties of a discharge through an ionized gas." [Vacuum tube. Wikipedia]
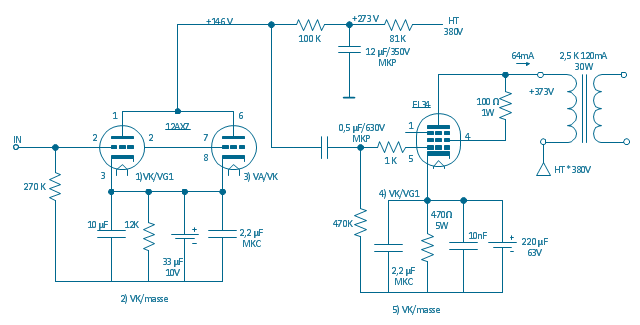
"The EL34 is a thermionic valve or vacuum tube of the power pentode type. It has an international octal base (indicated by the '3' in the part number) and is found mainly in the final output stages of audio amplification circuits and was designed to be suitable as a series regulator by virtue of its high permissible voltage between heater and cathode and other parameters. The American RETMA tube designation number for this tube is 6CA7. Russian analog is 6P27S (Cyrillic: 6П27C )" [EL34. Wikipedia]
This circuit diagram sample was redrawn from the Wikipedia Commons file: EL34 schematics (circuit diagram).gif. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:EL34_ schematics_ %28circuit_ diagram%29.gif]
The example "Circuit diagram - EL 34 schematics" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Vacuum tubes mostly rely on thermionic emission of electrons from a hot filament or a cathode heated by the filament. Some electron tube devices rely on the properties of a discharge through an ionized gas." [Vacuum tube. Wikipedia]
"The EL34 is a thermionic valve or vacuum tube of the power pentode type. It has an international octal base (indicated by the '3' in the part number) and is found mainly in the final output stages of audio amplification circuits and was designed to be suitable as a series regulator by virtue of its high permissible voltage between heater and cathode and other parameters. The American RETMA tube designation number for this tube is 6CA7. Russian analog is 6P27S (Cyrillic: 6П27C )" [EL34. Wikipedia]
This circuit diagram sample was redrawn from the Wikipedia Commons file: EL34 schematics (circuit diagram).gif. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:EL34_ schematics_ %28circuit_ diagram%29.gif]
The example "Circuit diagram - EL 34 schematics" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
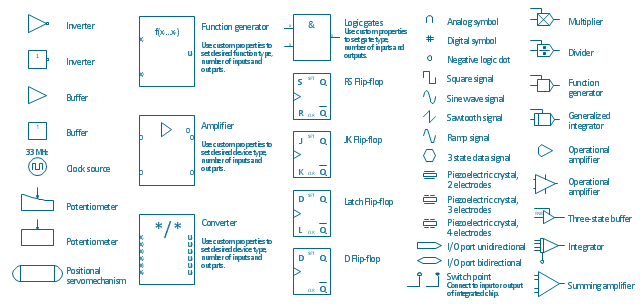
The vector stencils library "Analog and digital logic" contains 40 element symbols of logic (threshold) gates, bistable current switches, current controllers, regulators, electrical generators, and amplifiers.
Use it for drawing the digital and analog functions in electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"Analogue electronics (or analog in American English) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal." [Analogue electronics. Wikipedia]
"Digital electronics, or digital (electronic) circuits, represent signals by discrete bands of analog levels, rather than by a continuous range. All levels within a band represent the same signal state. Relatively small changes to the analog signal levels due to manufacturing tolerance, signal attenuation or parasitic noise do not leave the discrete envelope, and as a result are ignored by signal state sensing circuitry.
In most cases the number of these states is two, and they are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as "ground" or zero volts) and a value near the supply voltage, corresponding to the "false" ("0") and "true" ("1") values of the Boolean domain respectively.
Digital techniques are useful because it is easier to get an electronic device to switch into one of a number of known states than to accurately reproduce a continuous range of values.
Digital electronic circuits are usually made from large assemblies of logic gates, simple electronic representations of Boolean logic functions." [Digital electronics. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Analog and digital logic" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for drawing the digital and analog functions in electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"Analogue electronics (or analog in American English) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal." [Analogue electronics. Wikipedia]
"Digital electronics, or digital (electronic) circuits, represent signals by discrete bands of analog levels, rather than by a continuous range. All levels within a band represent the same signal state. Relatively small changes to the analog signal levels due to manufacturing tolerance, signal attenuation or parasitic noise do not leave the discrete envelope, and as a result are ignored by signal state sensing circuitry.
In most cases the number of these states is two, and they are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as "ground" or zero volts) and a value near the supply voltage, corresponding to the "false" ("0") and "true" ("1") values of the Boolean domain respectively.
Digital techniques are useful because it is easier to get an electronic device to switch into one of a number of known states than to accurately reproduce a continuous range of values.
Digital electronic circuits are usually made from large assemblies of logic gates, simple electronic representations of Boolean logic functions." [Digital electronics. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Analog and digital logic" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
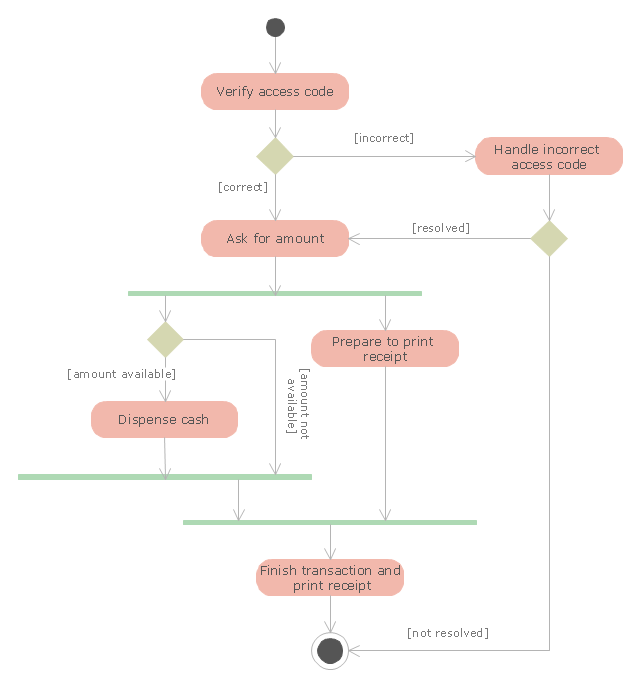
"An automated teller machine or automatic teller machine" (ATM) (American, Australian, Singaporean, Indian, and Hiberno-English), also known as an automated banking machine (ABM) (Canadian English), cash machine, cashpoint, cashline or hole in the wall (British, South African, and Sri Lankan English), is an electronic telecommunications device that enables the clients of a financial institution to perform financial transactions without the need for a cashier, human clerk or bank teller.
On most modern ATMs, the customer is identified by inserting a plastic ATM card with a magnetic stripe or a plastic smart card with a chip that contains a unique card number and some security information such as an expiration date or CVVC (CVV). Authentication is provided by the customer entering a personal identification number (PIN). The newest ATM at Royal Bank of Scotland allows customers to withdraw cash up to £100 without a card by inputting a six-digit code requested through their smartphones.
Using an ATM, customers can access their bank accounts in order to make cash withdrawals, get debit card cash advances, and check their account balances as well as purchase pre-paid mobile phone credit. If the currency being withdrawn from the ATM is different from that which the bank account is denominated in (e.g.: Withdrawing Japanese yen from a bank account containing US dollars), the money will be converted at an official wholesale exchange rate. Thus, ATMs often provide one of the best possible official exchange rates for foreign travellers, and are also widely used for this purpose." [Automated teller machine. Wikipedia]
The UML activity diagram example "Cash withdrawal from ATM" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
On most modern ATMs, the customer is identified by inserting a plastic ATM card with a magnetic stripe or a plastic smart card with a chip that contains a unique card number and some security information such as an expiration date or CVVC (CVV). Authentication is provided by the customer entering a personal identification number (PIN). The newest ATM at Royal Bank of Scotland allows customers to withdraw cash up to £100 without a card by inputting a six-digit code requested through their smartphones.
Using an ATM, customers can access their bank accounts in order to make cash withdrawals, get debit card cash advances, and check their account balances as well as purchase pre-paid mobile phone credit. If the currency being withdrawn from the ATM is different from that which the bank account is denominated in (e.g.: Withdrawing Japanese yen from a bank account containing US dollars), the money will be converted at an official wholesale exchange rate. Thus, ATMs often provide one of the best possible official exchange rates for foreign travellers, and are also widely used for this purpose." [Automated teller machine. Wikipedia]
The UML activity diagram example "Cash withdrawal from ATM" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
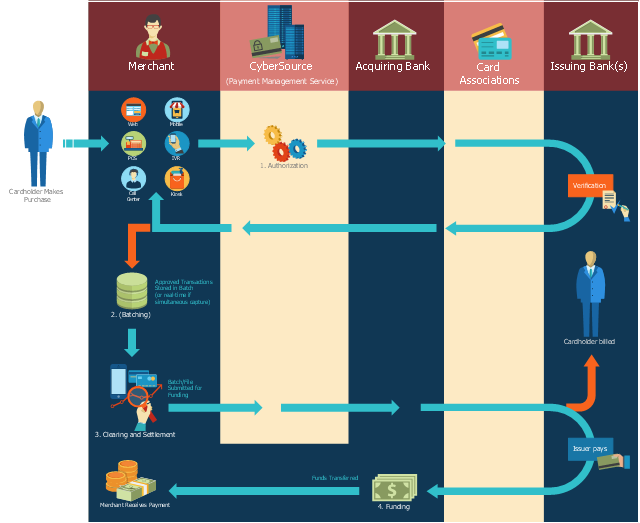
This payment process flowchart example was created on the base of the diagram of payment process using Global Payment Processing Services from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission website.
"Global Payment Processing Services. CyberSource Advanced enables merchants to accept payments made by all major credit and debit cards including American Express®, Discover®, Diners Club International®, JCB, MasterCard®, and Visa® cards. Our customers can also accept payment by corporate procurement cards, electronic checks, PayPal® Express Checkout, and the Bill Me Later® service. Merchants that have business models based on subscriptions can utilize the CyberSource recurring billing service with automated account updating services. For merchants selling internationally, we support direct debit, and bank transfers, as well as regional card brands such as Carte Bleue, Carta Si, Dankort, Laser, Solo, and Visa Electron. We provide these services for online, call center, kiosk, integrated voice response (“IVR”), and IP-enabled point of sale (“POS”) transactions."
[www.sec.gov/ Archives/ edgar/ data/ 934280/ 000119312510042764/ d10k.htm]
The flowchart example "Global Payment Solutions" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Sales Flowcharts solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Global Payment Processing Services. CyberSource Advanced enables merchants to accept payments made by all major credit and debit cards including American Express®, Discover®, Diners Club International®, JCB, MasterCard®, and Visa® cards. Our customers can also accept payment by corporate procurement cards, electronic checks, PayPal® Express Checkout, and the Bill Me Later® service. Merchants that have business models based on subscriptions can utilize the CyberSource recurring billing service with automated account updating services. For merchants selling internationally, we support direct debit, and bank transfers, as well as regional card brands such as Carte Bleue, Carta Si, Dankort, Laser, Solo, and Visa Electron. We provide these services for online, call center, kiosk, integrated voice response (“IVR”), and IP-enabled point of sale (“POS”) transactions."
[www.sec.gov/ Archives/ edgar/ data/ 934280/ 000119312510042764/ d10k.htm]
The flowchart example "Global Payment Solutions" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Sales Flowcharts solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Amplifier ...
- Simple switched supply - Circuit diagram | Electrical Drawing ...
- Electrical Diagram Software | Wiring Diagrams with ConceptDraw ...
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Electrical ...
- Design elements - Analog and digital logic | Engineering | Electrical ...
- Wiring Diagrams with ConceptDraw PRO | Bipolar current mirror ...
- How To use House Electrical Plan Software | Electrical Symbols ...
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Electrical ...
- Electrical Symbols, Electrical Diagram Symbols | Electrical Drawing ...
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Circuit diagram ...
- Circuits and Logic Diagram Software | Electrical Diagram Software ...
- What Is A Wiring Diagram In Electrical Engineering
- Process Flowchart | Network Diagram Software LAN Network ...
- Electrical Symbols — Analog and Digital Logic | Design elements ...
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Circuits and ...
- Electrical Symbols — Logic Gate Diagram | Design elements - Logic ...
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Circuits and ...
- Electronics Diagrams Schematics
- Electrical Symbols — Analog and Digital Logic | Design elements ...
- Design elements - Logic gate diagram | Circuits and Logic Diagram ...
- ERD | Entity Relationship Diagrams, ERD Software for Mac and Win
- Flowchart | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning
- Flowchart | Flowchart Design - Symbols, Shapes, Stencils and Icons
- Flowchart | Flow Chart Symbols
- Electrical | Electrical Drawing - Wiring and Circuits Schematics
- Flowchart | Common Flowchart Symbols
- Flowchart | Common Flowchart Symbols